Abstract
Introduction
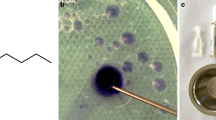
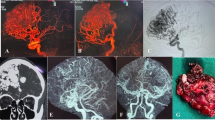
Intracranial artery-to-artery antegrade revascularization is a poorly recognized entity, more so when it involves main stem arteries. The etiology, appearance, and significance of this condition are not described in the literature.
Case presentation
We describe a case of spontaneous revascularization of a chronically occluded middle cerebral arterial branch by collaterals from the proximal segment reconstituting distal flow, mimicking a brain arteriovenous malformation in a 9-year old boy. We discuss the nature of these channels, presumed to be related to artery to artery collaterals that are either dilated adventitial vasa vasorum, or, more likely, leptomeningeal collaterals that are hypertrophied in response to cerebral demand. We review the literature regarding intracerebral vasa vasorum and leptomeningeal collaterals including their imaging.
Conclusion
Recognizing the tortuous channels associated with this type of vascular abnormality as normal vessels reconsituting distal flow may prevent unnecessary and potentially dangerous treatments.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iihara K, Murao K, Sakai N, Soeda A, Ishibashi-Ueda H, Yutani C et al (2003 Feb) Continued growth of and increased symptoms from a thrombosed giant aneurysm of the vertebral artery after complete endovascular occlusion and trapping: the role of vasa vasorum. Case report J Neurosurg 98(2):407–413
Gujral DM, Cheung WK, Shah BN, Chahal NS, Bhattacharyya S, Hooper J et al (2016 Jul) Contrast enhancement of carotid adventitial vasa vasorum as a biomarker of radiation-induced atherosclerosis. Radiother Oncol J Eur Soc Ther Radiol Oncol 120(1):63–68
Portanova A, Hakakian N, Mikulis DJ, Virmani R, Abdalla WMA, Wasserman BA (2013 Jun 1) Intracranial vasa Vasorum: insights and implications for imaging. Radiology 267(3):667–679
Martin MA, Marotta TR (1999 Feb 1) Vasa vasorum: another cause of the carotid string sign. Am J Neuroradiol 20(2):259–262
Arcidiacono MV, Rubinat E, Borras M, Betriu A, Trujillano J, Vidal T et al (2015) Left carotid adventitial vasa vasorum signal correlates directly with age and with left carotid intima-media thickness in individuals without atheromatous risk factors. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 13(1):20
Vavuranakis M, Sigala F, Vrachatis DA, Papaioannou TG, Filis K, Kavantzas N et al (2013 May) Quantitative analysis of carotid plaque vasa vasorum by CEUS and correlation with histology after endarterectomy. VASA Z Gefasskrankheiten 42(3):184–195
Partovi S, Loebe M, Noon GP, Davies MG, Karimi S, Zipp L et al (2011 Dec) Detection of adventitial vasa vasorum and intraplaque neovascularization in carotid atherosclerotic lesions with contrast-enhanced ultrasound and their role in atherosclerosis. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc J 7(4):37–40
Aydin F (1998 Jul) Do human intracranial arteries lack vasa vasorum? A comparative immunohistochemical study of intracranial and systemic arteries. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 96(1):22–28
Baik SK, Park J, Kim GC, Lee TH, Kim YS (2009) Vascular response to the vasa vasorum in a carotid artery dissecting aneurysm. Acta Neurochir 151(9):1159
Katano H, Yamada K, Sakurai K, Takahashi S (2014 Dec) Depiction of the vasa vasorum during carotid endarterectomy by intraoperative videoangiography. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc 23(10):2920–2927
Kim EY, Shin DH, Noh Y, Goh BH, Lee Y-B (2016 Sep) Comparison of imaging selection criteria for intra-arterial thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke with advanced CT. Eur Radiol 26(9):2974–2981
Menon BK, O’Brien B, Bivard A, Spratt NJ, Demchuk AM, Miteff F et al (2013 Mar) Assessment of leptomeningeal collaterals using dynamic CT angiography in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33(3):365–371
Winship IR. Cerebral collaterals and collateral therapeutics for acute ischemic stroke. Microcirc N Y N 1994. 2015 Apr;22(3):228–236.
