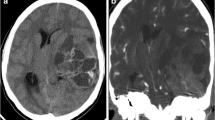
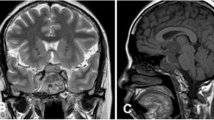
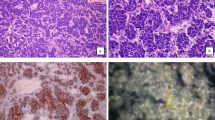
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose is to highlight the primary intracranial (meningeal-based) occurrence of Ewing sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor (ES/PNET).
Methods
This report is a collation of clinicopathological features of eight cases of molecularly and clinicoradiologically confirmed primary (non-metastatic) intracranial (non-osseous) meningeal ES/PNET.
Results
The age range was 1 to 33 years with a median age of 9 years. Male to female ratio was 0.6:1. All patients were diagnosed on the debulking surgical material (gross total resection, 2 cases; subtotal resection, 6 cases) and showed primitive embryonal histomorphology with diffuse membranous CD99 immunoexpression and EWSR1 gene rearrangement by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Seven of them showed a typical FISH pattern of split signals with break-apart probe, while one showed an unusual signal pattern of loss of green signals. EFT-2001 adjuvant protocol was followed along with focal radiotherapy (RT) in all cases (except case 8, full course of chemotherapy could not be completed). Two cases had local recurrence—one of them died of disease recurrence before the administration of further treatment.
Conclusion
This series adds non-osseous intracranial site to the list of uncommon sites of occurrence for ES/PNET and more importantly emphasizes the need to be considered in a differential list of primary intracranial primitive embryonal tumors before embarking as primary central nervous system (CNS) embryonal tumor, NOS.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data is associated with the manuscript.
Change history
10 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04881-3
References
DE Alava E, Lessnick SL, Sorensen PH (2013) Ewing sarcoma. In: Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F (eds) WHO Classification of Tumors of Soft Tissue and Bone. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 306–309
Antonescu CR, Paulus W, Perry A et al (2016) Ewing sarcoma/ peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor. In: Bosman FT, Jaffe ES, Lakhani SR, Ohgaki H (eds) WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System, Revised 4th edn. IARC, Lyon, pp 258–264
Khoury JD (2005) Ewing sarcoma family of tumors. Adv Anat Pathol 12:212–220
Kumar V, Singh A, Sharma V, Kumar M (2017) Primary intracranial dural-based Ewing sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor mimicking a meningioma: A rare tumor with review of literature. Asian J Neurosurg 12:351–357
Navarro R, Laguna A, de Torres C et al (2007) Primary Ewing sarcoma of the tentorium presenting with intracranial hemorrhage in a child. J Neurosurg 107:411–415
Jay V, Zielenska M, Lorenzana A, Drake J (1999) An unusual cerebellar primitive neuroectodermal tumor with t(11;22) translocation: pathological and molecular analysis. Pediatr Pathol Lab Med 16:119–128
Papotti M, Abbona G, Pagani A, Monga G, Bussolati G (1998) Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the meninges: an histological, immunohistochemical, ultrastructural, and cytogenetic study. Endocr Pathol 9:275–280
Antunes NL, Lellouch-Tubiana A, Kalifa C, Delattre O, Pierre-Kahn A, Rosenblum MK (2001) Intracranial Ewing sarcoma/‘peripheral’ primitive neuroectodermal tumor of dural origin with molecular genetic confirmation. J Neuro-Oncol 51:51–56
Ishii N, Hiraga H, Sawamura Y, Shinohe Y, Nagashima K (2001) Alternative EWS-FLI1 fusion gene and MIC2 expression in peripheral and central primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Neuropathology 21:40–44
Dedeurwaerdere F, Giannini C, Sciot R, Rubin BP, Perilongo G, Borghi L, Ballotta ML, Cornips E, Demunter A, Maes B, Dei Tos AP (2002) Primary peripheral PNET/Ewing’s sarcoma of the dura: a clinicopathologic entity distinct from central PNET. Mod Pathol 15:673–678
