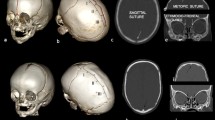
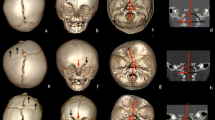
Abstract
Purpose
Craniofacial dysmorphology varies significantly along a wide spectrum of severity in metopic cranial synostosis (MCS). This study aimed to quantify craniofacial changes, in MCS, to investigate their relationships with the severity of trigonocephaly.
Methods
By combining the metopic ridge and interfrontal angles, we identified three groups of trigonocephaly severity (mild group n.14, moderate group n.19, severe group n.18). We perform a quantitative analysis using high-resolution CT images evaluating (1) cranial fossae dimensions; (2) vault indices and ratios: interparietal/ intercoronal (IPD/ICD), interparietal/intertemporal (IPD/ITD), cephalic index, vertico-longitudinal index; (3) orbito-facial distances (midfacial depth, maxillary height, upper facial index, orbital distances, globe protrusions), maxilla and orbital volumes; (4) supratentorial (ICV) and infratentorial (PCFV) cranial volumes and supratentorial (WBV) and infratentorial (PCFBV) brain volumes.
Results
In all groups, middle skull base lengths and upper midface index were increased. In moderate and severe groups: anterior hemifossa lengths were reduced, IPD/ICD and vertico-longitudinal index were changed; midfacial depth, anterior, mild, and lateral interorbital distances were reduced; globe protrusions were increased. The comparison between moderate and severe groups showed an increase of both globe protrusions and IPD/ICD. Among all groups, ICV and WBV were reduced in the severe group.
Conclusion
This morpho-volumetric study provides new insights in understanding the craniofacial changes occurring in infants at different severity of trigonocephaly. The increase of globe protrusions and the reduction of supratentorial volumes found in the severe group reflect the severity of trigonocephaly; these findings might have a clinical and surgical relevance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson PJ, Netherway DJ, Abbott A, David DJ (2004) Intracranial volume measurement of metopic craniosynostosis. J Craniofac Surg 15:1014–1016 discussion 1017-1018
Anolik RA, Allori AC, Pourtaheri N, Rogers GF, Marcus JR (2016) Objective assessment of the interfrontal angle for severity grading and operative decision-making in metopic synostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 137:1548–1555. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000002052
Applegren ND, Shock LA, Aldridge KJ, Derrick CD, Tanaka T, Baker CL, Muzaffar AR (2018) Relationship of a metopic ridge and anterior cranial volume measured by a noninvasive laser shape digitizer. J Craniofac Surg 29:76–81. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000004065
Badve CA, MM K, Iyer RS, Ishak GE, Khanna PC (2013) Craniosynostosis: imaging review and primer on computed tomography. Pediatr Radiol 43:728–742; quiz 725-727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-013-2673-6
Beckett JS, Chadha P, Persing JA, Steinbacher DM (2012) Classification of trigonocephaly in metopic synostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 130:442e-447e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e31825dc244
Bennett KG, Bickham RS, Robinson AB, Buchman SR, Vercler CJ (2016) Metopic craniosynostosis: a demographic analysis outside an urban environment. J Craniofac Surg 27:544–547. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000002532
Bentley RP, Sgouros S, Natarajan K, Dover MS, Hockley AD (2002) Changes in orbital volume during childhood in cases of craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 96:747–754. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2002.96.4.0747
Bentley RP, Sgouros S, Natarajan K, Dover MS, Hockley AD (2002) Normal changes in orbital volume during childhood. J Neurosurg 96:742–746. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2002.96.4.0742
Birgfeld CB, Saltzman BS, Hing AV, Heike CL, Khanna PC, Gruss JS, Hopper RA (2013) Making the diagnosis: metopic ridge versus metopic craniosynostosis. J Craniofac Surg 24:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e31826683d1
Bottero L, Lajeunie E, Arnaud E, Marchac D, Renier D (1998) Functional outcome after surgery for trigonocephaly. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:952–958 discussion 959-960
Calandrelli R, Pilato F, Massimi L, Panfili M, D'Apolito G, Gaudino S, Colosimo C (2018) Quantitative evaluation of facial hypoplasia and airway obstruction in infants with syndromic craniosynostosis: relationship with skull base and splanchnocranium sutural pattern. Neuroradiology 60:517–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-018-2005-5
