Abstract
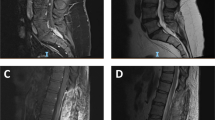
Myxopapillary ependymomas are almost exclusively seen at the conus medullaris/filum terminale/cauda equina region, usually as solitary space-occupying lesions. The authors report the case of a 14-year-old boy with double concomitant myxopapillary ependymoma, proximal and caudal on the filum terminale in which a totally gross removal was achieved in two stages. This presentation is rare and, so far, we have known just three similar cases that were previously reported in children. The true nature of these lesions is controversial, and while some argue that they are related to metastatic seeding, others consider them independent lesions developing synchronously. A review on dissemination of spinal myxopapillary ependymomas was done.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson DC, Cummings TJ, Friedman AH (2005) Myxopapillary ependymoma and fatty filum in an adult with tethered cord syndrome: a shared embryological lesion? Case report. Neurosurgery 57:E373
Andoh H, Kawaguchi Y, Seki S, Asanuma Y, Fukuoka J, Ishizawa S, Kimura T (2011) Multi-focal myxopapillary ependymoma in the lumbar and sacral regions requiring cranio-spinal radiation therapy: a case report. Asian Spine J 5:68–72
Bagley CA, Kothbauer KF, Wilson S, Bookland MJ, Epstein FJ, Jallo GI (2007) Resection of myxopapillary ependymomas in children. J Neurosurg 106(4 Suppl):261–267
Chan HS, Becker LE, Hoffman HJ, Humphreys RP, Hendrick EB, Fitz CR, Chuang SH (1984) Myxopapillary ependymoma of the filum terminale and cauda equina in childhood: report of seven cases and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 14:204–210
Choi BH, Kim RC, Suzuki M, Choe W (1992) The ventriculus terminalis and filum terminale of the human spinal cord. Hum Pathol 23:916–920
Davis C, Barnard RO (1985) Malignant behavior of myxopapillary ependymoma. Report of three cases. J Neurosurg 62:925–929
De Falco R, Scarano E, Celmo DDI, Civetta F, Guarnieri L (2008) Concomitant localization of a myxopapillary ependymoma at the middle thoracic part of the spinal cord and at the distal part of the filum terminale. Case report. J Neurosurg Sci 52:87–91
Gagliardi FM, Cervoni L, Domenicucci M, Celli P, Salvati M (1993) Ependymomas of the filum terminale in childhood: report of four cases and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 9:3–6
Gallia GL, Burger PC, Suk I, Bagley CA, Wolinsky J-P, Garonzik IM, Gokaslan ZL (2006) Concomitant conus medullaris ependymoma and filum terminale lipoma: case report. Neurosurgery 58:E1214
Gelabert-González M, Prieto-González A, Abdulkader-Nallib I, Cutrín-Prieto J (2001) Double ependymoma of the filum terminale. Childs Nerv Syst 17:106–108
Hallacq P, Labrousse F, Streichenberger N, Lisii D, Fischer G (2003) Bifocal myxopapillary ependymoma of the terminal filum: the end of a spectrum? J Neurosurg 98(3 Suppl):288–289
Kaliaperumal C, Suttner N, Herron B, Choudhari KA (2009) Rare case of primary spinal ependymomatosis occurring in a 26-year-old man: a case report. J Med Case Rep 3:72
Khalatbari MR, Jalaeikhoo H, Hamidi M, Moharamzad Y (2013) Craniospinal dissemination of filum myxopapillary ependymoma following spinal trauma: case report and literature review. Childs Nerv Syst 29:149–152
Kittel K, Gjuric M, Niedobitek G (2001) Metastasis of a spinal myxopapillary ependymoma to the inner auditory canal. HNO 49:298–302
Landriel F, Ajler P, Tedesco N, Bendersky D, Vecchi E (2012) Multicentric extramedullary myxopapillary ependymomas: two case reports and literature review. Surg Neurol Int 3:102
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer B, Kleihues P (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114:97–109
Martinez-Perez R, Hernandez-Lain A, Paredes I, Munarriz PM, Castaño-Leon AM, Lagares A (2012) Acute neurological deterioration as a result of two synchronous hemorrhagic spinal ependymomas. Surg Neurol Int 3:33
Mridha AR, Sharma MC, Sarcar C, Suri V, Rishi A, Garg A, Suri A (2007) Myxopapillary ependymoma of lumbosacral region with metastasis to both cerebellopontine angles: report of a rare case. Childs Nerv Syst 23:1209–1213
Nakama S, Higashi T, Kimura A, Yamamuro K, Kikkawa I, Hoshino Y (2005) Double myxopapillary ependymoma of the cauda equina. J Orthop Sci 10:543–545
Plans G, Brell M, Cabiol J, Villa S, Torres A, Acebes JJ (2006) Intracranial retrograde dissemination in filum terminale myxopapillary ependymomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148:343–346
Rasmussen TB, Kernohan JW, Adson AW (1940) Pathological classification, with surgical consideration, of intraspinal tumors. Ann Surg 111:513–530
Rezai AR, Woo HH, Lee M, Cohen H, Zagzag D, Epstein FJ (1996) Disseminated ependymomas of the central nervous system. J Neurosurg 85:618–624
Ross DA, McKeever PE, Sandler HM, Muraszko KM (1993) Myxopapillary ependymoma. Results of nucleolar organizing region staining. Cancer 71:3114–3118
Rubinstein LJ, Logan WJ (1970) Extraneural metastases in ependymoma of the cauda equina. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 33:763–770
Schweitzer JS, Batzdorf U (1992) Ependymoma of the cauda equina region: diagnosis, treatment, and outcome in 15 patients. Neurosurgery 30:202–207
Sonneland PR, Scheithauer BW, Onofrio BM (1985) Myxopapillary ependymoma. A clinicopathologic and immunocytochemical study of 77 cases. Cancer 56:883–893
Tubbs RS, Kelly DR, Mroczek-Musulman EC, Braune K, Reddy A, Georgeson K, Grabb PA, Oaks WJ (2005) Dwarfism, occult spinal dysraphism, and presacral myxopapillary ependymoma with an epidermoid cyst in a child. Acta Neurochir 147:299–302
Wang M, Wang H, Zhou Y, Zhan R, Wan S (2013) Myxopapillary ependymoma in the third ventricle area and sacral canal: dropped or retrograde metastasis? Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53:237–241
Wippold FJ 2nd, Smirniotopoulos JG, Moran CJ, Suojanen JN, VolImer DG (1995) Imaging of myxopapillary ependymoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 165:1263–1267
Woesler B, Moskopp D, Kuchelmeister K, Schul C, Wassmann H (1998) Intracranial metastasis of a spinal myxopapillary ependymoma. A case report. Neurosurg Rev 21:62–65
Wolf NI, Harting I, Hartmann M, Aschoff A, Sommer C, Rating D, Ebinger F (2003) Combination of caudal myxopapillary ependymoma and dermal sinus: a single shared embryologic lesion? Dev Med Child Neurol 45:568–570
Yücesoy K, Ozer E, Koyuncuoglu M (2001) Parenchymal brain metastasis of a spinal myxopapillary ependymoma after extradural manipulation. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 143:1071–1072
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salomão, J.F., de Andrade, C.V., Bellas, A.R. et al. The nature of double concomitant myxopapillary ependymoma: report of a case. Childs Nerv Syst 30, 527–530 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2251-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2251-0