Abstract
Introduction
Chronic subdural hematoma (cSDH) is a disease of the elderly population. Incidence in paediatric population is relatively uncommon. Child abuse, birth trauma, coagulopathy and shunt surgeries represent major causes. Major impact of the disease on life of patient due to recurrence and repeat surgical procedure is significant, not to mention the burden on health care system.
Material and methods
We retrospectively reviewed our institute data for chronic sub-dural cases for the past 10 years (2008–2018) and collected data on the demography, clinical features, metabolic workup, mode of treatment, recurrence rates, predisposing factors, laterality, hematoma characteristics and factors associated with recurrence in all cases with less than or equal to 18 years of age.
Results
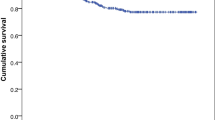
A total of 30 such cases were found in a period of 10 years (2008–2018). The mean patient age was 7.3 years (range 2 months–17 years), with 20 males (66.67%) and 10 females (33.33%). Raised intracranial pressure (n = 9) was the commonest presenting symptom in 30% of cases followed by seizures in 26.67% (n = 8). The previous shunt was the commonest predisposing factor seen in 43.33% (n = 13). cSDHs were unilateral in 56.67% cases (n = 17) and bilateral in 43.33% (n = 13). Burr hole craniostomy was done in 27 cases (90%), and conservative management was done in three cases (10%). Follow up was available for 27 cases (90%) with a mean follow up duration of 24 months. Recurrence rate was 30% (n = 9). Shunt surgery contributed to 77% of bilateral disease (p = 0.009). Child abuse was not reported in our series.
Conclusion
Presence of paediatric cSDH is alarming, and the physician should be alerted to look for underlying cause and rule out child abuse. Detailed metabolic, skeletal workup is required. Treatment of primary pathology should be the goal as CSF diversion is not the solution to all problems, but can definitely be the cause of all the problems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zouros A, Bhargava R, Hoskinson M, Aronyk KE (2004) Further characterization of traumatic subdural collections of infancy. Report of five cases. J Neurosurg 100:512–518. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped.2004.100.5.0512
Matsuo K, Akutsu N, Otsuka K et al (2016) The efficacy and safety of burr-hole craniotomy without continuous drainage for chronic subdural hematoma and subdural hygroma in children under 2 years of age. Child’s nervous system: ChNS: official journal of the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery 32:2369–2375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3233-9
Parent AD (1992) Pediatric chronic subdural hematoma: a retrospective comparative analysis. Pediatr Neurosurg 18:266–271. https://doi.org/10.1159/000120674
Swift DM, McBride L (2000) Chronic subdural hematoma in children. Neurosurg Clin N Am 11:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1042-3680(18)30106-2
Huang J, Li L, Zhang J et al (2019) Treatment of relapsed chronic subdural hematoma in four young children with atorvastatin and low‐dose dexamethasone. Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy 39:783–789. https://doi.org/10.1002/phar.2276
Erşahin Y, Mutluer S, Kocaman S. Continuous external subdural drainage in the management of infantile subdural collections: a prospective study. Childs Nerv Syst. 1997 Oct;13(10):526-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003810050131. PMID: 9403200
Hwang SK, Kim SL. Infantile head injury, with special reference to the development of chronic subdural hematoma. Childs Nerv Syst. 2000 Sep;16(9):590-4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003810000312. PMID: 11048634.
Vinchon M, Noulé N, Soto-Ares G, Dhellemmes P (2001) Subduroperitoneal drainage for subdural hematomas in infants: results in 244 cases. J Neurosurg 95:249–255. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2001.95.2.0249
Mori K, Yamamoto T, Horinaka N, Maeda M (2002) Arachnoid cyst is a risk factor for chronic subdural hematoma in juveniles: twelve cases of chronic subdural hematoma associated with arachnoid cyst. J Neurotrauma 19:1017–1027. https://doi.org/10.1089/089771502760341938
Lin CL, Hwang SL, Su YF et al (2004) External subdural drainage in the treatment of infantile chronic subdural hematoma. Journal of Trauma - Injury, Infection and Critical Care 57:104–107
Kurschel S, Puget S, Bourgeois M et al (2007) Factors influencing the complication rate of subduroperitoneal shunt placement for the treatment of subdural hematomas in infants. J Neurosurg 106:172–178. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped.2007.106.3.172
Blauwblomme T, di Rocco F, Bourgeois M et al (2015) Subdural to subgaleal shunts: alternative treatment in infants with nonaccidental traumatic brain injury?. J Neurosurg Pediatr 15:306–309. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.9.PEDS1485
Murat A, Murat Musluman A, Ozoner B et al (2018) Chronic subdural hematoma associated with arachnoid cyst of the middle fossa: surgical treatment and mid-term results in fifteen patients. Turk Neurosurg 28(5):776–782. https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.21513-17.3
Nguyen VN, Wallace D, Ajmera S et al (2020) Management of subdural hematohygromas in abusive head trauma. Clin Neurosurg 86:281–287. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyz076
