Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to clarify risk factors for poor neurological outcomes and distinctive characteristics in infants with traumatic brain injury.
Methods
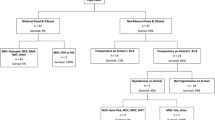
The study retrospectively reviewed data of 166 infants with traumatic intracranial hemorrhage from three tertiary institutions in Japan between 2002 and 2013. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to identify clinical symptoms, vital signs, physical findings, and computed tomography findings associated with poor neurological outcomes at discharge from the intensive care unit.
Results
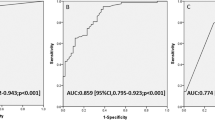
In univariate analysis, bradypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, dyscoria, retinal hemorrhage, subdural hematoma, cerebral edema, and a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of ≤ 12 were significantly associated with poor neurological outcomes (P < 0.05). In multivariate analysis, a GCS score of ≤ 12 (OR = 130.7; 95% CI, 7.3–2323.2; P < 0.001), cerebral edema (OR = 109.1; 95% CI, 7.2–1664.1; P < 0.001), retinal hemorrhage (OR = 7.2; 95% CI, 1.2–42.1; P = 0.027), and Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 score (OR = 1.6; 95% CI, 1.1–2.3; P = 0.018) were independently associated with poor neurological outcomes. Incidence of bradypnea in infants with a GCS score of ≤ 12 (25/42) was significantly higher than that in infants with GCS score of > 12 (27/90) (P = 0.001).
Conclusions
Infants with a GCS score of ≤ 12 are likely to have respiratory disorders associated with traumatic brain injury. Physiological disorders may easily lead to secondary brain injury, resulting in poor neurological outcomes. Secondary brain injury should be prevented through early interventions based on vital signs and the GCS score.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langlois JA, Rutland-Brown W, Thomas KE (2005) The incidence of traumatic brain injury among children in the United States: differences by race. J Head Trauma Rehabil 20(3):229–238. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001199-200505000-00006
MRC CRASH Trial Collaborators, Perel P, Arango M, Clayton T, Edwards P, Komolafe E, Poccock S, Roberts I, Shakur H, Steyerberg E, Yutthakasemsunt S (2008) Predicting outcome after traumatic brain injury: practical prognostic models based on large cohort of international patients. BMJ 336(7641):425–429. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39461.643438.25
Steyerberg EW, Mushkudiani N, Perel P, Butcher I, Lu J, McHugh GS, Murray GD, Marmarou A, Roberts I, Habbema JD, Maas AI (2008) Predicting outcome after traumatic brain injury: development and international validation of prognostic scores based on admission characteristics. PLoS Med 5(8, discussion e165):e165. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0050165
Lingsma HF, Roozenbeek B, Steyerberg EW, Murray GD, Maas AI (2010) Early prognosis in traumatic brain injury: from prophecies to predictions. Lancet Neurol 9(5):543–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70065-X
Heather NL, Derraik JG, Beca J, Hofman PL, Dansey R, Hamill J, Cutfield WS (2013) Glasgow Coma Scale and outcomes after structural traumatic head injury in early childhood. PLoS One 8(12):e82245. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082245
Tude Melo JR, Di Rocco F, Blanot S, Oliveira-Filho J, Roujeau T, Sainte-Rose C, Duracher C, Vecchione A, Meyer P, Zerah M (2010) Mortality in children with severe head trauma: predictive factors and proposal for a new predictive scale. Neurosurgery 67(6):1542–1547. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e3181fa7049
Randolph LC, Takacs M, Davis KA (2002) Resuscitation in the pediatric trauma population: admission base deficit remains an important prognostic indicator. J Trauma 53(5):838–842. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005373-200211000-00006
Campbell CG, Kuehn SM, Richards PM, Ventureyra E, Hutchison JS (2004) Medical and cognitive outcome in children with traumatic brain injury. Can J Neurol Sci 31(02):213–219. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0317167100053853
Scavarda D, Gabaudan C, Ughetto F, Lamy F, Imada V, Lena G, Paut O (2010) Initial predictive factors of outcome in severe non-accidental head trauma in children. Childs Nerv Syst 26(11):1555–1561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1150-x
Rhine T, Wade SL, Makoroff KL, Cassedy A, Michaud LJ (2012) Clinical predictors of outcome following inflicted traumatic brain injury in children. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 73(4 Suppl 3):S248–S253. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e31826b0062
Ilves P, Lintrop M, Talvik I, Sisko A, Talvik T (2010) Predictive value of clinical and radiological findings in inflicted traumatic brain injury. Acta Paediatr 99(9):1329–1336. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2010.01820.x
Chung CY, Chen CL, Cheng PT, See LC, Tang SF, Wong AM (2006) Critical score of Glasgow Coma Scale for pediatric traumatic brain injury. Pediatr Neurol 34(5):379–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2005.10.012
Shein SL, Bell MJ, Kochanek PM, Tyler-Kabara EC, Wisniewski SR, Feldman K, Makoroff K, Scribano PV, Berger RP (2012) Risk factors for mortality in children with abusive head trauma. J Pediatr 161(4):716–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.03.046
Bahloul M, Ben Hamida C, Chelly H, Chaari A, Kallel H, Dammak H, Rekik N, Bahloul K, Ben Mahfoudh K, Hachicha M, Bouaziz M (2009) Severe head injury among children: prognostic factors and outcome. Injury 40(5):535–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2008.04.018
Kapapa T, König K, Pfister U, Sasse M, Woischneck D, Heissler H, Rickels E (2010) Head trauma in children, part 1: admission, diagnostics, and findings. J Child Neurol 25(2):146–156. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073809332698
Chiaretti A, Piastra M, Pulitanò S, Pietrini D, De Rosa G, Barbaro R, Di Rocco C (2002) Prognostic factors and outcome of children with severe head injury: an 8-year experience. Childs Nerv Syst 18(3-4):129–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-002-0558-3
Ducrocq SC, Meyer PG, Orliaguet GA, Blanot S, Laurent-Vannier A, Renier D, Carli PA (2006) Epidemiology and early predictive factors of mortality and outcome in children with traumatic severe brain injury: experience of a French pediatric trauma center. Pediatr Crit Care Med 7(5):461–467. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PCC.0000235245.49129.27
White JR, Farukhi Z, Bull C, Christensen J, Gordon T, Paidas C, Nichols DG (2001) Predictors of outcome in severely head-injured children. Crit Care Med 29(3):534–540. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200103000-00011
Downard C, Hulka F, Mullins RJ, Piatt J, Chesnut R, Quint P, Mann NC (2000) Relationship of cerebral perfusion pressure and survival in pediatric brain-injured patients. J Trauma 49(4):654–658. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005373-200010000-00012
Hackbarth RM, Rzeszutko KM, Sturm G, Donders J, Kuldanek AS, Sanfilippo DJ (2002) Survival and functional outcome in pediatric traumatic brain injury: a retrospective review and analysis of predictive factors. Crit Care Med 30(7):1630–1635. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200207000-00038
Chiaretti A, De Benedictis R, Della Corte F, Piastra M, Viola L, Polidori G, Di Rocco C (2002) The impact of initial management on the outcome of children with severe head injury. Childs Nerv Syst 18(1-2):54–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-001-0533-4
Jagannathan J, Okonkwo DO, Yeoh HK, Dumont AS, Saulle D, Haizlip J, Barth JT, Jane JA Sr, Jane JA Jr (2008) Long-term outcomes and prognostic factors in pediatric patients with severe traumatic brain injury and elevated intracranial pressure. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2(4):240–249. https://doi.org/10.3171/PED.2008.2.10.240
Giza CC, Mink RB, Madikians A (2007) Pediatric traumatic brain injury: not just little adults. Curr Opin Crit Care 13:143–152
Keenan HT, Bratton SL (2006) Epidemiology and outcomes of pediatric traumatic brain injury. Dev Neurol 28:256–263
Keenan HT, Runyan DK, Marshall SW, Nocera MA, Merten DF, Sinal SH (2003) A population-based study of inflicted traumatic brain injury in young children. JAMA 290(5):621–626. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.290.5.621
Freeman SS, Udomphorn Y, Armstead WM, Fisk DM, Vavilala MS (2008) Young age as a risk factor for impaired cerebral autoregulation after moderate to severe pediatric traumatic brain injury. Anesthesiology 108(4):588–595. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e31816725d7