D’Antonio A, Caleo A, Garcia JF, Marsilia GM, De Dominicis G, Boscaino A (2004) Primary peripheral PNET/Ewing’s sarcoma of the dura with FISH analysis. Histopathology 45:651–654
Idrees M, Gandhi C, Betchen S, Strauchen J, King W, Wolfe D (2005) Intracranial peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the cavernous sinus: a diagnostic peculiarity. Arch Pathol Lab Med 129:e11–e15
Mazur MA, Gururangan S, Bridge JA, Cummings TJ, Mukundan S, Fuchs H, Larrier N, Halperin EC (2005) Intracranial ewing sarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 45:850–856
Mobley BC, Roulston D, Shah GV, Bijwaard KE, McKeever PE (2006) Peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor/Ewing’s sarcoma of the craniospinal vault: case reports and review. Hum Pathol 37:845–853
Pekala JS, Gururangan S, Provenzale JM, Mukundan S Jr (2006) Central nervous system extraosseous Ewing sarcoma: radiologic manifestations of this newly defined pathologic entity. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:580–583
Attabib NA, West M, Rhodes RH (2006) Peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the cavernous sinus: case report. Neurosurgery 58:E992
Kazmi SAJ, Perry A, Pressey JG, Wellons JC, Hammers Y, Palmer CA (2007) Primary Ewing sarcoma of the brain: a case report and literature review. Diagn Mol Pathol 16:108–111
Kobayashi H, Terasaka S, Yamaguchi S, Kubota K, Iwasaki Y (2008) Primary Ewing’s sarcoma: peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the jugular foramen. Acta Neurochir 150:817–821
Bano S, Yadav SN, Garga UC (2009) Case report: intracranial peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor – Ewing’s sarcoma of dura with transcalvarial-subgaleal extension: An unusual radiological presentation. Indian J Radiol Imaging 19:305–307
dos Santos RE, Harhangi B, Kros J, Vincent A, Dirven C (2010) A primary extraosseous Ewing sarcoma in the cerebellopontine angle of a child: review of relevant literature and case report. Neurosurgery 67:E1852–E18E6
Mellai M, Caldera V, Comino A, Fortunato M, Bernucci C, Schiffer D (2010) PNET/ESFT of the cranial vault: a case report. Clin Neuropathol 29:372–377
Choudhury KB, Sharma S, Kothari R, Majumder A (2011) Primary extraosseous intracranial Ewing’s sarcoma: case report and literature review. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 32:118–121
Burkhardt JK, Kockro RA, Dohmen-Scheufler H et al (2011) Small supratentorial, extraaxial primitive neuroectodermal tumor causing large intracerebral hematoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51:441–444
Antonelli M, Caltabiano R, Chiappetta C, Oliva MA, Giangaspero F, Lanzafame S (2011) Primary peripheral PNET/Ewing’s sarcoma arising in the meninges, confirmed by the presence of the rare translocation t(21;22) (q22;q12). Neuropathology 31:549–555
Tanboon J, Sitthinamsuwan B, Paruang T, Marrano P, Thorner PS (2012) Primary intracranial Ewing sarcoma with an unusually aggressive course: a case report and review of the literature. Neuropathology 32:293–300
Patibandla MR, Uppin SG, Thotakura AK, Panigrahi MK, Challa S (2013) Primary Ewings sarcoma of cavernous sinus in an infant: a case report and review of literature. Turk Neurosurg 23:98–103
Cole M, Parajuli S, Laske D et al (2014) Peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the dura in a 51-year-old woman following intensive treatment for breast cancer. Am J Case Rep 15:294–299
Velivela K, Rajesh A, Uppin MS, Purohit AK (2014) Primary intracranial peripheral PNET″--a case report and review. Neurol India 62:669–673
Stark AM, Leuschner I, Mehdorn HM et al (2014) Ewing sarcoma of the posterior fossa in an adolescent girl. Case Rep Med 2014:439830
