Abstract
Purpose
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is the most common intraocular tumor in children. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a crucial role in gene regulation and cell growth/apoptosis/differentiation. The current study aimed to investigate the role of miR-498 in Rb.
Methods
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (QRT-PCR) was used to test mRNA level of miR-498. http://www.targetscan.org and http://www.microrna.org were applied to predict target of miR-498. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was applied to investigate if miR-498 targeted cell cycle progression 1 (CCPG1). Western blot (WB) was carried out to assess CCPG1 protein levels. 3-(4, 5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2, 5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was used to evaluate cell proliferation. Annexin-V Fluorescein (FITC) was adopted to explore cell apoptosis.
Results
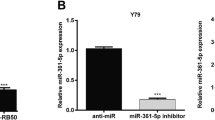
In Y79 cells, miR-498 was higher than in normal ARPE-19 cells. MiR-498 could recognize CCPG1-3′ untranslated region (UTR). CCPG1 protein level was remarkably decreased when overexpressed miR-498, nevertheless, significantly increased when inhibiting miR-498. Y79 cells that were transfected with miR-498 mimics manifested notable cell apoptosis down-regulation and cell proliferation promotion; whereas, those transfected with miR-498 inhibitor displayed significant cell apoptosis up-regulation and cell proliferation inhibition compared with control group.
Conclusion
Taken together, miR-498 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis in Rb by directly targeting CCPG1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Cancer Society (2003) Neoplasms of the Eye. Cancer Medicine. Hamilton, Ontario: BC Decker Inc 85
Bagnyukova TV, Pogribny IP, Chekhun VF (2006) MicroRNAs in normal and cancer cells: a new class of gene expression regulators. Exp Oncol 28:263–269
Balmer A, Zografos L, Munier F (2006) Diagnosis and current management of retinoblastoma. Oncogene 25:5341–5349
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, Sharon E, Spector Y, Bentwich Z (2005) Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet 37:766–770
Broaddus E, Topham A, Singh AD (2009) Incidence of retinoblastoma in the USA: 1975–2004. Br J Ophthalmol 93:21–23
Cavenee WK, Dryja TP, Phillips RA, Benedict WF, Godbout R, Gallie BL, Murphree AL, Strong LC, White RL (1983) Expression of recessive alleles by chromosomal mechanisms in retinoblastoma. Nature 305:779–784
Chen D, Livne-Bar I, Vanderluit JL, Slack RS, Agochiya M, Bremner R (2004) Cell-specific effects of RB or RB/p107 loss on retinal development implicate an intrinsically death-resistant cell-of-origin in retinoblastoma. Cancer Cell 5:539–551
Cong J, Liu R, Wang X, Wang J, Wang H, Hou J (2015) Low miR-498 expression levels are associated with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19:4762–4765
Deng S, Calin GA, Croce CM, Coukos G, Zhang L (2008) Mechanisms of microRNA deregulation in human cancer. Cell Cycle 7:2643–2646
Doe JM (2008) MicroRNA: cancer and future treatment applications. Basic Biotech e J 36–42
Du W, Pogoriler J (2006) Retinoblastoma family genes. Oncogene 25:5190–5200
Elkington AR, Khaw PT (1988) ABC of eyes. Squint. BMJ 297:608–611
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269
Faghihi MA, Kocerha J, Modarresi F, Engström PG, Chalk AM, Brothers SP, Koesema E, St Laurent G, Wahlestedt C (2010) RNAi screen indicates widespread biological function for human natural antisense transcripts. PLoS One 5:e13177
Hammond SM (2007) MicroRNAs as tumor suppressors. Nat Genet 39:582–583
Hobert O (2008) Gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Science 319:1785–1786
Iyer VR, Eisen MB, Ross DT, Schuler G, Moore T, Lee JC, Trent JM, Staudt LM, Hudson J Jr, Boguski MS, Lashkari D, Shalon D, Botstein D, Brown PO (1999) The transcriptional program in the response of human fibroblasts to serum. Science 283:83–87
Knudson AG Jr (1971) Mutation and cancer: statistical study of retinoblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 68:820–823
Liu R, Liu F, Li L, Sun M, Chen K (2015) MiR-498 regulated FOXO3 expression and inhibited the proliferation of human ovarian cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother 72:52–57
Lohmann DR, Gallie BL (2004) Retinoblastoma: revisiting the model prototype of inherited cancer. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 129C:23–28
MacCarthy A, Birch JM, Draper GJ, Hungerford JL, Kingston JE, Kroll ME, Onadim Z, Stiller CA, Vincent TJ, Murphy MF (2009) Retinoblastoma in Great Britain 1963–2002. Br J Ophthalmol 93:33–37
MacCarthy A, Draper GJ, Steliarova-Foucher E, Kingston JE (2006) Retinoblastoma incidence and survival in European children (1978–1997). Report from the automated childhood cancer information system project. Eur J Cancer 42:2092–2102
Pfeffer S, Voinnet O (2006) Viruses, microRNAs and cancer. Oncogene 25:6211–6219
Schepeler T, Reinert JT, Ostenfeld MS, Christensen LL, Silahtaroglu AN, Dyrskjot L, Wiuf C, Sørensen FJ, Kruhoffer M, Laurberg S, Kauppinen S, Orntoft TF, Andersen CL (2008) Diagnostic and prognostic MicroRNAs in stage II colon cancer. Cancer Res 68:6416–6424
Taft RJ, Pang KC, Mercer TR, Dinger M, Mattick JS (2010) Non-coding RNAs: regulators of disease. J Pathol 220:126–139
Ventura A, Jacks T (2009) MicroRNAs and cancer. Short RNAs go a long way. Cell 136:586–591
Wang M, Zhang Q, Wang J, Zhai Y (2015) MicroRNA-498 is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and correlates with tumor progression. J Cancer Res Ther 11:C107–C111
Zhang Z, Li Z, Gao C, Chen P, Chen J, Liu W, Xiao S, Lu H (2008) miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab Investig 88:1358–1366
Zhao JJ, Yang J, Lin JH, Yao N, Zhu YH, Zheng JH, JH X, Cheng JQ, Lin JY, Ma X (2009) Identification of miRNAs associated with tumorigenesis of retinoblastoma by miRNA microarray analysis. Childs Nerv Syst 25:13–20
Acknowledgements
We thank Chao Lu from Department of Pediatrics, The First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China, for his kind help in the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Wei, N., Wang, L. et al. miR-498 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis in retinoblastoma by directly targeting CCPG1. Childs Nerv Syst 34, 417–422 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3622-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3622-8