Abstract
Objective
Subcortical band heterotopia is a rare X-linked neuronal migration disorder primarily in females often associated with drug-resistant epilepsy. The aim of this study is to review the literature for non-pharmacological treatment options of drug-resistant epilepsy in subcortical band heterotopia.
Material and methods
In accordance with the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines, we performed a systematic review. Entering the keywords “double cortex,” “subcortical band heterotopia,” and “subcortical laminar heterotopia,” we searched Scopus and PubMed databases. We paid particular attention to type of invasive and non-invasive treatment, radiological presentation, and outcome. We also describe a related case report, managed at Alder Hey Children’s Hospital, Liverpool.
Results
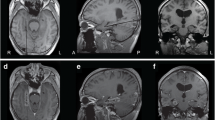
The systematic literature review yielded 25 patients with subcortical band heterotopia and drug-resistant epilepsy who underwent non-pharmacological treatment. Including our patient, 26 patients were reported. The patients’ mean age at seizure onset was 6.5 years (range 0.2–23) with a female sex predilection (5.25:1). The patients’ mean age at invasive or non-invasive treatment was 21.5 years (range 6.5–51). The 26 patients underwent 29 non-pharmacological treatments. Ten patients underwent corpus callosotomy; 8 patients had a formal temporal lobectomy. Three patients had focal cortical resection. Two patients respectively had multiple subpial transections, insertion of a vagal nerve stimulator, or deep brain stimulation of the bilateral anterior nuclei of the thalamus. One patient underwent responsive focal neurostimulation. Another patient had transcutaneous stimulation of the vagal nerve. Sixteen patients reported a reduction or the disappearance of the seizures; 1 patient had no improvement. The outcome of 2 patients was classified class I, of 1 patient class II, of 1 patient class III, and of 5 patients class IV according to the Engel Epilepsy Surgery Outcome Scale.
Conclusion
Mainly corpus callosotomy and formal temporal lobectomy have been performed as non-pharmacological treatment with few cases published overall. Several other invasive procedures and one non-invasive technique are based on case reports. The small number of reported cases prevents drawing a firm conclusion as to which non-pharmacological treatment is the best treatment option for refractive epilepsy in patients with subcortical band heterotopia.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Hehr U, Uyanik G, Aigner L, Couillard-Despres S, Winkler J (2007) DCX-related disorders. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Gripp KW, Mirzaa GM, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2022
Barkovich AJ, Guerrini R, Battaglia G, Kalifa G, N’Guyen T, Parmeggiani A, Santucci M, Giovanardi-Rossi P, Granata T, D’Incerti L (1994) Band heterotopia: correlation of outcome with magnetic resonance imaging parameters. Ann Neurol 36(4):609–617. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410360409
Dobyns WB, Andermann E, Andermann F, Czapansky-Beilman D, Dubeau F, Dulac O, Guerrini R, Hirsch B, Ledbetter DH, Lee NS, Motte J, Pinard JM, Radtke RA, Ross ME, Tampieri D, Walsh CA, Truwit CL (1996) X-linked malformations of neuronal migration. Neurology 47(2):331–339. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.47.2.331
Jacob H (1938) Genetisch verschiedene Gruppen entwicklungsgestörter Gehirne. Genetisch verschiedene Gruppen entwicklungsgestörter Gehirne. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 615–648
Palmini A, Andermann F, de Grissac H, Tampieri D, Robitaille Y, Langevin P, Desbiens R, Andermann E (1993) Stages and patterns of centrifugal arrest of diffuse neuronal migration disorders. Dev Med Child Neurol 35(4):331–339. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.1993.tb11645.x
Bahi-Buisson N, Souville I, Fourniol FJ, Toussaint A, Moores CA, Houdusse A, Lemaitre JY, Poirier K, Khalaf-Nazzal R, Hully M, Leger PL, Elie C, Boddaert N, Beldjord C, Chelly J, Francis F, SBH-LIS European Consortium (2013) New insights into genotype-phenotype correlations for the doublecortin-related lissencephaly spectrum. Brain 136(Pt 1):223–244. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws323
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PloS Med 6(7). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Palmini A, Andermann F, Aicardi J, Dulac O, Chaves F, Ponsot G, Pinard JM, Goutières F, Livingston J, Tampieri D et al (1991) Diffuse cortical dysplasia, or the ‘double cortex’ syndrome: the clinical and epileptic spectrum in 10 patients. Neurology 41(10):1656–1662. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.41.10.1656
Landy HJ, Curless RG, Ramsay RE, Slater J, Ajmone-Marsan C, Quencer RM (1993) Corpus callosotomy for seizures associated with band heterotopia. Epilepsia 34(1):79–83. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1993.tb02379.x
Raymond AA, Fish DR, Sisodiya SM, Alsanjari N, Stevens JM, Shorvon SD (1995) Abnormalities of gyration, heterotopias, tuberous sclerosis, focal cortical dysplasia, microdysgenesis, dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour and dysgenesis of the archicortex in epilepsy. Clinical, EEG and neuroimaging features in 100 adult patients. Brain 118 ( Pt 3):629–60. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/118.3.629
Vossler DG, Lee JK, Ko TS (1999) Treatment of seizures in subcortical laminar heterotopia with corpus callosotomy and lamotrigine. J Child Neurol 14(5):282–288. https://doi.org/10.1177/088307389901400503
