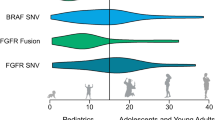
Abstract
Low-grade gliomas are the commonest brain tumor in children comprising heterogeneous pathological entities. Though the overall prognosis is good, unresectable, and recurrent or progressive tumors in eloquent areas of the brain remain major therapeutic challenge even with advances in chemotherapeutic strategies. With the evolving surge of molecular data, improved understanding of the biology of these tumors is now perceivable that could provide insights into novel therapies. We hope the new era will enable us to profile comprehensive histopathological/molecular classification and prognostic molecular markers in these tumors and guide us to tailor optimal targeted therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rickert CH, Paulus W (2005) Epidemiology of central nervous system tumors in childhood and adolescence based on the new WHO classification. Childs Nerv Syst 17:503–511
Qaddoumi I, Sultan I, Gajjar A (2009) Outcome and prognostic features in pediatric gliomas: a review of 6212 cases from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database. Cancer 115:5761–5770
Bleyer WA (1999) Epidemiologic impact of children with brain tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 15:758–763
Kleihues P, Louis DN, Scheithauer BW, Rorke LB, Reifenberger G, Burger PC et al (2002) The Who classification of tumors of the central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:215–225
Dolecek TA, Propp JM, Stroup C, Kruchko C (2012) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005-2009. Neuro Oncol 14(suppl 5):v1–v49
Heath JA, Zacharoulis S, Kieran MW (2012) Pediatric neuro-oncology: current status and future directions. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 8:223–231
Merchant TE, Conklin HM, Wu S, Lustig RH, Xiong X (2009) Late effects of conformal radiation therapy for pediatric patients with low-grade glioma, prospective evaluation of cognitive, endocrine and hearing deficits. J Clin Oncol 27:3691–3697
Stockland T, Liu JF, Ironside JW, Ellison DW, Taylor R, Robinson KJ et al (2010) A multivariate analysis of factors determining tumor progression in childhood low-grade glioma: a population-based cohort study (CCLG CNS9702). Neuro Oncol 12:1257–1268
Taphoorn MJ, Schiphorst AK, Snoek FJ, Lindeboom J, Wolbers JG, Karim A et al (1994) Cognitive functions and quality of life in patients with low-grade gliomas: the impact of radiotherapy. Ann Neurol 36:48–54
Ater JL, Zhou T, Holmes E, Mazeswki CM, Booth TN, Fryer DR et al (2012) Randomized study of two chemotherapy regimens for treatment of low-grade glioma in young children: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 30:2641–2647
Bouffet E, Jakacki R, Goldman S, Hargrave D, Hawkins C, Shroff M et al (2012) Phase II study of weekly vinblastine in recurrent or refractory pediatric low-grade glioma. J Clin Oncol 30:1358–1363
Massimino M, Spreafico F, Riva D, Biassoni V, Poggi G, Solero C et al (2010) A lower-dose, lower-toxicity cisplatin-etoposide regimen for childhood progressive low-grade glioma. J Neurooncol 100:65–71
Nicholson HS, Kretschmar CS, Krailo M, Bernstein M, Kadota R, Fort D et al (2007) Phase 2 study of temozolomide in children and adolescents with recurrent central nervous system tumors: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer 110:1542–1550
Hwang EI, Jakacki RI, Fisher MJ, Kilburn LB, Horn M, Vezina G et al (2013) Long-term efficacy and toxicity of bevacizumab-based therapy in children with recurrent low-grade gliomas. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60(5):776–782
Warren KE, Goldman S, Pollack IF, Fangusaro J, Schaiquevich P, Stewart CF et al (2011) Phase I trial of lenalidomide in pediatric patients with recurrent, refractory, or progressive primary CNS tumors: Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium study PBTC-018. J Clin Oncol 29:324–329. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.31.3601
