Abstract
Purpose
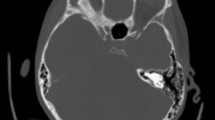
Subdural empyemas are considered neurosurgical emergencies, and the parafalcine location is particularly insidious. We revised the experience of general surgeons who are used to manage chronic pleural purulent collections with video-assisted thoracoscopy.
Methods
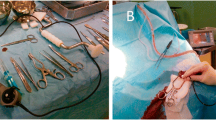
With a similar technique, we successfully aspirated a parafalcine empyema using a flexible scope avoiding a more invasive craniotomy. A review of the treatment options of empyematous collections is also provided, focusing particularly on the hazardous parafalcine location.
Results
The management of subdural empyemas poses different decision-making problems compared to common brain abscesses, urging a more rapid and holistic surgical treatment with minimally invasive approach. Endoscopic aspiration of parafalcine empyema was followed by complete recovery in our patient.
Conclusions
Flexible endoscopy is a promising method to obtain complete pus removal even from loculated collections through a bur hole, avoiding large craniotomies and consequent potential complications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adame N, Hedlund G, Byington CL (2005) Sinogenic intracranial empyema in children. Pediatrics 116:e461–e467
Adelstein LJ (1931) Gradenigo's syndrome and brain abscess: secondary to Otitis Media-Differential diagnosis report of cases. Cal West Med 34:23–26
Anagnostopoulos DI, Gortvai P (1973) Intracranial subdural abscess. Br J Surg 60:50–52
Atsumi H, Matsumae M, Hirayama A, Sato K, Shigematsu H, Inoue G, Nishiyama J, Yoshiyama M, Tominaga J (2011) Newly developed electromagnetic tracked flexible neuroendoscope. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51:611–616
Banerjee AD, Pandey P, Devi BI, Sampath S, Chandramouli BA (2009) Pediatric supratentorial subdural empyemas: a retrospective analysis of 65 cases. Pediatr Neurosurg 45:11–18
Bannister G, Williams B, Smith S (1981) Treatment of subdural empyema. J Neurosurg 55:82–88
Bauer BL, Hellwig D (1994) Minimally invasive endoscopic neurosurgery - a survey. Acta Neurochir Suppl 61:1–12
Bhandari YS, Sarkari NB (1970) Subdural empyema. A review of 37 cases. J Neurosurg 32:35–39
Bok AP, Peter JC (1993) Subdural empyema: burr holes or craniotomy? A retrospective computerized tomography-era analysis of treatment in 90 cases. J Neurosurg 78:574–578
Cassina PC, Hauser M, Hillejan L, Greschuchna D, Stamatis G (1999) Video-assisted thoracoscopy in the treatment of pleural empyema: stage-based management and outcome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 117:234–238
Ceci A, Onetti GB (1886) Ascesso intracranico, craniotomia esplorativa e trapanazione nell'angolo Inferiore posteriore del parietale sinistro Tip. Dell'istituto Sordomuti, Genova
Courville (1944) Subdural empyema secondary to purulent frontal sinusitis. Arch Otolaryngol 39(3):211–230
Dill SR, Cobbs CG, McDonald CK (1995) Subdural empyema: analysis of 32 cases and review. Clin Infect Dis 20:372–386
French H, Schaefer N, Keijzers G, Barison D, Olson S (2014) Intracranial subdural empyema: a 10-year case series. Ochsner J 14:188–194
Gupta S, Vachhrajani S, Kulkarni AV, Taylor MD, Dirks P, Drake JM, Rutka JT (2011) Neurosurgical management of extraaxial central nervous system infections in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 7:441–451
Heine B (1903) Deutsche med. Wochenschr 109
Hitchcock E, Andreadis A (1964) Subdural empyema: A review of 29 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 27:422–434
Hoyt DJ, Fisher SR (1991) Otolaryngologic management of patients with subdural empyema. Laryngoscope 101:20–24
Jansen J, Delstanche H. (1895) Berl. Klin. Wochenschr., H. 35, S. 763
Joubert MJ, Stephanov S (1977) Computerized tomography and surgical treatment in intracranial suppuration. report of 30 consecutive unselected cases of brain abscess and subdural empyema. J Neurosurg 47:73–78
Kalbarczyk A, Krauss JK, Seiler RW (1999) Endoscopic stereotactic surgery for intraventricular loculated empyema: case report. Surg Neurol 52:412–417
Kaufman DM, Miller MH, Steigbigel NH (1975) Subdural empyema: analysis of 17 recent cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 54:485–498
Keith WS (1949) Subdural empyema. J Neurosurg 6:127–139
Kirollos RW, Tyagi AK, Boles DM (1996) Endoscopy-assisted burr hole evacuation of subdural empyema. Br J Neurosurg 10:395–397
Korner O (1908) Nachtrage zur, dritten Aufl edn. der Otitischen Erkxankungen des Hirns &c, Wiesbaden
Kubik CS, Adam DR (1943) Subdural Empyema. Brain, doi: 10.1093/brain/66.1.18 18–42.