Kim SJ, Son TO, Kim KH, Jeon P, Hyun SH, Lee K-H et al (2014) Neovascularization precedes occlusion in moyamoya disease: angiographic findings in 172 pediatric patients. Eur Neurol 72(5–6):299–305
Bedini G, Blecharz KG, Nava S, Vajkoczy P, Alessandri G, Ranieri M et al (2016) Vasculogenic and angiogenic pathways in moyamoya disease. Curr Med Chem 23(4):315–345
Thust SC, Burke C, Siddiqui A (2014 May 21) Neuroimaging findings in sickle cell disease. Br J Radiol 87(1040):20130699
Ozgur HT, Kent Walsh T, Masaryk A, Seeger JF, Williams W, Krupinski E et al (2001 May 1) Correlation of cerebrovascular reserve as measured by acetazolamide-challenged SPECT with angiographic flow patterns and Intra- or extracranial arterial stenosis. Am J Neuroradiol 22(5):928–936
Mori N, Mugikura S, Higano S, Kaneta T, Fujimura M, Umetsu A et al (2009 May 1) The leptomeningeal “ivy sign” on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging in moyamoya disease: a sign of decreased cerebral vascular reserve? Am J Neuroradiol 30(5):930–935
Cho T-H, Nighoghossian N, Mikkelsen IK, Derex L, Hermier M, Pedraza S et al (2015 Jun) Reperfusion within 6 hours outperforms recanalization in predicting penumbra salvage, lesion growth, final infarct, and clinical outcome. Stroke J Cereb Circ 46(6):1582–1589
Takaba M, Endo S, Kurimoto M, Kuwayama N, Nishijima M, Takaku A (1998) Vasa vasorum of the intracranial arteries. Acta Neurochir 140(5):411–416
Yamazoe N, Hashimoto N, Kikuchi H, Kang Y, Nakatani H, Hazama F (1990 May 1) Study of the elastic skeleton of intracranial arteries in animal and human vessels by scanning electron microscopy. Stroke 21(5):765–770
Zervas NT, Liszczak TM, Mayberg MR, Black PM (1982 Apr) Cerebrospinal fluid may nourish cerebral vessels through pathways in the adventitia that may be analogous to systemic vasa vasorum. J Neurosurg 56(4):475–481
Bae H-J, Lee J, Park J-M, Kwon O, Koo J-S, Kim B-K et al (2007) Risk factors of intracranial cerebral atherosclerosis among asymptomatics. Cerebrovasc Dis Basel Switz 24(4):355–360
Nakatomi H, Segawa H, Kurata A, Shiokawa Y, Nagata K, Kamiyama H et al (2000 Apr) Clinicopathological study of intracranial fusiform and dolichoectatic aneurysms : insight on the mechanism of growth. Stroke J Cereb Circ. 31(4):896–900
Connolly ES, Huang J, Goldman JE, Holtzman RN (1996 Apr) Immunohistochemical detection of intracranial vasa vasorum: a human autopsy study. Neurosurgery 38(4):789–793
Tariq N, Khatri R (2008 Oct) Leptomeningeal collaterals in acute ischemic stroke. J Vasc Interv Neurol 1(4):91–95
Brozici M, van der Zwan A, Hillen B (2003 Nov) Anatomy and functionality of leptomeningeal anastomoses: a review. Stroke J Cereb Circ. 34(11):2750–2762
Menon BK, Smith EE, Coutts SB, Welsh DG, Faber JE, Goyal M et al (2013 Aug) Leptomeningeal collaterals are associated with modifiable metabolic risk factors. Ann Neurol 74(2):241–248
Van Der Zwan A, Hillen B (1990 Oct) Araldite F as injection material for quantitative morphology of cerebral vascularization. Anat Rec 228(2):230–236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Financial disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muthusami, P., Krings, T., Raybaud, C. et al. Intracranial artery to artery spontaneous revascularization in a child. Childs Nerv Syst 33, 2035–2038 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3498-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3498-7