Robison NJ, Campigotto F, Chi SN, Manley PE, Turner CD, Zimmerman MA et al (2014) A phase II trial of multi-agent oral antoangiogenic (metronomic) regimen in children with recurrent or progressive cancer. Pediatr Blood Cancer 61(4):636–642. doi:10.1002/pbc.24794
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A et al (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114(2):97–109
Takei HYS, Wong KK, Mehta V, Chintagumpala M, Dauser RC, Lau CC et al (2008) Expression of oligodendroglial differentiation markers in pilocytic astrocytoma identifies two clinical subsets and shows a significant clinical correlation with proliferation index and progression free survival. J Neurooncol 86:183–190
Buccoliero AM, Castiglione F, Degl'innocenti DR, Moncini D, Spacca B, Giordano F et al (2013) Angiocentric glioma: clinical, morphological, immunohistochemical and molecular features in three pediatric cases. Clin Neuropathol 32:107–113
Passone E, Pizzolitto S, D'Agostini S, Skrap M, Gardiman MP, Nocerino A et al (2006) Non-anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with neuroradiological evidences of leptomeningeal dissemination. Childs Nerv Syst 22(6):614–618
Hegedus B, Banerjee D, Yeh TH, Rothermich S, Perry A, Rubin JB et al (2008) Preclinical cancer therapy in a mouse model of neurofibromatosis-1 optic glioma. Cancer Res 68:1520–1528
Gutmann DH (2008) Using neurofibromatosis-1 to better understand and treat pediatric low-grade glioma. J Child Neurol 23:1186–1194
Chen Y-H, Gutmann DH (2014) The molecular and cell biology of pediatric low-grade gliomas. Oncogene 33:2019–2026
Tatevossian RG, Lawson ARJ, Forshew T, Hindley GFL, Ellison DW, Sheer D (2009) MAPK pathway activation and the origins of pediatric low-grade astrocytomas. J Cell Physiol 222:509–514
Hottinger AF, Khakoo Y (2009) Neurooncology of familial cancer syndromes. J Child Neurol 24:1526–1535. doi:10.1177/0883073809337539
Magri L, Cominelli M, Cambiaghi M, Cursi M, Leocani L, Minicucci F et al (2013) Timing of mTOR activation affects tuberous sclerosis complex neuropathology in mouse models. Dis Model Mech 6:1185–1197. doi:10.1242/dmm.012096
Kreiger PA, Okada Y, Simon S, Rorke LB, Louis DN, Golden JA (2005) Losses of chromosomes 1p and 19q are rare in pediatric oligodendrogliomas. Acta Neuropathol 109:387–392. doi:10.1007/s00401-004-0976-2
Bergthold G, Bandopadhayay P, Bi WL, Ramkissoon L, Stiles C, Segal RA (2014) Pediatric low-grade gliomas: how modern biology reshapes the clinical field. Biochim Biophys Acta 1845:294–307. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.02.004
Litofsky NS, Hinton D, Raffel C (1994) The lack of a role for p53 in astrocytomas in pediatric patients. Neurosurgery 34(6):967–972
Patt S, Gries H, Giraldo M, Cervos-Navarro J, Martin H, Janisch W et al (1996) P53 gene mutations in human astrocytic brain tumors including pilocytic astrocytomas. Hum Pathol 27(6):586–589
Jones DT, Kocialkowski S, Liu L, Pearson DM, Backlund LM, Ichimura K et al (2008) Tandem duplication producing a novel oncogenic BRAF fusion gene defines the majority of pilocytic astrocytomas. Cancer Res 68(21):8673–8677. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2097
Pfister S, Janzarik WG, Remke M, Ernst A, Werft W, Becker N et al (2008) BRAF gene duplication constitutes a mechanism of MAPK pathway activation in low-grade astrocytomas. J Clin Invest 118:1739–1749. doi:10.1172/JCI33656
Sievert AJ, Jackson EM, Gai X, Hakonarson H, Judkins AR, Resnick AC et al (2009) Duplication of 7q34 in pediatric low-grade astrocytomas detected by high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism-based genotype arrays results in a novel BRAF fusion gene. Brain Pathol 19:449–458. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00225.x
Cin H, Meyer C, Herr R, Janzarik WG, Lambert S, Jones DT (2011) Oncogenic FAM131B-BRAF fusion resulting from 7q34 deletion comprises an alternative mechanism of MAPK pathway activation in pilocytic astrocytoma. Acta Neuropathol 121:763–774. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0817-z
