Abstract
Background
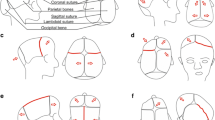
Non syndromic craniosynostoses are the most frequent craniofacial malformations worldwide. They represent a wide and heterogeneous group of entities, in which the dysmorphism may occur in a single (simple forms) or in multiple sutures (complex forms). Simple forms present a higher birth prevalence and are classified according to the involved suture and to the corresponding abnormal cranial shape: scaphocephaly (SC; sagittal suture), trigonocephaly (TC; metopic suture), anterior plagiocephaly (unilateral coronal suture), posterior plagiocephaly (unilateral lambdoid suture). They occur commonly as sporadic forms, although a familiar recurrence is sometimes observed, suggesting a mendelian inheritance. The genetic causes of simple craniosynostosis are still largely unknown, as mutations in common craniosynostosis-associated genes and structural chromosomal aberrations have been rarely found in these cases.
Aims
This review is intended to dissect comprehensively the state-of-the art on the genetic etiology of single suture craniosynostoses, in the attempt to categorize all known disease-associated genes and chromosomal aberrations. Possible genotype/phenotype correlations are discussed as useful clues towards the definition of optimized clinical management flowcharts.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen MJ (2000) Craniosynostosis: diagnosis, evaluation, and management. Oxford University Press, New York
Wilkie AO, Byren JC, Hurst JA, Jayamohan J, Johnson D, Knight SJ, Lester T, Richards PG, Twigg SR, Wall SA (2010) Prevalence and complications of single-gene and chromosomal disorders in craniosynostosis. Pediatrics 126(2):e391–400
Ursitti F, Fadda T, Papetti L, Pagnoni M, Nicita F, Iannetti G, Spalice A (2011) Evaluation and management of nonsyndromic craniosynostosis. Acta Paediatr 100(9):1185–1194
Di Rocco C, Velardi F (1988) Nosographic identification and classification of plagiocephaly. Childs Nerv Syst 4(1):9–15
Lajeunie E, Merrer ML, Bonaiti-Pellie C, Marchac D, Renier D (1996) Genetic study of scaphocephaly. Am J Med Genet 62(3):282–285
Boyadjiev SA, International Craniosynostosis Consortium (2007) Genetic analysis of non-syndromic craniosynostosis. Orthod Craniofac Res 10(3):129–137
Lajeunie E, Merrer ML, Bonaiti-Pellie C, Marchac D, Renier D (1995) Genetic study of nonsyndromic coronal craniosynostosis. Am J Med Genet 55(4):500–504
Lajeunie E, Merrer ML, Marchac D, Renier D (1998) Syndromal and nonsyndromal primary trigonocephaly: analysis of a series of 237 patients. Am J Med Genet 75(2):211–215
Huang MH, Gruss JS, Clarren SK, Mouradian WE, Cunningham ML, Roberts TS, Loeser JD, Cornell CJ (1996) The differential diagnosis of posterior plagiocephaly: true lambdoid synostosis versus positional molding. Plast Reconstr Surg 98(5):765–774
Selber J, Reid RR, Chike-Obi CJ, Sutton LN, Zackai EH, McDonald-McGinn D, Sonnad SS, Whitaker LA, Bartlett SP (2008) The changing epidemiologic spectrum of single-suture synostoses. Plast Reconstr Surg 122(2):527–533
Di Rocco F, Arnaud E, Renier D (2009) Evolution in the frequency of nonsyndromic craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr 4(1):21–25
van der Meulen J, van der Hulst R, van Adrichem L, Arnaud E, Chin-Shong D, Duncan C, Habets E, Hinojosa J, Mathijssen I, May P, Morritt D, Nishikawa H, Noons P, Richardson D, Wall S, van der Vlugt J, Renier D (2009) The increase of metopic synostosis: a pan-European observation. J Craniofac Surg 20(2):283–286
Jehee FS, Johnson D, Alonso LG, Cavalcanti DP, de Sá ME, Alberto FL, Kok F, Kim C, Wall SA, Jabs EW, Boyadjiev SA, Wilkie AO, Passos-Bueno MR (2005) Molecular screening for microdeletions at 9p22-p24 and 11q23-q24 in a large cohort of patients with trigonocephaly. Clin Genet 67(6):503–510
Wilkie AO, Bochukova EG, Hansen RM, Taylor IB, Rannan-Eliya SV, Byren JC, Wall SA, Ramos L, Venâncio M, Hurst JA, O'rourke AW, Williams LJ, Seller A, Lester T (2007) Clinical dividends from the molecular genetic diagnosis of craniosynostosis. Am J Med Genet A 143A(16):1941–1949
Seto ML, Hing AV, Chang J, Hu M, Kapp-Simon KA, Patel PK, Burton BK, Kane AA, Smyth MD, Hopper R, Ellenbogen RG, Stevenson K, Speltz ML, Cunningham ML (2007) Isolated sagittal and coronal craniosynostosis associated with TWIST box mutations. Am J Med Genet A 143(7):678–686
Johnson D, Wilkie AO (2001) Craniosynostosis. Eur J Hum Genet 19(4):369–376
