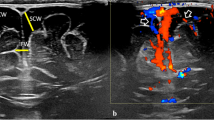
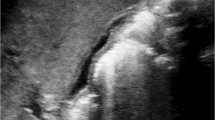
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to describe features of cystic periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) in a large consecutive cohort study including long-term neurodevelopmental follow-up.
Methods
We performed a retrospective single-centre cohort study including all preterm infants ≤35 weeks of gestational age with PVL diagnosed by ultrasound scans (US) from a tertiary care university hospital between 1988 and 2012.
Results
The majority of 160 consecutively diagnosed cases had a gestational age between 28 and 32 weeks (60.6 %), and male sex was predominant (60.6 %). The most common associated clinical findings included respiratory distress syndrome, preterm premature rupture of the membranes, and chorioamnionitis (57.5, 49.4, and 39.4 %, respectively). Infants presented with apnoeas in 66.3 and neonatal seizures in 23.1 %. Any kind of respiratory support was present in 75.0 %. Associated low-grade intraventricular haemorrhage was evident in 33.1, high-grade haemorrhage in 9.4 %. Cysts were located on both hemispheres in 75 % and PVL grades 3 and 4 were predominant (75.6 %). Neurodevelopmental follow-up of 146 cases at a median age of 72 months revealed normal development in 11.0, mental retardation in 50.0, and cerebral palsy in 83.6 %. Visual impairment was diagnosed in 21.9 % and hearing impairment in one case. A quarter of cases (27.4 %) developed seizure disorders. Outcome data were significantly better in unilateral compared to bilateral PVL.
Conclusions
Long-term neurodevelopmental outcome of bilateral PVL always was adverse and different from unilateral PVL. The latter might be negatively influenced by associated intra- and periventricular haemorrhages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argyropoulou MI (2010) Brain lesions in preterm infants: initial diagnosis and follow-up. Pediatr Radiol 40:811–818
Back SA (2006) Perinatal white matter injury: the changing spectrum of pathology and emerging insights into pathogenetic mechanisms. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 12:129–140
Baud O, d'Allest AM, Lacaze-Masmonteil T, Zupan V, Nedelcoux H, Boithias C, Delaveaucoupet J, Dehan M (1998) The early diagnosis of periventricular leukomalacia in premature infants with positive rolandic sharp waves on serial electroencephalography. J Pediatr 132:813–817
Blumenthal I (2004) Periventricular leukomalacia: a review. Eur J Pediatr 163:435–442
De Vries LS, Eken P, Dubowitz LMS (1992) The spectrum of leukomalacia using cranial ultrasound. Behav Brain Res 49:1–6
De Vries LS, Van Haastert IL, Rademaker KJ, Koopman C, Groenendaal F (2004) Ultrasound abnormalities preceding cerebral palsy in high-risk preterm infants. J Pediatr 144:815–820
Deng W, Pleasure J, Pleasure D (2008) Progress in periventricular leukomalacia. Arch Neurol 65:1291–1295
Fujimoto S, Yamaguchi N, Togari H, Wada Y, Yokochi K (1994) Cerebral palsy of cystic periventricular leukomalacia in low birth-weight infants. Acta Paediatr 83:397–401
Gagliardi L, Bellù R, Zanini R, Dammann O, Network Neonatale Lombardo Study Group (2009) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia and brain white matter damage in the preterm infant: a complex relationship. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 23:582–590
Hatzidaki E, Giahnakis E, Maraka S, Korakaki E, Manoura A, Saitakis E, Papamastoraki I, Margari KM, Giannakopoulou C (2009) Risk factors for periventricular leukomalacia. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 88:110–115
Humphreys P, Deonandan R, Whiting S, Barrowman N, Matzinger MA, Briggs V, Hurteau J, Wallace E (2007) Factors associated with epilepsy in children with periventricular leukomalacia. J Child Neurol 22:598–605
Krägeloh-Mann I, Cans C, Cerebral palsy update (2009) Brain Dev 31:537–544
Kumazaki K, Nakayama M, Sumida Y, Ozono K, Mushiake S, Suehara N, Wada Y, Fujimura M (2002) Placental features in preterm infants with periventricular leukomalacia. Pediatrics 109:650–655
Kusters CD, Chen ML, Follett PL, Dammann O (2009) “Intraventricular” hemorrhage and cystic periventricular leukomalacia in preterm infants: how are they related? J Child Neurol 24:1158–1170
Liu J, Li J, Qin GL, Chen YH, Wang Q (2008) Periventricular leukomalacia in premature infants in mainland China. Am J Perinatol 25:535–540
Pierrat V, Duquennoy C, van Haastert IC, Ernst M, Guilley N, de Vries LS (2001) Ultrasound diagnosis and neurodevelopmental outcome of localised and extensive cystic periventricular leucomalacia. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 84:F151–F156
Resch B, Resch E, Maurer U, Müller W (2011) Periventricular leukomalacia and neurodevelopmental outcome. J Pediatr 159:1049–1049
Resch B, Vollaard E, Maurer U, Haas J, Rosegger H, Müller W (2000) Risk factors and determinants of neurodevelopmental outcome in cystic periventricular leukomalacia. Eur J Pediatr 159:663–670
Rogers B, Msall M, Owens T, Guernsey K, Brody A, Buck G, Hudak M (1994) Cystic periventricular leukomalacia and type of cerebral palsy in preterm infants. J Pediatr 125:S1–S8
Shalak L, Perlman JM (2002) Hemorrhagic-ischemic cerebral injury in the preterm infant: current concepts. Clin Perinatol 29:745–763
Shinwell ES, Blickstein I, Lusky A, Reichman B (2004) Effect of birth order on neonatal morbidity and mortality among very low birthweight twins: a population based study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 89:F145–F148
Staneva KN, Bartolomaeus G, Plath C, Müller M, Uhlemann M, Terpe R (1997) Ultrasound and clinical studies of periventricular leukomalacia in high risk newborn infants. I. Neuro-ultrasound results. Zentralbl Gynakol 119:75–81
Staneva KN, Müller M, Plath C, Bartolomaeus G, Uhlemann M (1997) Ultrasound and clinical studies of periventricular leukomalacia in high risk newborn infants. II. Perinatal risk factors. Zentralbl Gynakol 119:100–105
Staudt M, Pavlova M, Böhm S, Grodd W, Krägeloh-Mann I (2003) Pyramidal tract damage correlates with motor dysfunction in bilateral periventricular leukomalacia (PVL). Neuropediatrics 34:182–188
van Haastert IC, Groenendaal F, Uiterwaal CS, Termote JU, van der Heide-Jalving M, Eijsermans MJ, Gorter JW, Helders PJ, Jongmans MJ, de Vries LS (2011) Decreasing incidence and severity of cerebral palsy in prematurely born children. J Pediatr 159:86–91, e1
Volpe JJ (2001) Neurobiology of periventricular leukomalacia in the premature infant. Pediatr Res 50:553–562
Zupan V, Gonzalez P, Lacaze-Masmonteil T, Boithias C, d'Allest AM, Dehan M, Gabilan JC (1996) Periventricular leukomalacia: risk factors revisited. Dev Med Child Neurol 38:1061–1067
Conflict of interest
The authors declare to have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Resch, B., Resch, E., Maurer-Fellbaum, U. et al. The whole spectrum of cystic periventricular leukomalacia of the preterm infant: results from a large consecutive case series. Childs Nerv Syst 31, 1527–1532 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2786-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2786-3