Zhang J, Wu G, Miller CP, Tatevossian RG, Dalton JD, Tang B et al (2013) Whole-genome sequencing identifies genetic alterations in pediatric low-grade gliomas. Nat Genet 45:602–612. doi:10.1038/ng.2611
Jones DT, Kocialkowski S, Liu L, Pearsion DM, Ichimura K, Collins VP (2009) Oncogenic RARF1 rearrangement and a novel BRAF mutation as alternative to KIAA1549:BRAF fusion in activating the MAPK pathway in pilocytic astrocytoma. Oncogene 28:2119–2123. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.73
Maldonado JL, Fridlyand J, Patel H, Jain AN, Busam K, Kageshita T et al (2003) Determinants of BRAF mutants in primary melanomas. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:1878–1890
Yeo YH, Byrne NP, Counelis GJ, Perry A (2013) Adult with cerebellar anaplastic pilocytic astrocytoma associated with BRAF V600E mutation and p16 loss. Clin Neuropathol 32:159–64. doi:10.1038/ng.2706
Schindler G, Capper D, Meyer J, Janzarik W, Omran H, Herold-Mende C et al (2011) Lysis of BRAF V600E mutation in 1,320 nervous system tumors reveals high mutation frequencies in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, ganglioglioma and extra-cerebellar pilocytic astrocytoma. Acta Neuropathol 121:397–405. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0802-6
Dias-Santagata D, Lam Q, Vernovsky K, Vena N, Lennerz JK, Borger DR et al (2011) BRAF V600E mutations are common in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. PLoS One 6(3):e17948. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017948
Roth JJ, Santi M, Rorke-Adams LB, Harding BN, Busse TM, Tooke LS et al (2014) Diagnostic application of high resolution single nucleotide polymorphism array analysis for children with brain tumors. Cancer Genet 207(4):111–123
Turcan S, Chan TA (2013) MAPping the genomic landscape of low-grade pediatric gliomas. Nat Genet 45:847–849. doi:10.1038/ng.2706
Jones DT, Hutter B, Jager N, Korshunov A, Kool M, Warnatz HJ et al (2013) Recurrent somatic alterations of FGFR1 and NTRK2 in pilocytic astrocytoma. Nat Genet 45:927–932. doi:10.1038/ng.2682
Dougherty MJ, Santi M, Brose MS, Ma C, Resnick AC, Sievert AJ et al (2010) Activating mutations in BRAF characterize a spectrum of pediatric low-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol 12:621–630. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noq007
Kaul A, Chen YH, Emnett RJ, Dahiya S, Gutmann DH (2012) Pediatric glioma-associated KIAA1549:BRAF expression regulates neuroglial cell growth in a cell type-specific and mTOR-dependent manner. Genes Dev 26:2561–2566. doi:10.1101/gad.200907.112
Tabori U, Rienstein S, Dromi Y, Leider-Trejo L, Constantini S, Burstein Y et al (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene amplification and expression in disseminated pediatric low-grade gliomas. J Neurosurg 103:357–361. doi:10.3171/ped.2005.103.4.0357
MacConaill LE, Campbell CD, Kehoe SM, Bass AJ, Hatton C, Niu L et al (2009) Profiling critical cancer gene mutations in clinical tumor samples. PLoS One 4(11):e7887
Chen D, Persson A, Sun Y, Salford LG, Nord DG, Englund E et al (2013). Better prognosis of patients with glioma expressing FGF2-dependent PDGFRA irrespective of morphological diagnosis. 8(4):e61556. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061556
Rush SZ, Abel TW, Valadez JG, Pearson M, Cooper MK (2010) Activation of the Hedgehog pathway in pilocytic astrocytomas. Neuro Oncol 12(8):790–798
Tatevossian RG, Tang B, Dalton J, Forshew T, Lawson AR, Ma J et al (2010) MYB upregulation and genetic aberrations in a subset of pediatric low-grade gliomas. Acta Neuropathol 120:731–743
Ramkissoon LA, Horowitz PM, Craig JM, Ramkissoon SH, Rich BE, Schumacher SE et al (2013) Genomic analysis of diffuse pediatric low-grade gliomas identifies recurrent oncogenic truncating rearrangements in the transcription factor MYBL1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:8188–8193
