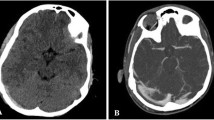
Abstract
Background
Primary idiopathic intracranial hypertension (PIIH) in children is rare and has a poorly understood pathophysiology. It is characterized by raised intracranial pressure (ICP) in the absence of an identified brain lesion. Diagnosis is usually confirmed by the measurement of a high cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) opening pressure and exclusion of secondary causes of intracranial hypertension. Refractory PIIH may lead to severe visual impairment. The purpose of this study was to evaluate a cranial morcellation decompression (CMD) technique as a new surgical alternative to stabilize intracranial pressure in PIIH.
Materials and methods
A literature review was carried out, disclosing only 7 pediatric cases of PIIH treated with surgical skull expansion. In addition, we describe here one case of our own experience treated by CMD.
Conclusions
CMD surgery is a safe and effective option to control refractory PIIH in selected patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abubaker K, Ali Z, Raza K, Bolger C, Rawluk D, O'Brien D (2011) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: lumboperitoneal shunts versus ventriculoperitoneal shunts—case series and literature review. Br J Neurosurg 25:94–99. https://doi.org/10.3109/02688697.2010.544781
Aiken AH, Hoots JA, Saindane AM, Hudgins PA (2012) Incidence of cerebellar tonsillar ectopia in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a mimic of the Chiari I malformation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:1901–1906. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3068
Ball AK, Clarke CE (2006) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. The Lancet Neurology 5:433–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70442-2
Binder DK, Horton JC, Lawton MT, McDermott MW (2004) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurosurgery 54:538–551 discussion 551-532
Bursztyn LL, Sharan S, Walsh L, LaRoche GR, Robitaille J, De Becker I (2014) Has rising pediatric obesity increased the incidence of idiopathic intracranial hypertension in children? Canadian journal of ophthalmology Journal canadien d'ophtalmologie 49:87–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcjo.2013.09.015
Corbett JJ, Mehta MP (1983) Cerebrospinal fluid pressure in normal obese subjects and patients with pseudotumor cerebri. Neurology 33:1386–1388
Corbett JJ, Savino PJ, Thompson HS, Kansu T, Schatz NJ, Orr LS, Hopson D (1982) Visual loss in pseudotumor cerebri. Follow-up of 57 patients from five to 41 years and a profile of 14 patients with permanent severe visual loss. Arch Neurol 39:461–474
Corbett JJ, Thompson HS (1989) The rational management of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Arch Neurol 46:1049–1051
Dandy WE (1937) Intracranial pressure without brain tumor: diagnosis and treatment. Ann Surg 106:492–513
Donaldson JO (1981) Pathogenesis of pseudotumor cerebri syndromes. Neurology 31:877–880
Ellis JA, Anderson RC, O'Hanlon J, Goodman RR, Feldstein NA, Ghatan S (2012) Internal cranial expansion surgery for the treatment of refractory idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurosurg Pediatr 10:14–20. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.3.peds11228
Farb R, Vanek I, Scott J, Mikulis D, Willinsky R, Tomlinson G (2003) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: the prevalence and morphology of sinovenous stenosis. Neurology 60:1418–1424
Foley J (1955) Benign forms of intracranial hypertension “toxic” and “otitic” hydrocephalus. Brain 78:1–41. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/78.1.1
Gideon P, Thomsen C, St F, Gjerris F, Henriksen O (1995) Increased brain water self-diffusion in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Am J Neuroradiol 16:381–387
Gillson N, Jones C, Reem RE, Rogers DL, Zumberge N, Aylward SC (2017) Incidence and demographics of pediatric intracranial hypertension. Pediatr Neurol 73:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2017.04.021
Gordon K (1997) Pediatric pseudotumor cerebri: descriptive epidemiology. The Canadian journal of neurological sciences Le journal canadien des sciences neurologiques 24:219–221
Greene CS Jr, Winston KR (1988) Treatment of scaphocephaly with sagittal craniectomy and biparietal morcellation. Neurosurgery 23:196–202
Hankinson TC, Mocco J, Kimball B, Anderson RC, Feldstein NA (2007) Internal cranial expansion procedure for the treatment of symptomatic intracranial hypertension. J Neurosurg 107:402–405. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped-07/11/402
Higgins J, Cousins C, Owler B, Sarkies N, Pickard J (2003) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: 12 cases treated by venous sinus stenting. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:1662–1666
Hoang KB, Hooten KG, Muh CR (2017) Shunt freedom and clinical resolution of idiopathic intracranial hypertension after bariatric surgery in the pediatric population: report of 3 cases. J Neurosurg Pediatr 20:1–6. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.6.peds17145
The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version) (2013). Cephalalgia : an international journal of headache 33:629–808. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102413485658
Istek S (2014) Chiari type 1 malformation in a pseudotumour cerebri patient: is it an acquired or congenital Chiari malformation? BMJ case reports 2014 2014:bcr2013201845. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2013-201845
Keltner JL (1988) Optic nerve sheath decompression. How does it work? Has its time come? Archives of ophthalmology (Chicago, Ill : 1960) 106:1365–1369
Kessler LA, Novelli PM, Reigel DH (1998) Surgical treatment of benign intracranial hypertension—subtemporal decompression revisited. Surg Neurol 50:73–76
King JJ (1938) Oxycephaly: a new operation and its results (a preliminary report). Arch Neurol Psychiatr 40:1205–1219. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurpsyc.1938.02270120155009
