Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to determine the safety and effectiveness of intraventricular antibiotics in neonates with meningitis and/or ventriculitis and analyze the quality of available evidence.
Methods
Design
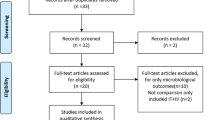
Systematic review and meta-analysis. Data sources: PubMed, EMBASE, LILACS, and SCOPUS up to 17 February 2023. Eligibility criteria for selecting studies: Randomized experimental and observational studies were included. The Cochrane methodology was used for systematic reviews.
Results
Twenty-six observational studies and one randomized clinical trial involving 272 patients were included. The risk of bias in both pediatric and neurosurgical studies was high, and the quality of evidence was low (evidence level C). In the pediatric studies, no significant differences in mortality were found between intraventricular antibiotics and only systemic antibiotic [25.4% vs 16.1%, OR = 0.96 (0.42–2.24), P = 0.93]. However, when analyzing the minimum administered doses, we found a lower mortality when a minimum duration of 3 days for intraventricular antibiotics was used compared to only systemic antibiotic [4.3% vs 17%, OR = 0.22 (0.07–0.72), P = 0.01]. In the neurosurgical studies, the use of intraventricular antibiotics in ventriculitis generally results in a mortality of 5% and a morbidity of 25%, which is lower than that in cases where intraventricular antibiotics were not used, with an average mortality of 37.3% and a morbidity of 50%.
Conclusion
Considering the low quality of evidence in pediatric and neurosurgical studies, we can conclude with a low level of certainty that intraventricular antibiotics may not significantly impact mortality in neonatal meningitis and ventriculitis. However, reduced mortality was observed in cases treated with a minimum duration of 3 days of intraventricular antibiotic, particularly the multidrug-resistant or treatment-refractory infections. Higher-quality studies are needed to improve the quality of evidence and certainty regarding the use of intraventricular antibiotics for treating neonatal meningitis and ventriculitis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data analyzed in this study are available in the original papers.
References
Furyk J, Swann O, Molyneux E (2011) Systematic review: neonatal meningitis in the developing world. Trop Med Int Health 16(6):672–679
Ku L, Boggess K, Cohen-Wolkowiez M (2015) Bacterial meningitis in infants. Clin Perinatol 42(1):29–45
Baud O, Aujard Y (2013) Neonatal bacterial meningitis. Handb Clin Neurol 112:1109–1113
Peros T, van SJ, Bohte A, Hodiamont C, Aronica E, de Haan T (2020) Neonatal bacterial meningitis versus ventriculitis: a cohort-based overview of clinical characteristics, microbiology and imaging. Eur J Pediatr 179(12):1969–1977
Gaschignard J, Levy C, Romain O, Cohen R, Bingen E, Aujard Y et al (2011) Neonatal bacterial meningitis: 444 cases in 7 years. Pediatr Infect Dis J 30(3):212–217
Heath P, Okike I, Oeser C (2011) Neonatal meningitis: can we do better? Adv Exp Med Biol 11–24
Bedford H, de Louvois J, Halket S, Peckham C, Hurley R, Harvey D (2001) Meningitis in infancy in England and Wales: follow up at age 5 years. BMJ 323(7312):533–536
de Louvois J, Halket S, Harvey D (2005) Neonatal meningitis in England and Wales: sequelae at 5 years of age. Eur J Pediatr 164(12):730–734
Defeating meningitis by 2030: baseline situation analysis. World Health Organization. February 2019. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/defeating-meningitis-2030-baseline-situation-analysis
Kaul S, D’Cruz J, Rapkin R, Glista B, Behrle FC (1978) Ventriculitis, aqueductal stenosis and hydrocephalus in neonatal meningitis: diagnose and treatment. Infection 6(1):8–11
Rios I, Klimek J, Maderazo E, Quintiliani R (1978) Flavobacterium meningosepticum meningitis: report of selected aspects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 14(3):444–447
Lee E, Robinson M, Thong M, Puthucheary S, Ong T, Ng K (1977) Intraventricular chemotherapy in neonatal meningitis. J Pediatr 91(6):991–995
Kaiser A, Wright P, McGee Z (1980) Dupont W. Intraventricular gentamicin in meningitis. Lancet 2(2)
Yeung C (1976) Intrathecal antibiotic therapy for neonatal meningitis. Arch Dis Child 51(9):686–690
McCracken GJ, Mize S, Threlkeld N (1980) Intraventricular gentamicin therapy in gram-negative bacillary meningitis of infancy. Report of the Second Neonatal Meningitis Cooperative Study Group. Lancet 1980;12(1):787–91
Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hróbjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, McKenzie JE (2021) PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372:n160. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n160. PMID: 33781993; PMCID: PMC8005925
Higgins J, Thomas J, Chandler J et al (2022) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane
Tunkel A, Hasbun R, Bhimraj A et al (2017) 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America’s clinical practice guidelines for healthcare-associated ventriculitis and meningitis. Clin Infect Dis 64(6):e34–e65
Helgason EA, Oskarsdottir T, Brynjarsson H, Olafsson IH, Thors V (2022) Intraventricular vancomycin treatment for shunt-related ventriculitis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a preterm infant: a case report. Pediatr Infect Dis J 41(4):340–342
Pratheep R, Ray S, Mukhopadhyay K et al (2019) First case report of intraventricular tigecycline in a neonate with extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii ventriculitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J 38(8):e172–e174
Joshi P, Shah B, Joshi V, Kumar A, Singhal T (2019) Treatment of Elizabethkingia meningoseptica neonatal meningitis with combination systemic and intraventricular therapy. Indian J Pediatr 86(4):379–381
Piparsania S, Rajput N, Bhatambare G (2012) Intraventricular polymyxin B for the treatment of neonatal meningo-ventriculitis caused by multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii–case report and review of literature. Turk J Pediatr 54(5):548–554
Nava-Ocampo A, Mojica-Madera J, Villanueva-García D, Caltenco-Serrano R (2006) Antimicrobial therapy and local toxicity of intraventricular administration of vancomycin in a neonate with ventriculitis. Ther Drug Monit 28(3):474–476
Laborada G, Cruz F, Nesin M (2005) Serial cytokine profiles in shunt-related ventriculitis treated with intraventricular vancomycin. Chemotherapy 51(6)
Greene G, Heitlinger L, Madden J (1983) Citrobacter ventriculitis in a neonate responsive to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Clin Pediatr 22(7):515–517
Wirt T, McGee Z, Oldfield E, Meacham W (1979) Intraventricular administration of amikacin for complicated Gram-negative meningitis and ventriculitis. J Neurosurg 50(1):95–99
Helms P, Relapsing E (1977) coli K1 antigen meningitis in a newborn. Arch Dis Child 52(2):152–154
Al Yazidi L, McMullan B, Kohan S, Palasanthiran P (2018) Persistent gram-negative neurosurgical meningitis in a neonate, successfully treated with intraventricular colistin: case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Infect Dis J 37(3):e79–e81
Alaoui S, Nejmi S, Chakir A, Hmamouchi B, Chlilek A (2011) Méningite néonatale à Acinetobacter baumanii traitée par la colistine intraventriculaire [intraventricular colistin use in neonatal meningitis caused by Acinetobacter baumanii]. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim 30(11):854–855
Serafettin Tekgunduz K, Kara M, Caner I, Demirelli Y, Tekgündüz KŞ (2015) Safety and efficacy of intravenous colistin in neonates with culture proven sepsis. Iran J Pediatr 25(4):e453
Hiremath P, Rangappa P, Jacob I, Rao K (2018) Cerebrospinal fluid lactate as a prognostic indicator in postneurosurgical bacterial meningitis and use of intrathecal colistin. Indian J Crit Care Med 22(4):297–299
Bhat RR, Batra P, Sachan R, Singh G (2020) Neonatal ventriculitis: a case series and review of literature. Trop Doct 50(3):266–270
Matsunaga N, Hisata K, Shimizu T (2015) An investigation into the vancomycin concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid due to vancomycin intraventricular administration in newborns: a study of 13 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 94(22):e922
James H, Bejar R, Gluck L et al (1984) Ventriculoperitoneal shunts in high risk newborns weighing under 2000 grams: a clinical report. Neurosurgery 15(2):198–202
Mangi R, Holstein L, Andriole V (1977) Treatment of Gram-negative bacillary meningitis with intrathecal gentamicin. Yale J Biol Med 50(1):31–41
Del Rincón NN, de Alba RC, Nadal PE et al (2000) Ventriculitis: experiencia en un servicio de neonatología [experience with ventriculitis at a neonatology department]. An Esp Pediatr 52(3):245–250
Haddaway N, Page MJ, Pritchard C, McGuinness L (2022) PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst Rev 18
Wright P, Kaiser A, Bowman C, McKee KJ, Trujillo H, McGee Z (1981) The pharmacokinetics and efficacy of an aminoglycoside administered into the cerebral ventricles in neonates: implications for further evaluation of this route of therapy in meningitis. J Infect Dis 143(2):141–147
Hussain K, Sohail Salat M, Ambreen G, Iqbal J (2021) Neurodevelopment outcome of neonates treated with intraventricular colistin for ventriculitis caused by multiple drug-resistant pathogens-a case series. Front Pediatr 20(8)
Ambreen G, Salat M, Hussain K et al (2020) Efficacy of colistin in multidrug-resistant neonatal sepsis: experience from a tertiary care center in Karachi. Pakistan Arch Dis Child 105(9):830–836
Dellagrammaticas HD, Christodoulou CH, Megaloyanni E, Papadimitriou M, Kapetanakis J, Kourakis G (2000) Treatment of gram-negative bacterial meningitis in term neonates with third generation cephalosporins plus amikacin. Biol Neonate 77(3):139–146