Yuen BT, Knoepfler PS (2013) Histone H3.3 mutations: a variant path to cancer. Cancer Cell 24:567–574. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2013.09.015
Deshmukh H, Yeh TH, Yu J, Sharma MK, Perry A, Leonard JR et al (2008) High-resolution, dual-platform aCGH analysis reveals frequent HIPK2 amplification and increased expression in pilocytic astrocytomas. Oncogene 27:4745–4751
Yu J, Deshmukh H, Gutmann RJ, Emnett RJ, Rodriguez FJ, Watson MA et al (2009) Alterations of BRAF and HIPK2 loci predominate in sporadic pilocytic astrocytoma. Neurology 73:1526–1531
Melendez B, Fiano C, Ruano Y, Hernandez-Moneo JL, Mollejo M, Martinez P (2006) BCR gene disruption in a pilomyxoid astrocytoma. Neuropathology 26:442–446
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J et al (2011) Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med 364:2507–2516
Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Demidov LV, Jouary T, Gutzmer R, Millward M et al (2012) Dafarenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: a multicenter, open-label, phase 3 randomized controlled trial. Lancet 380:358–365
Dasgupta T, Yang X, Hashizume R, Olow A, Kolkowitz I, Weiss W et al (2012) Survival advantage with radiation combined with a selective BRAF V600E inhibitor in an orthotopic, intracranial model of BRAFV600E-mutated high-grade gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83(suppl3):S125
Skrypek M, Foreman N, Guillaume D, Moertel C (2014) Pilomyxoid astrocytoma treated successfully with vemurafenib. Pediatr Blood Cancer 61:2099–2100. doi:10.1002/pbc.25084
Bautista F, Paci A, Minard-Colin V, Dufour C, Grill J, Lacroix L et al (2014) Vemurafenib in pediatric patients with BRAFV600E mutated high-grade gliomas. Pediatr Blood Cancer 61:1101–1103. doi:10.1002/pbc.24891
Robinson GW, Orr BA, Gajjar A (2014) Complete clinical regression of a BRAF V600E- mutant pediatric glioblastoma. BMC Cancer 14:258. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-258
Sievert AJ, Lang SS, Boucher KL, Madsen PJ, Slaunwhite E, Choudhari N et al (2013) Paradoxical activation and RAF inhibitor resistance of BRAF protein kinase fusions characterizing pediatric astrocytomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:5957–5962. doi:10.1073/pnas.1219232110
Lang S, Sievert AL, Boucher KL, Madsen PJ, Slaunwhite E, Brewington D et al (2012) Development of pediatric glioma models for BRAF-targeted therapy. Neurosurgery 71:E575
Jang S, Atkins MB (2013) Which drug, and when, for patients with BRAF-mutant melanoma? Lancet Oncol 14:e60–e69. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70539-9
Poulikakos PI, Zhang C, Bollag G, Shokat KM, Rosen N (2010) RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF. Nature 464:427–430. doi:10.1038/nature08902
Karajannis MA, Legault G, Fisher MJ, Milla SS, Cohen KJ, Wisoff JH et al (2014) Phase II study of sorafenib in children with recurrent or progressive low-grade astrocytomas. Neuro Oncol 16:1408–1416. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nou059
Momota H, Nerio E, Holland C (2005) Perifosine inhibits multiple signaling pathways in glial progenitors and cooperates with temozolomide to arrest cell proliferation in gliomas in vivo. Cancer Res 67:7429–7435
Park SJ, Hong SW, Moon JH, Jin DH, Kim JS, Lee CK et al (2013) The MEK1/2 inhibitor AS703026 circumvents resistance to the BRAF inhibitor PLX4032 in human malignant melanoma cells. Am J Med Sci 346:494–498. doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e318298a185
Atefi M, von Euw E, Attar N, Ng C, Chu C, Guo D, Nazarian R et al (2011) Reversing melanoma cross-resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors by co-targeting the AKT/mTOR pathway. PLoS One 6(12):e28973. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028973
Fan QW, Knight ZA, Goldenberg DD, Yu W, Mostov KE, Stokoe D et al (2006) A dual PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor reveals emergent efficacy in glioma. Cancer Cell 9:341–349