VandenHeuvel KA, Al-Rohil RN, Stevenson ME et al (2015) Primary intracranial Ewing’s sarcoma with unusual features. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:260–274
Ke C, Duan Q, Yang H, Zhu F, Yan M, Xu SP, Zhou S, Wan F, Shu K, Lei T, Xia LM (2017) Meningeal Ewing sarcoma/peripheral PNET: clinicopathological, immunohistochemical and FISH study of four cases. Neuropathology 37:35–44
Mattogno PP, Nasi D, Iaccarino C, Oretti G, Santoro L, Romano A (2017) First case of primary sellar/suprasellar-intraventricular Ewing sarcoma: case report and review of the literature. World Neurosurg 98:869e1–869e5
Yang MJ, Whelan R, Madden J, Mulcahy Levy JM, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Hankinson TC, Foreman NK, Handler MH (2018) Intracranial Ewing sarcoma: four pediatric examples. Childs Nerv Syst 34:441–448
Chen J, Li M, Zheng Y, Zheng L, Fan F, Wang Y (2019) Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of patients with primary spinal ewing sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Front Oncol 9:555
Shimada H, Newton WA Jr, Soule EH, Qualman SJ, Aoyama C, Maurer HM (1988) Pathologic features of extraosseous Ewing’s sarcoma: a report from the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. Hum Pathol 19:442–453
Hsiao IH, Chen CH, Lee HC, Cho DY (2017) Primary Leptomeningeal PNETs Mimicking TB Meningitis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Turk Neurosurg 27:155–159
Sturm D, Orr BA, Toprak UH, Hovestadt V, Jones DTW, Capper D, Sill M, Buchhalter I, Northcott PA, Leis I, Ryzhova M, Koelsche C, Pfaff E, Allen SJ, Balasubramanian G, Worst BC, Pajtler KW, Brabetz S, Johann PD, Sahm F, Reimand J, Mackay A, Carvalho DM, Remke M, Phillips JJ, Perry A, Cowdrey C, Drissi R, Fouladi M, Giangaspero F, Łastowska M, Grajkowska W, Scheurlen W, Pietsch T, Hagel C, Gojo J, Lötsch D, Berger W, Slavc I, Haberler C, Jouvet A, Holm S, Hofer S, Prinz M, Keohane C, Fried I, Mawrin C, Scheie D, Mobley BC, Schniederjan MJ, Santi M, Buccoliero AM, Dahiya S, Kramm CM, von Bueren AO, von Hoff K, Rutkowski S, Herold-Mende C, Frühwald MC, Milde T, Hasselblatt M, Wesseling P, Rößler J, Schüller U, Ebinger M, Schittenhelm J, Frank S, Grobholz R, Vajtai I, Hans V, Schneppenheim R, Zitterbart K, Collins VP, Aronica E, Varlet P, Puget S, Dufour C, Grill J, Figarella-Branger D, Wolter M, Schuhmann MU, Shalaby T, Grotzer M, van Meter T, Monoranu CM, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Snuderl M, Forrester LA, Koster J, Versteeg R, Volckmann R, van Sluis P, Wolf S, Mikkelsen T, Gajjar A, Aldape K, Moore AS, Taylor MD, Jones C, Jabado N, Karajannis MA, Eils R, Schlesner M, Lichter P, von Deimling A, Pfister SM, Ellison DW, Korshunov A, Kool M (2016) New brain tumor entities emerge from molecular classification of CNS-PNETs. Cell 164:1060–1072
Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Herrmann F, Penetrante R, Beck A, Sait S, Block AM, Odunsi K, Fisher J, Balos L, Cheney RT (2006) Diagnostic utility of FLI-1 monoclonal antibody and dual-colour, break-apart probe fluorescence in situ (FISH) analysis in Ewing’s sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor (EWS/PNET). A comparative study with CD99 and FLI-1 polyclonal antibodies. Histopathology 49:569–575
Spence T, Sin-Chan P, Picard D, Barszczyk M, Hoss K, Lu M, Kim SK, Ra YS, Nakamura H, Fangusaro J, Hwang E, Kiehna E, Toledano H, Wang Y, Shi Q, Johnston D, Michaud J, la Spina M, Buccoliero AM, Adamek D, Camelo-Piragua S, Peter Collins V, Jones C, Kabbara N, Jurdi N, Varlet P, Perry A, Scharnhorst D, Fan X, Muraszko KM, Eberhart CG, Ng HK, Gururangan S, van Meter T, Remke M, Lafay-Cousin L, Chan JA, Sirachainan N, Pomeroy SL, Clifford SC, Gajjar A, Shago M, Halliday W, Taylor MD, Grundy R, Lau CC, Phillips J, Bouffet E, Dirks PB, Hawkins CE, Huang A (2014) CNS-PNETs with C19MC amplification and/or LIN28 expression comprise a distinct histogenetic diagnostic and therapeutic entity. Acta Neuropathol 128:291–303
