Abstract
Purpose
There is no consensus on how to treat surgically high-dysplastic developmental spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. Although reducing spinal deformity seems mandatory, the issue of surgical reduction versus in situ fusion remains controversial.
Methods
The files of 12 consecutive patients surgically treated for a grade 3 or 4 spondylolisthesis were reviewed. The treatment consisted in L4 to sacrum reduction and fusion by posterior approach. The reduction of lumbopelvic imbalance was made intraoperatively using a trans-sacral rod fixation technique.
Results
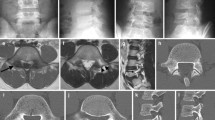
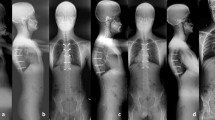
Mean preoperative L5 anterior slippage was 72.3 % (60 to 95 %). The mean preoperative lumbosacral tilt angle was 70.5° (43 to 92°). Mean final lumbosacral tilt angle was 102° (91 to 114°). Mean final L5 anterior slippage was 19 % (7 to 63 %). Neurological complications (radicular L5 or S1 deficits) were noted in five patients. At final follow-up L4 to S1 fusion was achieved in all patients. No patient had persistent deficit or radicular pain.
Conclusions
The fusion rate in our series proved to be optimal. Thanks to the trans-sacral rod fixation, lumbosacral kyphosis correction was very good. The intrasacral positioning of the screws reduces the risk of implant prominence especially in such pediatric patients. We stress the importance to avoid complete slip reduction in such patients to minimize stretching on L5 and S1 roots. No additional immobilization is needed due to solid posterior instrumentation. Doing such procedure only by posterior approach avoids anterior approach-related complications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sailhan F, Gollogly S, Roussouly P (2006) The radiographic results and neurologic complications of instrumented reduction and fusion of high-grade spondylolisthesis without decompression of the neural elements: a retrospective review of 44 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:161–169, discussion 170
Bollini G, Jouve JL, Launay F, Glard Y, Jacopin S, Blondel B (2011) High-grade child spondylolisthesis: a custom-made cannulated screw to treat the so-called double instability. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 97:179–185
Bradford DS (1979) Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis. A combined approach for reduction and stabilization. Spine 4:423–429
Chung JY, Parthasarathy S, Avadhani A, Rajasekaran S (2010) Reduction of high-grade listhesis. Eur Spine J 19:353–354
Doita M, Uno K, Maeno K, Shimomura T, Nishida K, Fujioka H, Kurosaka M (2008) Two-stage decompression, reduction, and interbody fusion for lumbosacral spondyloptosis through a posterior approach using Ilizarov external fixation. J Neurosurg 8:186–192
Dubousset J (1997) Treatment of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. Clin Orthop 337:77–85
Grzegorzewski A, Kumar SJ (2000) In situ posterolateral spine arthrodesis for grades III, IV, and V spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Orthop 20:506–511
Helenius I, Remes V, Poussa M (2008) Uninstrumented in situ fusion for high-grade childhood and adolescent isthmic spondylolisthesis: long-term outcome. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(Suppl 2 Pt 1):145–152
Hresko MT, Hirschfeld R, Buerk AA, Zurakowski D (2009) The effect of reduction and instrumentation of spondylolisthesis on spinopelvic sagittal alignment. J Pediatr Orthop 29:157–162
Hu SS, Bradford DS, Transfeldt EE, Cohen M (1996) Reduction of high-grade spondylolisthesis using Edwards instrumentation. Spine 21:367–371
Ilharreborde B, Fitoussi F, Morel E, Bensahel H, Pennecot GF, Mazda K (2007) Jackson’s intrasacral fixation in the management of high-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Pediatr Orthop 16:16–18
Jalanko T, Helenius I, Remes V, Lamberg T, Tervahartiala P, Yrjonen T, Poussa M, Schlenzka D (2011) Operative treatment of isthmic spondylolisthesis in children: a long-term, retrospective comparative study with matched cohorts. Eur Spine J 20:766–775
Lakshmanan P, Ahuja S, Lewis M, Howes J, Davies PR (2009) Transsacral screw fixation for high-grade spondylolisthesis. Spine J 9:1024–1029
Laursen M, Thomsen K, Eiskjaer SP, Hansen ES, Bunger CE (1999) Functional outcome after partial reduction and 360° fusion in grade III-V spondylolisthesis in adolescent and adult patients. J Spinal Disord 12:300–306
Mehdian SH, Arun R (2011) A new three-stage spinal shortening procedure for reduction of severe adolescent isthmic spondylolisthesis: a case series with medium- to long-term follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 36:E705–E711
Moshirfar A, Khanna AJ, Kebaish KM (2007) Treatment of symptomatic spondyloptosis in an adult previously treated with in situ fusion and instrumentation by L5 vertebrectomy and L4-S1 instrumented reduction. Spine J 7:100–105
Osterman K, Lindholm TS, Laurent LE (1976) Late results of removal of the loose posterior element (Gill’s operation) in the treatment of lytic lumbar spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop 117:121–128
Roca J, Ubierna MT, Caceres E, Iborra M (1999) One-stage decompression and posterolateral and interbody fusion for severe spondylolisthesis. An analysis of 14 patients. Spine 24:709–714
