Abstract
Purpose
There are few papers in the literature comparing outcomes between antero-posterior and posterior-only approaches for treating thoracolumbar tuberculosis (T10–L2) in children
Methods
We performed a retrospective review of 47 children who were diagnosed and treated as thoracolumbar tuberculosis (T10–L2) in our department from January 2005 to June 2009. Forty-seven cases of thoracolumbar tuberculosis were treated by two different surgical approaches. All the cases were divided into two groups: 25 cases in group A underwent one-stage posterior debridement, transforaminal fusion, and instrumentation, and 22 cases in group B underwent anterior debridement, bone graft, and posterior instrumentation in a single- or two-stage procedure. Two approaches were compared in terms of average operative time, blood loss, hospitalizations, bony fusion, intraoperative and postoperative complications, the Oswestry disability index score, neurological status, and the angle of kyphosis.
Results
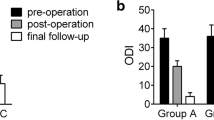
All 47 patients (24 M/23F), averaged 9.1 ± 2.6 years old (range 5 to 14 years), who were followed up for mean of 49.3 ± 8.6 months (range 36 to 65 months). Spinal tuberculosis (TB) was completely cured, and the grafted bones were fused in 9 months in all cases. It was obviously that the average operative time, blood loss, hospitalization, and complication rate of group A was less than those of group B. Good clinical outcomes were achieved in both groups.
Conclusions
Both the antero-posterior and posterior approaches can effectively heal T10–L2 vertebral tuberculosis, but the average surgical time, blood loss, complications, and hospital stay following the posterior approach are prominently less than those following the antero-posterior approach. It might be a better surgical treatment for thoracic spinal tuberculosis in children with poor health status, especially for cases in early phase of bone destruction and/or mild and moderate kyphosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mankin HJ (2001) Tuberculosis of bone and joints: the Red King lives! Curr Opin Orthop 12:489–498
Rajasekaran S (2001) The natural history of post-tubercular kyphosis in children. Radiological signs which predict late increase in deformity. J Bone Joint Surg, Br Vol 83:954–962
Luk K (1999) Tuberculosis of the spine in the new millennium. Eur Spine J 8:338–345
Jeanneret B, Magerl F (1994) Treatment of osteomyelitis of the spine using percutaneous suction/irrigation and percutaneous external spinal fixation. J Spinal Disord Tech 7:185–205
Ozturk C, Aydinli U, Vural R, Sehirlioglu A, Mutlu M (2007) Simultaneous versus sequential one-stage combined anterior and posterior spinal surgery for spinal infections (outcomes and complications). Int Orthop 31:363–366
Oguz E, Sehirlioglu A, Altinmakas M, Ozturk C, Komurcu M, Solakoglu C, Vaccaro A (2008) A new classification and guide for surgical treatment of spinal tuberculosis. Int Orthop 32:127–133
Hong-Qi Z, Yu-Xiang W, Chao-Feng G, Jin-Yang L, Jian-Huang W, Jing C, Dai G, Ming-Xing T (2010) One-stage posterior approach and combined interbody and posterior fusion for thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis with kyphosis in children. Orthopedics 33
Huang Q-S, Zheng C, Hu Y, Yin X, Xu H, Zhang G, Wang Q (2009) One-stage surgical management for children with spinal tuberculosis by anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation. Int Orthop 33:1385–1390
Jain S (2010) Comment on Huang et al.: one-stage surgical management for children with spinal tuberculosis by anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation. Int Orthop 34:769–770
Tuli S (2007) Tuberculosis of the spine: a historical review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 460:29–38
Jain A (2010) Tuberculosis of the spine a fresh look at an old disease. J Bone Joint Surg, Br Vol 92:905–913
Rajasekaran S, Shetty AP, Dheenadhayalan J, Reddy JS, Naresh-Babu J, Kishen T (2006) Morphological changes during growth in healed childhood spinal tuberculosis: a 15-year prospective study of 61 children treated with ambulatory chemotherapy. J Pediatr Orthop 26:716–724
Rajasekaran S (2002) The problem of deformity in spinal tuberculosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 398:85–92
JCTDJ F, Couper J, O’Brien J (1980) The Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire. Physiotherapy 66:271–273