Bernasconi A, Martinez V, Rosa-Neto P, D’Agostino D, Bernasconi N, Berkovic S, MacKay M, Harvey AS, Palmini A, da Costa JC, Paglioli E, Kim HI, Connolly M, Olivier A, Dubeau F, Andermann E, Guerrini R, Whisler W, de Toledo-Morrell L, Morrell F, Andermann F (2001) Surgical resection for intractable epilepsy in “double cortex” syndrome yields inadequate results. Epilepsia 42(9):1124–1129. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1528-1157.2001.39900.x
Russo GL, Tassi L, Cossu M, Cardinale F, Mai R, Castana L, Colombo N, Bramerio M (2003) Focal cortical resection in malformations of cortical development. Epileptic Disord 5(Suppl 2):S115–S123
Kawai K, Shimizu H, Yagishita A, Maehara T, Tamagawa K (2004) Clinical outcomes after corpus callosotomy in patients with bihemispheric malformations of cortical development. J Neurosurg 101(1 Suppl):7–15. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped.2004.101.2.0007
Tai PC, McKean JD, Wheatley BM, Gross DW (2004) Surgical resection for intractable epilepsy in “double cortex” syndrome can yield adequate results. Epilepsia 45(5):562–3, author reply 563–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0013-9580.2004.t01-2-62803.x
Saito Y, Sugai K, Nakagawa E, Sakuma H, Komaki H, Sasaki M, Maegaki Y, Ohno K, Sato N, Kaneko Y, Otsuki, (2009) Treatment of epilepsy in severely disabled children with bilateral brain malformations. J Neurol Sci 277(1–2):37–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2008.10.009
Cukiert A, Mariani PP, Burattini JA, Cukiert CM, Forster C, Baise C, Argentoni-Baldochi M, Mello V (2009) Parkinsonism induced by VNS in a child with double-cortex syndrome. Epilepsia 50(12):2667–2669. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02255.x
Franco A, Pimentel J, Campos AR, Morgado C, Pinelo S, Ferreira AG, Bentes C (2016) Stimulation of the bilateral anterior nuclei of the thalamus in the treatment of refractory epilepsy: two cases of subcortical band heterotopia. Epileptic Disord 18(4):426–430. https://doi.org/10.1684/epd.2016.0878
Damiano JA, Do H, Ozturk E, Burgess R, Kalnins R, Jones NC, Dobrovic A, Berkovic SF, Hildebrand M (2017) Sensitive quantitative detection of somatic mosaic mutation in “double cortex” syndrome. Epileptic Disord 19(4):450–455. https://doi.org/10.1684/epd.2017.0944
von Wrede R, Moskau-Hartmann S, Rüber T, Helmstaedter C, Surges R (2019) Sustained seizure freedom with transcutaneous vagal nerve stimulation in drug-resistant epilepsy caused by subcortical band heterotopias. Seizure 70:25–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2019.06.026
Gilliam FG, Ssentongo P, Sather M, Kawasawa YI (2021) Case report: PAFAH1B1 mutation and posterior band heterotopia with focal temporal lobe epilepsy treated by responsive neurostimulation. Front Neurol 12:779113. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.779113
Matsuhashi A, Matsuo T, Kumada S (2022) Incremental changes in interhemispheric functional connectivity after two-stage corpus callosotomy in a patient with subcortical band heterotopia. Epilepsy Behav Rep 18:100525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebr.2022.100525
Engel J Jr, Ness V, Rassmussen TB, Ojemann LM (1993) Outcome with respect to epileptic seizures. In: Engel J (ed) Surgical treatment of the epilepsies, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 609–621
Morrell F, Whisler WW, Bleck TP (1989) Multiple subpial transection: a new approach to the surgical treatment of focal epilepsy. J Neurosurg 70(2):231–239. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1989.70.2.0231
Smith MC (1998) Multiple subpial transection in patients with extratemporal epilepsy. Epilepsia 39(Suppl 4):S81–S89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1998.tb05128.x
Durnford AJ, Rodgers W, Kirkham FJ, Mullee MA, Whitney A, Prevett M, Kinton L, Harris M, Gray WP (2011) Very good inter-rater reliability of Engel and ILAE epilepsy surgery outcome classifications in a series of 76 patients. Seizure 20(10):809–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2011.08.004
Hect JL, Alattar AA, Harford EE, Reecher H, Fernandes DT, Esplin N, McDowell M, Abel TJ (2022) Stereotactic laser interstitial thermal therapy for the treatment of pediatric drug-resistant epilepsy: indications, techniques, and safety. Childs Nerv Syst 38(5):961–970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-022-05491-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ARK: conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting the article, approved the final version of the manuscript on behalf of all authors. BC: analysis and interpretation of data, critically revising the article. AI: analysis and interpretation of data, critically revising the article. JRE: conception and design, analysis and interpretation of data, critically revising the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval and consent to participate were not necessary by the local Ethics Committee.
Consent for publication
The patient’s guardians have consented to submission of this manuscript to the journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kurzbuch, A.R., Cooper, B., Israni, A. et al. Non-pharmacological treatment options of drug-resistant epilepsy in subcortical band heterotopia: systematic review and illustrative case. Childs Nerv Syst 39, 451–462 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-022-05638-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-022-05638-w