Wang WJ, Long LM, Yang N, Zhang QQ, Ji WJ, Zhao JH et al (2013) NVP-BEZ235, a novel dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, enhances the radiosensitivity of human glioma stem cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34:681–690
Rodriguez EF, Scheithauer BW, Giannini C, Rynearson A, Cen L, Hoesley B et al (2011) PI3K/AKT pathway alterations are associated with clinically aggressive and histologically anaplastic subsets of pilocytic astrocytoma. Acta Neuropathol 121:407–420. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0784-9
Hütt-Cabezas M, Karajannis MA, Zagzag D, Shah S, Horkayne-Szakaly I, Rushing EJ et al (2013) Activation of mTORC1/mTORC2 signaling in pediatric low-grade glioma and pilocytic astrocytoma reveals mTOR as a therapeutic target. Neuro Oncol 15:1604–1614. doi:10.1093/neuonc/not132
Malone CF, Fromm JA, Maertens O, DeRaedt T, Ingraham R, Cichowski K (2014) Defining key signaling nodes and therapeutic biomarkers in NF1-mutant cancers. Cancer Discov 4:1062–1073. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0159
Cardamone M, Flanagan D, Mowat D, Kennedy SE, Chopra M, Lawson JA (2014) Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors for intractable epilepsy and subependymal giant cell astrocytomas in tuberous sclerosis. J Pediatr 164:1195–1200. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.12.053
Kieran M, Yao X, Macy M, Geyer R, Cohen K, MacDonald T et al (2013) A prospective multi-institutional phase II study of everolimus (RAD001), a mTOR inhibitor, in pediatric patients with recurrent or progressive low-grade gliomas. A POETIC consortium trial. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60(S3):19
Luchman HA, Stechishin OD, Nguyen SA, Lun XQ, Cairncross JG, Weiss S (2014) Dual mTORC1/2 blockade inhibits glioblastoma brain tumor initiating cells in vitro and in vivo and synergizes with temozolomide to increase orthotopic xenograft survival. Clin Cancer Res 20(22):5756–5767
Kang MH, Reynolds CP, Maris JM, Gorlick R, Kolb EA, Lock R et al (2014) Initial testing (stage 1) of the investigational mTOR kinase inhibitor MLN0128 by the pediatric preclinical testing program. Pediatr Blood Cancer 61:1486–1489. doi:10.1002/pbc.24989
Ciombor KK, Bekaii-Saab T (2015) Selumetinib for the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 24:111–123
Kolb EA, Gorlick R, Houghton PJ, Morton CL, Neale G, Keir ST et al (2010) Initial testing (stage 1) of AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) by the Pediatric Preclinical Testing Program. Pediatr Blood Cancer 55:668–677
Bid HK, Kibler A, Phelps DA, Manap S, Xiao L, Lin J et al (2013) Development, characterization, and reversal of acquired resistance to the MEK1 inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244) in an in vivo model of childhood astrocytoma. Clin Cancer Res 19:6716–6729
Yalon M, Rood B, MacDonald TJ, McCowage G, Kane R, Constantini S et al (2013) A feasibility and efficacy study of rapamycin and erlotinib for recurrent pediatric low-grade glioma (LGG). Pediatr Blood Cancer 60:71–76. doi:10.1002/pbc.24142
Gessi M, Moneim YA, Hammes J, Goschzik T, Scholz M, Denkhaus D et al (2014) FGFR1 mutations in Rosette-forming glioneuronal tumors of the fourth ventricle. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 73:580–584
Parker BC, Engels M, Annala M, Zhang W (2014) Emergence of FGFR family gene fusions as therapeutic targets in a wide spectrum of solid tumors. J Pathol 232:4–15
Conflict of Interest
The authors report no financial or nonfinancial competing interests to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khatua, S., Wang, J. & Rajaram, V. Review of low-grade gliomas in children—evolving molecular era and therapeutic insights. Childs Nerv Syst 31, 643–652 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2653-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2653-2