Abstract
Subjects
Edaravone is a free radical scavenger with brain protection properties and is recommended by “The Japanese Guidelines for the Management of Stroke 2009” for administration to adult patients, in whom it has been shown to improve neurological deficits after cerebral infarction. However, its dosage and effects have not yet been established in children.
Methods
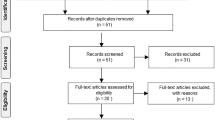
Seventeen pediatric patients with cerebral ischemia were administered edaravone at a dose based on body weight from the standard dose given to adults. Functional outcomes were evaluated using mRS and PSOM (modified ranking scale and pediatric stroke outcome scale, respectively).
Results
Immediate post-treatment results were mostly positive, with no liver or renal complications. In some cases, neurological symptoms markedly improved after the administration of edaravone.
Conclusions
The efficacy of edaravone has not yet been examined in pediatric patients. The results of the present study suggest that edaravone has potential in the treatment of children safely with promising results similar to those in adults.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Masaoka N, Nakajima Y, Watanabe M, Hayakawa Y, Nagaishi M, Yamamoto T, Honma T, Oinuma T, Nemoto N (2006) MCI-186 administered to the maternal circulation inhibits fetal brain injury resulting from total umbilical cord occlusion in the chronically instrumented fetal lamb. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 19:625–631
Noor JI, Ikeda T, Ueda Y, Ikenoue T (2005) A free radical scavenger, edaravone, inhibits lipid peroxidation and the production of nitric oxide in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage of neonatal rats. Am J Obstet Gynecol 193:1703–1708
Kaku Y, Iihara K, Nakajima N, Kataoka H, Fukuda K, Masuoka J, Fukushima K, Iida H, Hashimoto N (2012) Cerebral blood flow and metabolism of hyperperfusion after cerebral revascularization in patients with moyamoya disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:2066–2075
Yasuoka N, Nakajima W, Ishida A, Takada G (2004) Neuroprotection of edaravone on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 151:129–139
Watanabe T, Morita I, Nishi H, Murota S (1988) Preventive effect of MCI-186 on 15-HPETE induced vascular endothelial cell injury in vitro. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids 33:81–87
Abe K, Yuki S, Kogure K (1988) Strong attenuation of ischemic and postischemic brain edema in rats by a novel free radical scavenger. Stroke 19:480–485
Nishi H, Watanabe T, Sakurai H, Yuki S, Ishibashi A (1989) Effect of MCI-186 on brain edema in rats. Stroke 20:1236–1240
Watanabe T, Yuki S, Egawa M, Nishi H (1994) Protective effects of MCI-186 on cerebral ischemia: possible involvement of free radical scavenging and antioxidant actions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:1597–1604
Kawai H, Nakai H, Suga M, Yuki S, Watanabe T, Saito KI (1997) Effects of a novel free radical scavenger, MCl-186, on ischemic brain damage in the rat distal middle cerebral artery occlusion model. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281:921–927
Mizuno A, Umemura K, Nakashima M (1998) Inhibitory effect of MCI-186, a free radical scavenger, on cerebral ischemia following rat middle cerebral artery occlusion. Gen Pharmacol 30:575–578
Yamamoto T, Yuki S, Watanabe T, Mitsuka M, Saito KI, Kogure K (1997) Delayed neuronal death prevented by inhibition of increased hydroxyl radical formation in a transient cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 762:240–242
Andoh K, Kimura T, Saeki I, Tabata R, Yamazaki S, Eguchi I, Hanazuka M, Horii D, Munt PL, Davis AS, et al. (1994) General pharmacological properties of the human corticotropin-releasing hormone corticorelin (human). Arzneimittelforschung 44:715–726
Ohta Y, Takamatsu K, Fukushima T, Ikegami S, Takeda I, Ota T, Goto K, Abe K (2009) Efficacy of the free radical scavenger, edaravone, for motor palsy of acute lacunar infarction. Intern Med 48:593–596
Shinohara Y, Saito I, Kobayashi S, Uchiyama S (2009) Edaravone (radical scavenger) versus sodium ozagrel (antiplatelet agent) in acute noncardioembolic ischemic stroke (EDO trial). Cerebrovasc Dis 27:485–492
Johnston MV, Trescher WH, Ishida A, Nakajima W (2001) Neurobiology of hypoxic-ischemic injury in the developing brain. Pediatr Res 49:735–741
Kawashima H, Nishimata S, Ishii C, Yamanaka G, Kashiwagi Y, Takekuma K, Hoshika A, Watanabe Y (2011) New treatment of free-radical scavenger in adrenoleukodystrophy. J Clin Pharm Ther 36:412–415
Chan PH (1996) Role of oxidants in ischemic brain damage. Stroke 27:1124–1129
Fujimura M, Kaneta T, Shimizu H, Tominaga T (2007) Symptomatic hyperperfusion after superficial temporal artery-middle cerebral artery anastomosis in a child with moyamoya disease. Childs Nerv Syst 23:1195–1198
Fujimura M, Tominaga T, Chan PH (2005) Neuroprotective effect of an antioxidant in ischemic brain injury: involvement of neuronal apoptosis. Neurocrit Care 2:59–66
Ogasawara K, Inoue T, Kobayashi M, Endo H, Fukuda T, Ogawa A (2004) Pretreatment with the free radical scavenger edaravone prevents cerebral hyperperfusion after carotid endarterectomy. Neurosurgery 55:1060–1067
Anderson BJ, Holford NH (2008) Mechanism-based concepts of size and maturity in pharmacokinetics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 48:303–332
Mahmood I (2006) Prediction of drug clearance in children from adults: a comparison of several allometric methods. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:545–557
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Kostadin Karagiozov for his advice and manuscript review and David Huang for his guidance, and gratefully acknowledge the radiological technologists, nurses, and staff of the Department of Neurosurgery, Tokyo Women’s Medical University in preparing this manuscript.
Declaration of funding source
This study was supported by research funds from the Department of Neurosurgery, Tokyo Women’s Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no personal financial or institutional interest in any of the materials or devices described in this study. The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this study to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamoto, H., Aihara, Y., Yamaguchi, K. et al. Efficacy, safety, and outcomes in 17 pediatric cases treated with the free radical scavenger edaravone. Childs Nerv Syst 31, 1533–1540 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2814-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2814-3