Calandrelli R, Pilato F, Massimi L, Panfili M, Di Rocco C, Colosimo C (2019) The unseen third dimension: a novel approach for assessing head shape severity in infants with isolated sagittal synostosis. Childs Nerv Syst. 35:1351–1356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-019-04246-5
Captier G, Leboucq N, Bigorre M, Canovas F, Bonnel F, Bonnafe A, Montoya P (2003) Plagiocephaly: morphometry of skull base asymmetry. Surg Radiol Anat 25:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-003-0118-x
Cho MJ, Kane AA, Seaward JR, Hallac RR (2016) Metopic “ridge” vs. “craniosynostosis”: quantifying severity with 3D curvature analysis. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 44:1259–1265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2016.06.019
Currarino G, Silverman FN (1960) Orbital hypotelorism, arhinencephaly, and trigonocephaly. Radiology 74:206–217. https://doi.org/10.1148/74.2.206
Derderian C, Seaward J (2012) Syndromic craniosynostosis. Semin Plast Surg 26:64–75. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1320064
Domeshek LF, Das RR, Van Aalst JA, Mukundan S Jr, Marcus JR (2011) Influence of metopic suture fusion associated with sagittal synostosis. J Craniofac Surg 22:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181f6c56b
Ezaldein HH, Metzler P, Persing JA, Steinbacher DM (2014) Three-dimensional orbital dysmorphology in metopic synostosis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 67:900–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2014.03.009
Farkas LG (1996) Accuracy of anthropometric measurements: past, present, and future. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 33:10–18; discussion 19-22. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_1996_033_0010_aoampp_2.3.co_2
Freudlsperger C, Steinmacher S, Bachli H, Somlo E, Hoffmann J, Engel M (2015) Metopic synostosis: measuring intracranial volume change following fronto-orbital advancement using three-dimensional photogrammetry. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 43:593–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2015.02.017
Friede H, Alberius P, Lilja J, Lauritzen C (1990) Trigonocephaly: clinical and cephalometric assessment of craniofacial morphology in operated and nontreated patients. Cleft Palate J 27:362–367 discussion 368
Haas LL (1952) Roentgenological skull measurements and their diagnostic applications. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 67:197–209
Hill CA, Vaddi S, Moffitt A, Kane AA, Marsh JL, Panchal J, Richtsmeier JT, Aldridge K (2011) Intracranial volume and whole brain volume in infants with unicoronal craniosynostosis. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 48:394–398. https://doi.org/10.1597/10-051
Jaskolka MS (2017) Current controversies in metopic suture craniosynostosis. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 29:447–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coms.2017.07.003
Jeyasingh P, Agarwal AK, Gupta SC, Arora AK, Gupta CD (1988) A study of cranio-facial indices in Uttar Pradesh crania. Anat Anz 165:345–349
Kellogg R, Allori AC, Rogers GF, Marcus JR (2012) Interfrontal angle for characterization of trigonocephaly: part 1: development and validation of a tool for diagnosis of metopic synostosis. J Craniofac Surg 23:799–804. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e3182518ad2
Kolar JC, Salter EM (1997) Preoperative anthropometric dysmorphology in metopic synostosis. Am J Phys Anthropol 103:341–351. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-8644(199707)103:3<341::AID-AJPA4>3.0.CO;2-T
Kranioti EF, Iscan MY, Michalodimitrakis M (2008) Craniometric analysis of the modern Cretan population. Forensic Sci Int 180(110):e111–e115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2008.06.018
Langford RJ, Sgouros S, Natarajan K, Nishikawa H, Dover MS, Hockley AD (2003) Maxillary volume growth in craniosynostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:1598–1604. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000057972.87632.ec
Maltese G, Tarnow P, Wikberg E, Bernhardt P, Lagerlof JH, Tovetjarn R, Kolby L (2014) Intracranial volume before and after surgical treatment for isolated metopic synostosis. J Craniofac Surg 25:262–266. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000000423
McEwan TW, Martin AL, Tanaka T, Aldridge K, Muzaffar AR (2016) Evaluating children with metopic craniosynostosis: the cephalic width-intercoronal distance ratio. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 53:e95–e100. https://doi.org/10.1597/14-310
Mendonca DA, White N, West E, Dover S, Solanki G, Nishikawa H (2009) Is there a relationship between the severity of metopic synostosis and speech and language impairments? J Craniofac Surg 20:85–88; discussion 89. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181955244
Paige KT, Cohen SR, Simms C, Burstein FD, Hudgins R, Boydston W (2003) Predicting the risk of reoperation in metopic synostosis: a quantitative CT scan analysis. Ann Plast Surg 51:167–172. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.SAP.0000058498.64113.11
Patel KB, Skolnick GB, Mulliken JB (2016) Anthropometric outcomes following fronto-orbital advancement for metopic synostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 137:1539–1547. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000002129
Posnick JC, Armstrong D, Bite U (1995) Metopic and sagittal synostosis: intracranial volume measurements prior to and after cranio-orbital reshaping in childhood. Plast Reconstr Surg 96:299–309 discussion 310-295
Ruiz-Correa S, Starr JR, Lin HJ, Kapp-Simon KA, Sze RW, Ellenbogen RG, Speltz ML, Cunningham ML (2008) New severity indices for quantifying single-suture metopic craniosynostosis. Neurosurgery 63:318–324; discussion 324-315. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000316417.06500.DA
Shimoji T, Shimabukuro S, Sugama S, Ochiai Y (2002) Mild trigonocephaly with clinical symptoms: analysis of surgical results in 65 patients. Childs Nerv Syst 18:215–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-002-0568-1
Singh RP, Dhariwal D, Bhujel N, Shaikh Z, Davies P, Nishikawa H, Solanki G, Dover MS (2010) Role of parental risk factors in the aetiology of isolated non-syndromic metopic craniosynostosis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 48:438–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2009.06.233
Smartt JM Jr, Elliott RM, Reid RR, Bartlett SP (2011) Analysis of differences in the cranial base and facial skeleton of patients with lambdoid synostosis and deformational plagiocephaly. Plast Reconstr Surg 127:303–312. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181f95cd8
Sumkovski R, Kocevski I, Micunovic M (2019) Trigonocephaly: case report, review of literature and a technical note. Open Access Maced J Med Sci 7:117–120. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2019.031
van der Meulen J (2012) Metopic synostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 28:1359–1367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1803-z
Waitzman AA, Posnick JC, Armstrong DC, Pron GE (1992) Craniofacial skeletal measurements based on computed tomography: part II. Normal values and growth trends. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 29:118–128. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_1992_029_0118_csmboc_2.3.co_2
Wang JY, Dorafshar AH, Liu A, Groves ML, Ahn ES (2016) The metopic index: an anthropometric index for the quantitative assessment of trigonocephaly from metopic synostosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr 18:275–280. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.2.PEDS15524
Weinzweig J, Kirschner RE, Farley A, Reiss P, Hunter J, Whitaker LA, Bartlett SP (2003) Metopic synostosis: defining the temporal sequence of normal suture fusion and differentiating it from synostosis on the basis of computed tomography images. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:1211–1218. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000080729.28749.A3
Wes AM, Paliga JT, Goldstein JA, Whitaker LA, Bartlett SP, Taylor JA (2014) An evaluation of complications, revisions, and long-term aesthetic outcomes in nonsyndromic metopic craniosynostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 133:1453–1464. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000000223
Yee ST, Fearon JA, Gosain AK, Timbang MR, Papay FA, Doumit G (2015) Classification and management of metopic craniosynostosis. J Craniofac Surg 26:1812–1817. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000001866
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Rosalinda Calandrelli declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Fabio Pilato declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Luca Massimi declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Antonio Marrazzo declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Marco Panfili declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Concezio Di Rocco declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Cesare Colosimo declares that he is a scientific consultant for Bracco Diagnostics Inc. and Bayer HealthCare.
Research involving human participants
We declare that all procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calandrelli, R., Pilato, F., Massimi, L. et al. Orbito-facial dysmorphology in patients with different degrees of trigonocephaly severity: quantitative morpho-volumetric analysis in infants with non-syndromic metopic craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 36, 1263–1273 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-019-04456-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-019-04456-x