Lattanzi W, Bernardini C (2011) Genes and molecular pathways of the osteogenic process. In: Lin Y(ed) Osteogenesis, InTech, Available at http://www.intechopen.com/books/osteogenesis/genes-and-molecular-pathways-of-the-osteogenic-process
Mefford HC, Shafer N, Antonacci F, Tsai JM, Park SS, Hing AV, Rieder MJ, Smyth MD, Speltz ML, Eichler EE, Cunningham ML (2010) Copy number variation analysis in single-suture craniosynostosis: multiple rare variants including RUNX2 duplication in two cousins with metopic craniosynostosis. Am J Med Genet A 152A(9):2203–10
Cunningham ML, Horst JA, Rieder MJ, Hing AV, Stanaway IB, Park SS, Samudrala R, Speltz ML (2011) IGF1R variants associated with isolated single suture craniosynostosis. Am J Med Genet A 155A(1):91–97
Kress W, Schropp C, Lieb G, Petersen B, Büsse-Ratzka M, Kunz J, Reinhart E, Schäfer WD, Sold J, Hoppe F, Pahnke J, Trusen A, Sörensen N, Krauss J, Collmann H (2006) Saethre-Chotzen syndrome caused by TWIST 1 gene mutations: functional differentiation from Muenke coronal synostosis syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 14(1):39–48
Paznekas WA, Cunningham ML, Howard TD, Korf BR, Lipson MH, Grix AW, Feingold M, Goldberg R, Borochowitz Z, Aleck K, Mulliken J, Yin M, Jabs EW (1998) Genetic heterogeneity of Saethre-Chotzen syndrome, due to TWIST and FGFR mutations. Am J Hum Genet 62(6):1370–1380
McGillivray G, Savarirayan R, Cox TC, Stojkoski C, McNeil R, Bankier A, Bateman JF, Roscioli T, Gardner RJ, Lamandé SR (2005) Familial scaphocephaly syndrome caused by a novel mutation in the FGFR2 tyrosine kinase domain. J Med Genet 42(8):656–62
Moloney DM, Wall SA, Ashworth GJ, Oldridge M, Glass IA, Francomano CA, Muenke M, Wilkie AOM (1997) Prevalence of pro250arg mutation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 in coronal craniosynostosis. Lancet 349(9058):1059–1062
Muenke M, Gripp KW, McDonald-McGinn DM, Gaudenz K, Whitaker LA, Bartlett SP, Markowitz RI, Robin NH, Nwokoro N, Mulvihill JJ, Losken W, Mulliken JB, Guttmacher AE, Wilroy RS, Clarke LA, Hollway G, Ades LC, Haan EA, Mulley JC, Cohen MM Jr, Bellus GA, Francomano CA, Moloney DM, Wall SA, Wilkie AOM, Zackai EH (1997) A unique point mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 gene (FGFR3) defines a new craniosynostosis syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 60(3):555–564
Renier D, El-Ghouzzi V, Bonaventure J, Le Merrer M, Lajeunie E (2000) Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 mutation in nonsyndromic coronal synostosis: clinical spectrum, prevalence, and surgical outcome. J Neurosurg 92(4):631–6
Mulliken JB, Gripp KW, Stolle CA, Steinberger D, Müller U (2004) Molecular analysis of patients with synostotic frontal plagiocephaly (unilateral coronal synostosis). Plast Reconstr Surg 113(7):1899–909
Keller MK, Hermann NV, Darvann TA, Larsen P, Hove HD, Christensen L, Schwartz M, Marsh JL, Kreiborg S (2007) Craniofacial morphology in Muenke syndrome. J Craniofac Surg 18(2):374–386
Tsai FJ, Wu JY, Lee CC, Tsa CH (2000) A unique point mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 gene (FGFR3) causes non-syndromic craniosynostosis. Acta Paediatr 89(6):672–4
Johnson D, Wall SA, Mann S, Wilkie AO (2000) A novel mutation, Ala315Ser, in FGFR2: a gene-environment interaction leading to craniosynostosis? Eur J Hum Genet 8(8):571–577
Pedersen C (1976) Letter: partial trisomy 15 as a result of an unbalanced 12/15 translocation in a patient witha cloverleaf skull anomaly. Clin Genet 9(3):378–380
Van Allen MI, Siegel-Bartelt J, Feigenbaum A, Teshima IE (1992) Craniosynostosis associated with partial duplication of 15q and deletion of 2q. Am J Med Genet 43(4):688–692
Van den Enden A, Verschraegen-Spae MR, Van Roy N, Decaluwe W, De Praeter C, Speleman F (1996) Mosaic tetrasomy 15q25–>qter in a newborn infant with multiple anomalies. Am J Med Genet 63(3):482–485
Zollino M, Tiziano F, Di Stefano C, Neri G (1999) Partial duplication of the long arm of chromosome 15: confirmation of a causative role in craniosynostosis and definition of a 15q25-qter trisomy syndrome. Am J Med Genet 87(5):391–394
Hu J, McPherson E, Surti U, Hasegawa SL, Gunawardena S, Gollin SM (2002) Tetrasomy 15q25.3 –>qter resulting from an analphoid supernumerary marker chromosome in a patient with multiple anomalies and bilateral Wilms tumors. Am J Med Genet 113(1):82–88
Kress W, Petersen B, Collmann H, Grimm T (2000) An unusual FGFR1 mutation (fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 mutation) in a girl with non-syndromic trigonocephaly. