Abstract
Objective
Epidermoid cysts of the cerebellopontine angle (CPA) can be a surgical challenge for the pediatric neurosurgeon. Ideally, total removal must be achieved; however, occasional adhesions of these tumors to vital neurovascular structures and extension far beyond the midline may preclude their total removal. The aims of this article are to present an alternative surgical approach to these lesions and to provide the rationale for this technique.
Material and methods
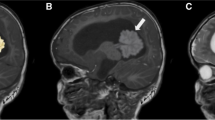
A 16-year-old boy was admitted to our pediatric neurosurgery department with a 1-year history of nonspecific headaches. His neurological examination showed right-sided dysmetria and gait ataxia. Magnetic resonance scans showed a space-occupying lesion on the right CPA with low intensity on T1-weighted images and high intensity on T2-weighted images.
Results
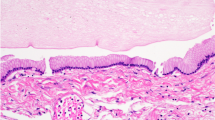
Craniotomy for tumor excision via pre- and subtemporal transtentorial approach was performed disclosing a 3.5 × 3 × 2.8-cm3 well-encapsulated tumor, which was confirmed to be an epidermoid cyst. The postoperative course was uneventful.
Conclusions
A combined pre- and subtemporal approach utilizes a wide opening of the tentorium and the option of supratentorial retraction of the cerebellum to provide an excellent angle of approach to CPA lesions involving the anterolateral aspect of the brain stem in children.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed I, Auguste KI, Vachhrajani S, Dirks PB, Drake JM, Rutka JT (2009) Neurosurgical management of intracranial epidermoid tumors in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 4:91–96
Altschuler EM, Jungries CA, Sekhar LN, Jannetta PJ, Shertak PE (1990) Operative treatment of intracranial epidermoid cysts and cholesterol granulomas: report of 21 cases. Neurosurgery 26:606–614
Bohara M, Yonezawa H, Hanaya R, Takeshita S, Sumida M, Arita K (2011) Posterior fossa epidermoid cysts presenting with unusual radiological appearances—two case reports. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51:85–88
Caldarelli M, Massimi L, Kondageski C, Di Rocco C (2004) Intracranial midline dermoid and epidermoid cysts in children. J Neurosurg (Pediatr) 100:473–480
Cruveilhier J (1829) Anatomie pathologique du corps humain, vol 1, book 2. Baillere, Paris
Drake CG (1968) The surgical treatment of aneurysms of the basilar artery. J Neurosurg 29:436–446
Fornari M, Solero CL, Lasio G, Lodrini S, Balestrini MR, Cimino C, Visintini S, Pluchino F (1990) Surgical treatment of intracranial dermoid and epidermoid cysts in children. Childs Nerv Syst 6:66–70
Giliberto G, Lanzimo DJ, Diehn FE, Factor D, Flemming KD, Lanzimo G (2010) Brainstem cavernous malformations: anatomical, clinical, and surgical considerations. Neurosurg Focus 29:1–22
Gupta PK, Anjaneyulu A, Borgohain R, Dinakar I (1994) Extrinsic infratentorial lesion causing ataxic hemiparesis—a new localization. J Neurol Sci 125:212–214
Guttal KS, Naikmasur VG, Joshi SK, Bathi RJ (2009) Trigeminal neuralgia secondary to epidermoid cyst at the cerebellopontine angle: case report and brief overview. Odontology 1:54–56
Kemaloğlu S, Ozkan U, Ziyal I, Bukte Y, Ceviz A (2002) Coexistence of a cerebellopontine epidermoid cyst with a pituitary adenoma. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 104:364–366
Mohanty A, Venkatrama SK, Rao BR, Chandramouli BA, Jayakumar PN, Das BS (1997) Experience with cerebellopontine angle epidermoids. Neurosurgery 40:24–30
Pitelli SD, Almeida GG, Nakagawa EJ, Marchese AJ, Cabral ND (1986) Basilar aneurysm surgery: the subtemporal approach with section of the zygomatic arch. Neurosurgery 18:125–128
Rhoton AL Jr (2000) Tentorial incisura. Neurosurgery 47:131–153
Russell DS, Rubinstein LF (eds) (1989) Pathology of tumors of the nervous system, 5th edn. Edward Arnold, London, pp 690–695
Safavi-Abbasi S, Di Rocco F, Bambakidis N, Talley MC, Gharabaghi A, Luedemann W, Samii M, Samii A (2008) Has management of epidermoid tumors of the cerebellopontine angle improved? A surgical synopsis of the past and present. Skull Base 18:85–98
Schiefer TK, Link MJ (2008) Epidermoids of the cerebellopontine angle: a 20-year experience. Surg Neurol 70:584–590
Schroeder HW, Oertel J, Gaab MR (2004) Endoscope-assisted microsurgical resection of epidermoid tumors of the cerebellopontine angle. J Neurosurg 101:227–232
Smith ER, Chapman PH, Ogilvy CS (2003) Far posterior subtemporal approach to the dorsolateral brainstem and tentorial ring: technique and clinical experience. Neurosurgery 52:364–373
Spiller WG, Frazier CH (1901) The division of the sensory root of the trigeminus for relief of tic douloureux: an experimental pathological and clinical study with a preliminary report of one surgical successful case. Phila Med J 8:1039–1049
Vinchon M, Pertuzon B, Lejeune JP, Assaker R, Pruvo JP, Christiaens JL (1995) Intradural epidermoid cysts of the cerebellopontine angle: diagnosis and surgery. Neurosurgery 36:52–57
Yasargil MG, Abernathey CD, Sarioglu AC (1989) Microsurgical treatment of intracranial dermoid and epidermoid tumors. Neurosurgery 24:561–567
Zúccaro G, Sosa F (2007) Cerebellopontine angle lesions in children. Childs Nerv Syst 23:177–183
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, R.S., Maia, W.S., Santos, M.V. et al. Combined pre- and subtemporal transtentorial approach for epidermoid cysts of the cerebellopontine angle. Childs Nerv Syst 28, 2137–2142 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1904-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1904-8