Tinois J, Bretonnier M, Proisy M et al (2020) Ruptured intracranial arachnoid cysts in the subdural space: evaluation of subduro-peritoneal shunts in a pediatric population. Child’s Nervous System 36:2073–2078
Wright JN, Feyma TJ, Ishak GE et al (2019) Subdural hemorrhage rebleeding in abused children: frequency, associations and clinical presentation. Pediatr Radiol 49:1762–1772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-019-04483-5
Palmer AW, Albert GW (2019) Minicraniotomy with a subgaleal pocket for the treatment of subdural fluid collections in infants. J Neurosurg Pediatr 23:480–485. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.11.PEDS18322
Caldarelli M, Di Rocco C, Romani R (2002) Surgical treatment of chronic subdural hygromas in infants and children. Acta neurochirurgica 144:581–588; discussion 588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-002-0947-0
Hasegawa M, Yamashima T, Kida S, Yamashita J (1997) Membranous ultrastructure of human arachnoid cells. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:1217–1227. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005072-199711000-00006
Wang H-K, Chen H-J, Lu K et al (2010) A pediatric chronic subdural hematoma after dodgeball head injury. Pediatr Emerg Care 26:667–668. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0b013e3181f05475
Aoki N (1990) Chronic subdural hematoma in infancy. Clinical analysis of 30 cases in the CT era. J Neurosurg 73:201–205. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1990.73.2.0201
Christensen E, Husby J (1963) Chronic subdural hematoma in infancy. Acta Neurol Scand 39:323–342. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.1963.tb05334.x
Suh DY, Davis PC, Hopkins KL et al (2001) Nonaccidental pediatric head injury: diffusion-weighted imaging findings. Neurosurg 49:309–318; discussion 318–20. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200108000-00011
Litofsky NS, Raffel C, McComb JG (1992) Management of symptomatic chronic extra-axial fluid collections in pediatric patients. Neurosurgery 31:445–450. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-199209000-00009
Melo JRT, Di Rocco F, Bourgeois M et al (2014) Surgical options for treatment of traumatic subdural hematomas in children younger than 2 years of age. J Neurosurg Pediatr 13:456–461. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.1.PEDS13393
Almenawer SA, Farrokhyar F, Hong C et al (2014) Chronic subdural hematoma management. Ann Surg 259:449–457. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000000255
Liu W, Bakker NA, Groen RJM (2014) Chronic subdural hematoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of surgical procedures. J Neurosurg 121:665–673. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.5.JNS132715
Santarius T, Kirkpatrick PJ, Ganesan D et al (2009) Use of drains versus no drains after burr-hole evacuation of chronic subdural haematoma: a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet 374:1067–1073. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61115-6
Tsutsumi K, Maeda K, Iijima A et al (1997) The relationship of preoperative magnetic resonance imaging findings and closed system drainage in the recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma. J Neurosurg 87:870–875. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1997.87.6.0870
Wright D, Pereira EA, Magdum SA (2015) A pediatric chronic subdural hematoma: more than meets the eye. J Pediatr Neurosci 10(4):376–378. https://doi.org/10.4103/1817-1745.174451
Xu H, Wang ZX, Liu F, Tan GW, Zhu HW, Chen DH (2013) Programmable shunt valves for the treatment of hydrocephalus: a systematic review. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 17(5):454–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2013.04.001 (Epub 2013 Jul 3 PMID: 23830575)
Hutchinson PJ, Edlmann E, Bulters D, Zolnourian A, Holton P, Suttner N, Agyemang K, Thomson S, Anderson IA, Al-Tamimi YZ, Henderson D, Whitfield PC, Gherle M, Brennan PM, Allison A, Thelin EP, Tarantino S, Pantaleo B, Caldwell K, Davis-Wilkie C, Mee H, Warburton EA, Barton G, Chari A, Marcus HJ, King AT, Belli A, Myint PK, Wilkinson I, Santarius T, Turner C, Bond S, Kolias AG (2020) British Neurosurgical Trainee Research Collaborative; Dex-CSDH Trial Collaborators. Trial of Dexamethasone for Chronic Subdural Hematoma. N Engl J Med. 31;383(27):2616–2627. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2020473. Epub 2020 Dec 16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HD, AJ: collection of data and writing of manuscript; HD, RG: concept and idea and critical revisions; DS: study supervision and critical revisions; VV: supervision and critical revisions; SK: supervision and critical revisions; ARP: supervision and critical revisions; AS: supervision and critical revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Study design is retrospective; hence, approval of ethical committee was not sought.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deora, H., Mishra, A., Gupta, R. et al. Paediatric chronic subdural haematoma: what are the predisposing factors and outcomes in management of these cases?. Childs Nerv Syst 38, 123–132 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-021-05341-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-021-05341-2