Kuczkowski J, Narozny W, Mikaszewski B, Stankiewicz C (2005) Suppurative complications of frontal sinusitis in children. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 44:675–682
Le Beau J, Creissard P, Harispe L, Redondo A (1973) Surgical treatment of brain abscess and subdural empyema. J Neurosurg 38:198–203
Leys D, Destee A, Petit H, Warot P (1986) Management of subdural intracranial empyemas should not always require surgery. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49:635–639
List CF (1950) Interhemispheral subdural suppuration. J Neurosurg 7:313–324
Longatti P, Perin A, Ettorre F, Fiorindi A, Baratto V (2006) Endoscopic treatment of brain abscesses. Childs Nerv Syst 22:1447–1450
Luh SP, Chou MC, Wang LS, Chen JY, Tsai TP (2005) Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery in the treatment of complicated parapneumonic effusions or empyemas: outcome of 234 patients. Chest 127:1427–1432
Luken MG, Whelan MA (1980) Recent diagnostic experience with subdural empyema. J Neurosurg 52:764–771
Mackinlay TAA (1996) VATS Debridement versus thoracotomy in the treatment of loculated postpneumonia empyema. Ann Thorac Surg 61(6):1626–1630
Mat Nayan SA, Mohd Haspani MS, Abd Latiff AZ, Abdullah JM, Abdullah S (2009) Two surgical methods used in 90 patients with intracranial subdural empyema. J Clin Neurosci 16:1567–1571
Mauser HW, Van Houwelingen HC, Tulleken CA (1987) Factors affecting the outcome in subdural empyema. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 50:1136–1141
Nathoo N, Nadvi SS, Gouws E, van Dellen JR (2001) Craniotomy improves outcomes for cranial subdural empyemas: computed tomography-era experience with 699 patients. Neurosurgery 49:872–877 discussion 877-878
Nathoo N, Nadvi SS, van Dellen JR (1999) Cranial extradural empyema in the era of computed tomography: a review of 82 cases. Neurosurgery 44:748–753 discussion 753-744
Obana WG, Rosenblum ML (1992) Nonoperative treatment of neurosurgical infections. Neurosurg Clin N Am 3:359–373
Pathak A, Sharma BS, Mathuriya SN, Khosla VK, Khandelwal N, Kak VK (1990) Controversies in the management of subdural empyema. A study of 41 cases with review of literature. Acta Neurochir 102:25–32
Pattisapu JV, Parent AD (1987) Subdural empyemas in children. Pediatr Neurosci 13:251–254
Renaudin JW, Frazee J (1980) Subdural empyema–importance of early diagnosis. Neurosurgery 7:477–479
Richter Aug. (1772) Observationes de morbis sinuum frontalium
Schiller F, Cairns H, Russell DS (1948) The treatment of purulent pachymeningitis and subdural suppuration with special reference to penicillin. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 11:143–182
Shearman CP, Lees PD, Taylor JC (1987) Subdural empyema: a rational management plan. the case against craniotomy. Br J Neurosurg 1:179–183
Singh B, Van Dellen J, Ramjettan S, Maharaj TJ (1995) Sinogenic intracranial complications. J Laryngol Otol 109:945–950
Smith HP, Hendrick EB (1983) Subdural empyema and epidural abscess in children. J Neurosurg 58:392–397
Stephanov S, Joubert M, Welchman JM (1979) Combined convexity and parafalx subdural empyema. Surg Neurol 11(2):147–151
Tewari MK, Sharma RR, Shiv VK, Lad SD (2004) Spectrum of intracranial subdural empyemas in a series of 45 patients: current surgical options and outcome. Neurol India 52:346–349
Tsai YD, Chang WN, Shen CC, Lin YC, Lu CH, Liliang PC, Su TM, Rau CS, Lu K, Liang CL (2003) Intracranial suppuration: a clinical comparison of subdural empyemas and epidural abscesses. Surg Neurol 59:191–196 discussion 196
Van Alphen HA, Dreissen JJ (1976) Brain abscess and subdural empyema. Factors influencing mortality and results of various surgical techniques. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 39: 481–490
Viola S, Montoya G, Arnold J (2009) Streptococcus pyogenes subdural empyema not detected by computed tomography. Int J Infect Dis 13:e15–e17
Wanson MS, O'Tuama LA (1986) Development of paranasal and mastoid sinuses: a computed tomographic pilot study. J Child Neurol 1:46–49
Weinman D, Samarasinghe HH (1972) Subdural empyema. Aust N Z J Surg 41:324–330
Witsuoka H, Tsunoda A, Mori K, Tajima A, Maeda M (1995) Hypertrophic anterior falx artery associated with interhemispheric subdural empyema. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 35:830–832
Wong AM, Zimmerman RA, Simon EM, Pollock AN, Bilaniuk LT (2004) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of subdural empyemas in children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1016–1021
Wood PH (1952) Diffuse subdural suppuration. J Laryngol Otol 66:496–515
Yilmaz N, Kiymaz N, Yilmaz C, Bay A, Yuca SA, Mumcu C, Caksen H (2006) Surgical treatment outcome of subdural empyema: a clinical study. Pediatr Neurosurg 42:293–298
Youmans Neurological surgery, 5th Ed (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no industry affiliation.
Funding
No funding or financial support was received for this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sammartino, F., Feletti, A., Fiorindi, A. et al. Aspiration of parafalcine empyemas with flexible scope. Childs Nerv Syst 32, 1123–1129 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3082-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3082-6