Bridge RS, Rajaram V, Dehner LP, Pfeifer JD, Perry A (2006) Molecular diagnosis of Ewing sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor in routinely processed tissue: a comparison of two FISH strategies and RT-PCR in malignant round cell tumors. Mod Pathol 19:1–8
Vargas AC, Selinger CI, Satgunaseelan L, Cooper WA, Gupta R, Stalley P, Brown W, Soper J, Schatz J, Boyle R, Thomas DM, Tattersall MHN, Bhadri VA, Maclean F, Bonar SF, Scolyer RA, Karim RZ, McCarthy SW, Mahar A, O’Toole SA (2016) Atypical Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1 fluorescence in-situ hybridization signal patterns in bone and soft tissue tumors: diagnostic experience with 135 cases. Histopathology 69:1000–1011
Paulussen M, Ahrens S, Dunst J, Winkelmann W, Exner GU, Kotz R, Amann G, Dockhorn-Dworniczak B, Harms D, Müller-Weihrich S, Welte K, Kornhuber B, Janka-Schaub G, Göbel U, Treuner J, Voûte PA, Zoubek A, Gadner H, Jürgens H (2001) Localized Ewing tumor of bone: final results of the cooperative Ewing’s Sarcoma Study CESS 86. J Clin Oncol 19:1818–1829
Womer RB, West DC, Krailo MD, Dickman PS, Pawel BR, Grier HE, Marcus K, Sailer S, Healey JH, Dormans JP, Weiss AR (2012) Randomized controlled trial of interval-compressed chemotherapy for the treatment of localized Ewing sarcoma: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 30:4148–4154
Parambil BC, Vora T, Sankaran H et al (2020) Outcomes with nondose-dense chemotherapy for Ewing sarcoma: a practical approach for the developing world [published online ahead of print, 2020 Jul 24]. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2020:e28604. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.28604
Rodríguez-Galindo C, Liu T, Krasin MJ, Wu J, Billups CA, Daw NC, Spunt SL, Rao BN, Santana VM, Navid F (2007) Analysis of prognostic factors in Ewing sarcoma family of tumors: review of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital studies. Cancer 110:375–384
Acknowledgments
The authors like to acknowledge Mr. Sandeep Dhanwade and Mr. Vinayak Kadam for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived, interpretation (cases diagnosed), facilitation of retrieving the relevant data, drafting, and final editing by Dr. Sridhar Epari; gathering the clinical data and interpretation of certain laboratory findings by Dr. Gauri Deshpande (for the cases 5–8) and Dr. Chavvi Gupta (for the cases 1–4); contribution in preparing the initial draft by Dr. Gauri Deshpande, partly assisted by Dr. Chavvi Gupta; scientific contributions by Dr. Omshree Shetty and Ms. Mamta Gurav; clinical and therapeutic contributions provided by Dr. Girish Chinnaswamy, Dr. Aliasgar Moiyadi, and Dr. Tejpal Gupta. All the authors have read the manuscript and concurred with the findings.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethics approval
This is an observational report made by retrieving the cases from archives and anonymizes all the details of the patients. Thus, this has been granted review exemption from institutional ethics committee.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Due to an internal mistake during production the name of one of the co-authors, Aliasgar Moiyadi, was omitted from the original publication. With this Erratum the name of the co-author is included again and the original publication has been modified accordingly. SpringerNature apologizes for this and for any inconvenience associated therewith.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deshpande, G., Epari, S., Gupta, C. et al. Primary intracranial Ewing sarcoma/ peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor, an entity of unacquaintance: a series of 8 cases. Childs Nerv Syst 37, 839–849 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04850-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04850-w