Abstract
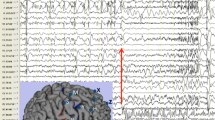
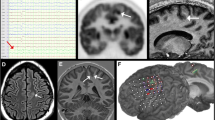
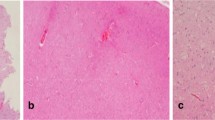
Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) was first described as a distinct neuropathological entity in 1971 by Taylor and colleagues. FCD is thought to be an embryological migration disorder and is thus considered a non-progressive, unchangeable disease throughout life. A 9-year-old right-handed boy was referred from a local hospital for medically intractable epileptic seizures. Serial magnetic resonance images (MRI) showed intensity changes that indicated exacerbation and remission. After presurgical evaluations including intracranial video-electroencephalogram monitoring, we performed a lesionectomy aided by MRI and epileptic focus resection. He has been free from seizures for more than 3 years. Neuropathological findings showed FCD type Ib. We surgically treated a patient with FCD, which showed MRI intensity changes indicating exacerbation and remission. Although FCD type Ib is generally invisible on MRI, in this patient, changes in intensity on MRI made FCD type Ib visible.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guerrini R, Duchowny M, Jayakar P, Krsek P, Kahane P, Tassi L, Melani F, Polster T, Andre VM, Cepeda C, Krueger DA, Cross JH, Spreafico R, Cosottini M, Gotman J, Chassoux F, Ryvlin P, Bartolomei F, Bernasconi A, Stefan H, Miller I, Devaux B, Najm I, Giordano F, Vonck K, Barba C, Blumcke I (2015) Diagnostic methods and treatment options for focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsia 56:1669–1686
Hauptman JS, Mathern GW (2012) Surgical treatment of epilepsy associated with cortical dysplasia: 2012 update. Epilepsia 53(Suppl 4):98–104
Fujimoto A, Ochi A, Imai K, Chan D, Sharma R, Viljoen A, Chu B, Holowka S, Kemp SM, Chuang SH, Matsumura A, Ayuzawa S, Snead OC 3rd, Otsubo H (2009) Magnetoencephalography using total intravenous anesthesia in pediatric patients with intractable epilepsy: lesional vs nonlesional epilepsy. Brain Dev 31:34–41
Taylor DC, Falconer MA, Bruton CJ, Corsellis JA (1971) Focal dysplasia of the cerebral cortex in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 34:369–387
Blumcke I, Aronica E, Miyata H, Sarnat HB, Thom M, Roessler K, Rydenhag B, Jehi L, Krsek P, Wiebe S, Spreafico R (2016) International recommendation for a comprehensive neuropathologic workup of epilepsy surgery brain tissue: a consensus task force report from the ILAE commission on diagnostic methods. Epilepsia 57:348–358
Forgacs PB, Sarkis R, Folkerth R, Golby A, Hsu L, Bubrick EJ, Dworetzky BA (2014) Focal cortical dysplasia IIb presenting as slowly progressive aphasia mimicking a brain tumor. Seizure 23:161–163
Owens C, Bradley L, Farrell M, O’Brien D, King MD, Ryan SP (2010) Seizure-induced inflammation in focal cortical dysplasia resulting in imaging progression that simulates neoplasia. J Neuroimaging 20:208–210
Wang D, Blumcke I, Gui Q, Zhou W, Zuo H, Lin J, Luo Y (2013) Clinico-pathological investigations of Rasmussen encephalitis suggest multifocal disease progression and associated focal cortical dysplasia. Epileptic Disord 15:32–43
Finn MA, Blumenthal DT, Salzman KL, Jensen RL (2007) Transient postictal MRI changes in patients with brain tumors may mimic disease progression. Surg Neurol 67:246–250
Yang T, Zhou D, Stefan H (2010) Why mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis is progressive: uncontrolled inflammation drives disease progression? J Neurol Sci 296:1–6
Kim JA, Chung JI, Yoon PH, Kim DI, Chung TS, Kim EJ, Jeong EK (2001) Transient MR signal changes in patients with generalized tonicoclonic seizure or status epilepticus: periictal diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1149–1160
Hubers A, Thoma K, Schocke M, Fauser S, Ludolph AC, Kassubek J, Pinkhardt EH (2018) Acute DWI reductions in patients after single epileptic seizures - more common than assumed. Front Neurol 9:550
Ruber T, David B, Luchters G, Nass RD, Friedman A, Surges R, Stocker T, Weber B, Deichmann R, Schlaug G, Hattingen E, Elger CE (2018) Evidence for peri-ictal blood-brain barrier dysfunction in patients with epilepsy. Brain 141:2952–2965
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Written informed consent for publication of case details was obtained from the patient’s parents. This study was approved by the ethics committee at the Seirei Hamamatsu General Hospital.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuroda, N., Fujimoto, A., Enoki, H. et al. A case of focal cortical dysplasia type Ib atypically showing reversible intensity changes on magnetic resonance imaging which could be affected by epileptic discharge activity. Childs Nerv Syst 35, 883–887 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-019-04093-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-019-04093-4