Kaplan S, Patrick C (1990) Cefotaxime and aminoglycoside treatment of meningitis caused by gram-negative enteric organisms. Pediatr Infect Dis J 9(11):810–814
Sterne J, Savović J, Page M et al (2019) RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC et al (2016) ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 355
Feferbaum R, Vaz F, Krebs V, Diniz E, Ramos S, Manissadjian A (1993) Meningite bacteriana no período neonatal. Evolução clínica e complicações em 109 casos [Bacterial meningitis in the neonatal period. Clinical evaluation and complications in 109 cases]. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 51(1)
Topjian A, Stuart A, Pabalan A et al (2014) Risk factors associated with infections and need for permanent cerebrospinal fluid diversion in pediatric intensive care patients with externalized ventricular drains. Neurocrit Care 21(2):294–299
Boethun A, Vissing N, Mathiasen R, Skjøth-Rasmussen J, Foss-Skiftesvik J (2023) CNS infection in children with brain tumors: adding ventriculostomy to brain tumor resection increases risk more than 20-fold. Childs Nerv Syst 39(2):387–394
Thatrimontrichai A, Janjindamai W, Dissaneevate S, Maneenil G (2021) Neonatal multidrug-resistant bacterial meningitis: a 29-year study from a tertiary hospital in Thailand. J Infect Dev Ctries 15(7):1021–1026
Alnaami I, Alahmari Z (2022) Intrathecal/intraventricular colistin for antibiotic-resistant bacterial CNS infections in pediatric population: a systematic review. Trop Med Infect Dis 7(3)
Spader H, Hertzler D, Kestle J, Riva-Cambrin J (2015) Risk factors for infection and the effect of an institutional shunt protocol on the incidence of ventricular access device infections in preterm infants. J Neurosurg Pediatr 15(2):156–160
Lakomkin N, Hadjipanayis C (2021) The role of prophylactic intraventricular antibiotics in reducing the incidence of infection and revision surgery in pediatric patients undergoing shunt placement [published correction appears in Neurosurgery 2021;88(5):1042]. Neurosurgery 82(2):301–305
Moussa W, Mohamed M (2016) Efficacy of postoperative antibiotic injection in and around ventriculoperitoneal shunt in reduction of shunt infection: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 143:144–149
Meade R (1985) Bacterial meningitis in the neonatal infant. Med Clin North Am 69(2):257–267
Mustafa M, Mertsola J, Ramilo O, Sáez-Llorens X, Risser R, McCracken GJ (1989) Increased endotoxin and interleukin-1 beta concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of infants with coliform meningitis and ventriculitis associated with intraventricular gentamicin therapy. J Infect Dis 160(5):891–895
Nunan D, Aronson J, Bankhead C (2018) Catalogue of bias: attrition bias. BMJ Evid Based Med 23(1):21–22
Kavuncuoğlu S, Gürsoy S, Türel Ö, Aldemir E, Hoşaf E (2013) Neonatal bacterial meningitis in Turkey: epidemiology, risk factors, and prognosis. J Infect Dev Ctries 7(2):73–81
Ríos-Reátegui E, Ruiz-González L, Murguía-de-Sierra T (1998) Meningitis bacteriana neonatal en una institución de tercer nivel de atención [Neonatal bacterial meningitis in a tertiary treatment center] [published correction appears in Rev Invest Clin 1998;50(3):262]. Rev Invest Clin 50(1):31–36
Basmaci R, Bonacorsi S, Bidet P et al (2015) Escherichia coli meningitis features in 325 children from 2001 to 2013 in France. Clin Infect Dis 61(5):779–786
Shah S, Ohlsson A, Shah V (2012) Intraventricular antibiotics for bacterial meningitis in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (7)
Acknowledgements
We thank the technical support of the National Autonomous University of Nicaragua and particularly the professors from the Department of Statistics: Juan Ricardo Orozco (MSc) and José David García (MSc) for the statistical review. We also thank the independent review done by Drs. Dennis McDonnell (MD) and Abul Ariza Manzano (MD) for their invaluable contributions. Additionally, we appreciate the artistic work of drawing and diagrams made by Gloria Sarmiento Rodriguez (graphic designer). Lastly, we thank our families for their economic support, especially Marlene Valdivia, Alejandrino Perera, Elias Torres, and Tania Perera.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: D.P. Acquisition of data: D.P. and E.H Analysis and interpretation of data: D.P. ; E.H.; L.Z. and K.H. Critically revising the article: D.P. ; E.H.; L.Z. and K.H. Drafting the article: D.P.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Valdivia, D.A.P., Pérez, E.A.H., Vega, L.R.Z. et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of intraventricular antibiotics for neonatal meningitis and ventriculitis. Childs Nerv Syst 40, 1019–1030 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-023-06240-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-023-06240-4