Abstract
Purpose
We have diagnosed 35 cases of the supposedly rare condition metopic-sagittal synostosis in the past 20 years. Here, we introduce their clinical symptoms, neuroradiological findings, and surgical treatment methods, as well as discuss the relevant literature.
Methods
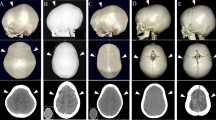
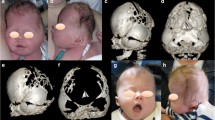
Subjects included 35 patients (33 boys and 2 girls; mean age 4.2 years; range 1–8 years). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) confirmed that there were no abnormal findings in the brain. Thirty patients presented with symptoms including speech delay, hyperactivity, autistic tendency, motor impairment, self-mutilation, and panic/temper tantrum behaviors. No other congenital malformation was observed, and all cases were considered to be the non-syndromic type. The final diagnosis was made using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT) scans. The surgery was done the fronto-orbital advancement in addition to remove the large parts of sphenoid bones including sphenoid ridges at the skull base and trimmed the calvarium as necessary to reduce pressure.
Results
Surgical intervention improved clinical symptoms in nearly all 35 patients; cosmetic problems in patients with scaphocephaly were also corrected.
Conclusions
In the cases of child patients with metopic-sagittal synostosis who had clinical symptoms, surgical intervention improved such symptoms, suggesting its potential utility for metopic-sagittal synostosis with clinical symptoms. A surgical procedure focusing on the skull base was important for our successes. Based on the fact that metopic-sagittal synostosis was diagnosed in 35 patients at one institution over a relatively short period of time, this pathological condition may not be as rare as is currently believed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson FM (1981) Treatment of coronal and metopic synostosis: 107 cases. Neurosurgery 8:143–149
Bottero L, Lajeunie E, Arnard E, Marchac D, Renier D (1988) Functional outcome after surgery for trigonocephaly. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:952–958
Chumas PD, Cinalli G, Arnaud E, Marchac D, Renier D (1997) Classification of previously unclassified cases of craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 86:177–181
Dapretto M, Davies MS, Pfeifer JH, Scott AA, Sigman M, Bookheimer SY, Iacoboni M (2006) Understanding emotions in others: mirror neuron dysfunction in children with autism spectrum disorders. Nat Neurosci 9:28–30
Genitori L, Lena GL, Dollo C, Choux M (1991–92) Skull base in trigonocephaly. Pediatr Neurosurg 17:175–181
Hoffman HJ, Hendrick EB (1979) Early neurosurgical repair in craniofacial dysmorphism. J Neurosurg 51:796–803
Inagaki T, Kyutoku S, Kawamoto K (2009) Study of showed a rare cranial form craniosynostosis cases (in Japanese). Nerv Syst Chidren 34:56–60
Inagaki T, Kyutoku S, Kawamoto K, Seno T, Kawaguchi T, Yamahara T, Oshige H, Yamanouchi Y, Kawamoto K (2007) The intracranial pressure of the patients with mild form of craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 23:1455–1459
Kapp-Simon KA (1998) Mental development and learning disorders in children with single suture craniosynostosis. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 35:197–203
Kapp-Simon KA, Speltz ML, Cunningham ML, Patel PK, Tomita T (2007) Neurodevelopment of children with single suture craniosynostosis; a review. Childs Nerv Syst 23:269–281
Kelleher MO, Murray DJ, McGillivray A, Kamel MH, Allcutt D, Earley MJ (2006) Behavioral, developmental, and educational problems in children with nonsyndromic trigonocephaly. J Neurosurg 105:382–384
Kodera T, Kurai N, Satake T (2010) National Rehabilitation Center Sign-Significance Test (S-S test) test manual, 4th edn. Escor. Co. Ltd., Chiba (in Japanese)
Marchac D (1978) Radical forehead remodeling for craniosynostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 61:823–835
McCarthy JG, Coccaro PJ, Epstein F, Converse JM (1978) Early skeletal release in the infant with craniofacial dysostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 62:335–346
McCarthy JG (1979) New concepts in the surgical treatment of the craniofacial synostosis in the infant. Clin Plast Surg 6:201–226
Morritt DG, Yeh FJ, Wall SA, Richards PG, Jayamohan J, Johnson D (2010) Management of isolated sagittal synostosis in the absence of scaphocephaly: a series of eight cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 126:572–580
Raimondi AJ, Gutierrez FA (1977) A new surgical approach to the treatment of coronal synostosis. J Neurosurg 46:210–214
Renier D, Sainte-Rose C, Marchac D, Hirsch JF (1982) Intracranial pressure in craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 57:370–377
Seeger JF, Gabrielsen TO (1971) Premature closure of the frontosphenoidal suture in synostosis of the coronal suture. Radiology 101:631–635
Shimoji T, Shimabukuro S, Sugama S, Ochiai Y (2002) Mild trigonocephaly with clinical symptoms: analysis of surgical results in 65 patients. Childs Nerv Syst 18:215–224
Shimoji T, Tomiyama N (2004) Mild trigonocephaly and intracranial pressure: report of 56 patients. Childs Nerv Syst 20:749–756
Shimoji T, Shimoji K, Yamashiro K, Nagamine T, Kawakubo J (2009) Mild trigonocephaly—report of 300 operative cases. Nerv Sys Chidren 34:63–73
Shimoji T, Tominaga D, Shimoji K, Miyajima M, Tasato K (2015) Analysis of pre- and post-operative symptoms of patients with mild trigonocephaly using several developmental and psychological tests. Childs Nerv Syst 31:433–440
Sidoti EJ Jr, Marsh JF, Marty-Grames L, Noetzel MJ (1996) Long-term studies of metopic synostosis: frequency of cognitive impairment and behavioral disturbances. Plast Reconstr Surg 97:276–281
Speltz ML, Kapp-Simon KA, Cunningham M, Marsch J, Dawson G (2004) Single-suture craniosynostosis: a review of neurobehavioral research and theory. J Pediatr Psychol 29:651–668
Thompson DNP, Malcolm GP, Jones BM, Harkness WJ, Hayward RD (1995) Intracranial pressure in single-suture craniosynostosis. Pediatr Neurosurg 22:235–240
van der Meulen J (2012) Metopic synostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 28:1359–1367
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimoji, T., Kimura, T., Shimoji, K. et al. The metopic-sagittal craniosynostosis—report of 35 operative cases. Childs Nerv Syst 33, 1335–1348 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3430-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3430-1