Lim MJ, Pushparajah K, Jan W, Calver D, Lin JP (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging changes in idiopathic intracranial hypertension in children. J Child Neurol 25:294–299. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073809338874
Martins AN (1973) Resistance to drainage of cerebrospinal fluid: clinical measurement and significance. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 36:313–318
Mokri B (2001) The Monro-Kellie hypothesis: applications in CSF volume depletion. Neurology 56:1746–1748
Mukherjee N, Bhatti MT (2014) Update on the surgical management of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports 14:438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-014-0438-8
Nakajima H, Sakamoto Y, Tamada I, Ohara H, Kishi K (2011) Dynamic total skull remodeling by a combination of morcellation craniotomy with distraction osteogenesis: the MoD procedure. The Journal of craniofacial surgery 22:1240–1246. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e31821c0fef
Orefice G, Celentano L, Scaglione M, Davoli M, Striano S (1992) Radioisotopic cisternography in benign intracranial hypertension of young obese women. A seven-case study and pathogenetic suggestions. Acta neurologica 14:39–50
Paruchuri SR, Lawlor M, Kleinhomer K, Mason L, Johnson C (1993) Risk of cerebellar tonsillar herniation after diagnostic lumbar puncture in pseudotumor cerebri. Anesth Analg 77:403–404
Puffer RC, Mustafa W, Lanzino G (2013) Venous sinus stenting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a review of the literature. Journal of neurointerventional surgery 5:483–486. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2012-010468
Quincke H (1896) Ueber Meningitis serosa und verwandte Zustände. J Neurol 9:149–168
Raichle ME, Grubb RL Jr, Phelps ME, Gado MH, Caronna JJ (1978) Cerebral hemodynamics and metabolism in pseudotumor cerebri. Ann Neurol 4:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410040203
Renier D, Lajeunie E, Arnaud E, Marchac D (2000) Management of craniosynostoses. Child’s nervous system : ChNS : official journal of the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery 16:645–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003810000320
Rubin RC, Henderson ES, Ommaya AK, Walker MD, Rall DP (1966) The production of cerebrospinal fluid in man and its modification by acetazolamide. J Neurosurg 25:430–436. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1966.25.4.0430
Simpson A, Wong AL, Bezuhly M (2017) Surgical correction of nonsyndromic sagittal craniosynostosis: concepts and controversies. Ann Plast Surg 78:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1097/sap.0000000000000713
Spitze A, Malik A, Lee AG (2014) Surgical and endovascular interventions in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Curr Opin Neurol 27:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1097/wco.0000000000000049
Swanson JW, Aleman TS, Xu W, Ying GS, Pan W, Liu GT, Lang SS, Heuer GG, Storm PB, Bartlett SP, Katowitz WR, Taylor JA (2017) Evaluation of optical coherence tomography to detect elevated intracranial pressure in children. JAMA ophthalmology 135:320–328. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.0025
Tamburrini G, Caldarelli M, Massimi L, Santini P, Di Rocco C (2005) Intracranial pressure monitoring in children with single suture and complex craniosynostosis: a review. Child's nervous system : ChNS : official journal of the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery 21:913–921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-1117-x
Tarrats L, Hernandez G, Busquets JM, Portela JC, Serrano LA, Gonzalez-Sepulveda L, Sanchez-Perez JR (2017) Outcomes of endoscopic optic nerve decompression in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. International forum of allergy & rhinology 7:615–623. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.21927
Thambisetty M, Lavin PJ, Newman NJ, Biousse V (2007) Fulminant idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology 68:229–232. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000251312.19452.ec
Wall M (1990) The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia : an international journal of headache 10:331–335. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1468-2982.1990.1006331.x
Wall M (2010) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurol Clin 28:593–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2010.03.003
Wall M, George D (1991) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a prospective study of 50 patients. Brain 114(Pt 1A):155–180
Wang SJ, Silberstein SD, Patterson S, Young WB (1998) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension without papilledema: a case-control study in a headache center. Neurology 51:245–249
Wang VY, Barbaro NM, Lawton MT, Pitts L, Kunwar S, Parsa AT, Gupta N, McDermott MW (2007) Complications of lumboperitoneal shunts. Neurosurgery 60:1045–1048; discussion 1049. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000255469.68129.81
Weinzweig J, Bartlett SP, Chen JC, Losee J, Sutton L, Duhaime AC, Whitaker LA (2008) Cranial vault expansion in the management of postshunt craniosynostosis and slit ventricle syndrome. Plast Reconstr Surg 122:1171–1180. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181858c84
Winner P, Bello L (1996) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension in a young child without visual symptoms or signs. Headache 36:574–576
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There was no financial support nor industry affiliations involved in this work. None of the authors has any personal or institutional financial interest in drugs, materials, or devices.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ballestero, M.F.M., Teixeira, T.L., Augusto, L.P. et al. Cranial morcellation decompression for refractory idiopathic intracranial hypertension in children. Childs Nerv Syst 34, 1111–1117 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3766-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3766-1