Sundararaj G, Behera S, Ravi V, Venkatesh K, Cherian V, Lee V (2003) Role of posterior stabilisation in the management of tuberculosis of the dorsal and lumbar spine. J BoneJoint Surg Br Vol 85:100–106
Rajasekaran S, Soundarapandian S (1989) Progression of kyphosis in tuberculosis of the spine treated by anterior arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg 71:1314–1323
Alter AH (1973) Tuberculosis of the spine in children: Operative findings and results in one-hundred consecutive patients treated by removal of the lesion and anterior grafting: HL Bailey, M. Gabriel, AR Hodgson, and JS Shin. J Bone Joint Surg 54: A1633–1657 (December), 1972. J Pediatr Surg 8:567–568
Fountain S, Hsu L, Yau A, Hodgson A (1975) Progressive kyphosis following solid anterior spine fusion in children with tuberculosis of the spine. A long-term study. J Bone Joint Surg 57:1104–1107
Upadhyay S, Sell P, Saji M, Sell B, Leong J (1993) 17-year prospective study of surgical management of spinal tuberculosis in children: Hong Kong operation compared with debridement surgery for short- and long-term outcome of deformity. Spine 18:1704–1711
Schulitz K-P, Kothe R, Leong JC, Wehling P (1997) Growth changes of solidly fused kyphotic bloc after surgery for tuberculosis: comparison of four procedures. Spine 22:1150–1155
Hirakawa A, Miyamoto K, Masuda T, Fukuta S, Hosoe H, Iinuma N, Iwai C, Nishimoto H, Shimizu K (2010) Surgical outcome of 2-stage (posterior and anterior) surgical treatment using spinal instrumentation for tuberculous spondylitis. J Spinal Disord Tech 23:133–138
Kim D-J, Yun Y-H, Moon S-H, Riew KD (2004) Posterior instrumentation using compressive laminar hooks and anterior interbody arthrodesis for the treatment of tuberculosis of the lower lumbar spine. Spine 29:E275–E279
Fukuta S, Miyamoto K, Masuda T, Hosoe H, Kodama H, Nishimoto H, Sakaeda H, Shimizu K (2003) Two-stage (posterior and anterior) surgical treatment using posterior spinal instrumentation for pyogenic and tuberculotic spondylitis. Spine 28:E302–E308
Klöckner C, Valencia R (2003) Sagittal alignment after anterior debridement and fusion with or without additional posterior instrumentation in the treatment of pyogenic and tuberculous spondylodiscitis. Spine 28:1036–1042
Rangel-Castilla L, Hwang SW, Whitehead WE, Curry DJ, Luerssen TG, Jea A (2012) Surgical treatment of thoracic Pott disease in a 3-year-old child, with vertebral column resection and posterior-only circumferential reconstruction of the spinal column: case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr 9:447–451
Pang X, Li D, Wang X, Shen X, Luo C, Xu Z, Zeng H, Wu P, Zhang P, Peng W (2014) Thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis in children with severe post-tubercular kyphotic deformities treated by single-stage closing–opening wedge osteotomy: preliminary report a 4-year follow-up of 12 patients. Childs Nerv Syst 30:903–909
Sahoo MM, Mahapatra SK, Sethi GC, Dash SK (2012) Posterior-only approach surgery for fixation and decompression of thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis: a retrospective study. J Spinal Disord Tech 25:E217–E223
Güzey FK, Emel E, Bas NS, Hacisalihoglu S, Seyithanoglu H, Karacor SE, Özkan N, Alatas I, Sel B (2005) Thoracic and lumbar tuberculous spondylitis treated by posterior debridement, graft placement, and instrumentation: a retrospective analysis in 19 cases. J Neurosurg Spine 3:450–458
Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F (2005) The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine 30:2024–2029
Roussouly P, Nnadi C (2010) Sagittal plane deformity: an overview of interpretation and management. Eur Spine J 19:1824–1836
Jin D, Qu D, Chen J, Zhang H (2004) One-stage anterior interbody autografting and instrumentation in primary surgical management of thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis. Eur Spine J 13:114–121
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81271940) and the Project of Furong Scholar of Hunan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests concerning this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, X.H., Zhou, Z.H., Yu, H.G. et al. Comparison between the antero-posterior and posterior only approaches for treating thoracolumbar tuberculosis (T10-L2) with kyphosis in children: a minimum 3-year follow-up. Childs Nerv Syst 32, 127–133 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2935-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2935-8