Philip S, Udomphorn Y, Kirkham FJ, Vavilala MS (2009) Cerebrovascular pathophysiology in pediatric traumatic brain injury. J Trauma 67(Supplement):S128–S134. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3181ad32c7
Amagasa S, Matsui H, Tsuji S, Moriya T, Kinoshita K (2016) Accuracy of the history of injury obtained from the caregiver in infantile head trauma. Am J Emerg Med 34(9):1863–1867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2016.06.085
Fiser DH (1992) Assessing the outcome of pediatric intensive care. J Pediatr 121(1):68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3476(05)82544-2
Fleming S, Thompson M, Stevens R, Heneghan C, Plüddemann A, Maconochie I, Tarassenko L, Mant D (2011) Normal ranges of heart rate in children from birth to 18 years of age: a systematic review of observational studies. Lancet 377(9770):1011–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62226-X
Moss AJ (1981) Blood pressure in infants, children and adolescents. West J Med 134(4):296–314
James HE (1986) Neurologic evaluation and support in the child with an acute brain insult. Pediatr Ann 15(1):16–22. https://doi.org/10.3928/0090-4481-19860101-05
Gennarelli TA, Wodzin E (2006) AIS 2005: a contemporary injury scale. Injury 37(12):1083–1091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2006.07.009
Slater A, Shann F, Pearson G, Paediatric Index of Mortality (PIM) Study Group (2003) PIM2: a revised version of the paediatric index of mortality. Intensive Care Med 29:278–285
Boyd CR, Tolson MA, Copes WS (1987) Evaluating trauma care: the TRISS method. Trauma score and the injury severity score. J Trauma 27(4):370–380. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005373-198704000-00005
Hall JR, Reyes HM, Meller JL, Loeff DS, Dembek R (1996) The outcome for children with blunt trauma is best at a pediatric trauma center. J Pediatr Surg 31(1):72–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3468(96)90322-X
Teasdale G, Maas A, Lecky F, Manley G, Stocchetti N, Murray G (2014) The Glasgow coma scale at 40 years: standing the test of time. Lancet Neurol 13(8):844–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70120-6
Zebrack M, Dandoy C, Hansen K, Scaife E, Mann NC, Bratton SL (2009) Early resuscitation of children with moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury. Pediatrics 124(1):56–64. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-1006
Dunham CM, Barraco RD, Clark DE, Daley BJ, Davis FE 3rd, Gibbs MA, Knuth T, Letarte PB, Luchette FA, Omert L, Weireter LJ, Wiles CE 3rd, EAST Practice Management Guidelines Work Group (2003) Guidelines for emergency tracheal intubation immediately after traumatic injury. J Trauma 55:162–179
Duhaime AC, Christian CW, Rorke LB, Zimmerman RA (1998) Non-accidental head injury in infants-the “shaken-baby syndrome.”. N Engl J Med 338(25):1822–1829. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199806183382507
Piteau SJ, Ward MG, Barrowman NJ, Plint AC (2012) Clinical and radiographic characteristics associated with abusive and nonabusive head trauma: a systematic review. Pediatrics 130(2):315–323. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-1545
Kemp AM, Jaspan T, Griffirhs J, Stoodley N, Mann MK, Tempest V, Maguire SA (2011) Neuroimaging: what neuroradiological features distinguish abusive from non-abusive head trauma? A systematic review. Arch Dis Child 96(12):1103–1112. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2011-300630
Kelly P, John S, Vincent AL, Reed P (2015) Abusive head trauma and accidental head injury: a 20-year comparative study of referrals to a hospital child protection team. Arch Dis Child 100(12):1123–1130. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2014-306960
Deans KJ, Minneci PC, Lowell W, Groner JI (2013) Increased morbidity and mortality of traumatic brain injury in victims of nonaccidental trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 75(1):157–160. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3182984acb
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The Ethical Board of Nagano Children’s Hospital approved this retrospective study (Receipt number 27-57).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amagasa, S., Tsuji, S., Matsui, H. et al. Prognostic factors of acute neurological outcomes in infants with traumatic brain injury. Childs Nerv Syst 34, 673–680 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3695-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3695-4