Rodriguez-Olaverri JC, Zimick NC, Merola A, Vicente J, Rodriguez J, Tabuenca A, Loste A, Sunen E, Burgos J, Hevia E, Piza-Vallespir G (2008) Comparing the clinical and radiological outcomes of pedicular transvertebral screw fixation of the lumbosacral spine in spondylolisthesis versus unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) with posterior fixation using anterior cages. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:1977–1981
Sasso RC, Shively KD, Reilly TM (2008) Transvertebral transsacral strut grafting for high-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis L5-S1 with fibular allograft. J Spinal Disord Tech 21:328–333
Smith JA, Hu SS (1999) Management of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in the pediatric and adolescent population. Orthop Clin North Am 30:487–499, ix
Wiltse LL, Jackson DW (1976) Treatment of spondylolisthesis and spondylolysis in children. Clin Orthop 117):92–100
Hensinger RN (1989) Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am 71:1098–1107
Lenke LG, Bridwell KH (2003) Evaluation and surgical treatment of high-grade isthmic dysplastic spondylolisthesis. Instr Course Lect 52:525–532
Lonstein JE (1999) Spondylolisthesis in children. Cause, natural history, and management. Spine 24:2640–2648
Oakley RH, Carty H (1984) Review of spondylolisthesis and spondylolysis in pediatric practice. Br J Radiol 57:877–885
Vialle R, Miladi L, Wicart P, Dubousset J (2005) Surgical treatment of lumbosacral spondylolisthesis with major displacement in children and adolescents: a continuous series of 20 patients with mean 5-year follow-up. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 91:5–14
Vialle R, Charosky S, Padovani JP, Rigault P, Glorion C (2006) Surgical treatment of high-grade lumbosacral spondylolisthesis in childhood, adolescent, and young adult by the "double-plate" technique: a past experience. Eur Spine J 15:1210–1218
Labelle H, Roussouly P, Chopin D, Berthonnaud E, Hresko T, O’Brien M (2008) Spino-pelvic alignment after surgical correction for developmental spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 17:1170–1176
Lakshmanan P, Ahuja S, Lewis M, Howes JP, Davies PR (2009) Achieving 360° fusion in high-grade spondylolisthesis using HMA screws. Surg Technol Int 18:219–222
Meyerding H (1932) Spondylolisthesis. Surg Gynecol Obstet 54:371–377
Vialle R, Schmit P, Dauzac C, Wicart P, Glorion C, Guigui P (2005) Radiological assessment of lumbosacral dystrophic changes in high-grade spondylolisthesis. Skelet Radiol 34:528–535
Vialle R, Ilharreborde B, Dauzac C, Guigui P (2006) Intra and interobserver reliability of determining degree of pelvic incidence in high-grade spondylolisthesis using a computer-assisted method. Eur Spine J 15:1449–1453
Vialle R, Dauzac C, Khouri N, Wicart P, Glorion C, Guigui P (2007) Sacral and lumbar-pelvic morphology in high-grade spondylolisthesis. Orthopedics 30:642–649
Vialle R, Ilharreborde B, Dauzac C, Lenoir T, Rillardon L, Guigui P (2007) Is there a sagittal imbalance of the spine in isthmic spondylolisthesis? A correlation study. Eur Spine J 16:1641–1649
Boxall D, Bradford DS, Winter RB, Moe JH (1979) Management of severe spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am 61:479–495
Fredrickson BE, Baker D, McHolick WJ, Yuan HA, Lubicky JP (1984) The natural history of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 66:699–707
Lamartina C, Zavatsky JM, Petruzzi M, Specchia N (2009) Novel concepts in the evaluation and treatment of high-dysplastic spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 18(Suppl 1):133–142
Marchetti P, Bartolozzi P (1997) Classification of spondylolisthesis as a guideline for treatment. In: Bridwell K (ed) Textbook of spinal surgery. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 345–357
Molinari RW, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Ungacta FF, Riew KD (1999) Complications in the surgical treatment of pediatric high-grade, isthmic dysplastic spondylolisthesis. A comparison of three surgical approaches. Spine 24:1701–1711
Newton PO, Johnston CE 2nd (1997) Analysis and treatment of poor outcomes following in situ arthrodesis in adolescent spondylolisthesis. J Pediatr Orthop 17:754–761
Karampalis C, Grevitt M, Shafafy M, Webb J (2012) High-grade spondylolisthesis: gradual reduction using Magerl’s external fixator followed by circumferential fusion technique and long-term results. Eur Spine J 21(Suppl 2):S200–S206
Min K, Liebscher T, Rothenfluh D (2012) Sacral dome resection and single-stage posterior reduction in the treatment of high-grade high dysplastic spondylolisthesis in adolescents and young adults. Eur Spine J 21(Suppl 6):S785–S791
Kostuik JP, Valdevit A, Chang HG, Kanzaki K (1998) Biomechanical testing of the lumbosacral spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 23:1721–1728
Petraco DM, Spivak JM, Cappadona JG, Kummer FJ, Neuwirth MG (1996) An anatomic evaluation of L5 nerve stretch in spondylolisthesis reduction. Spine 21:1133–1138, discussion 1139
Conflicts of interest
The authors confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouyer, B., Bachy, M., Courvoisier, A. et al. High-grade lumbosacral spondylolisthesis reduction and fusion in children using transsacral rod fixation. Childs Nerv Syst 30, 505–513 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2260-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2260-z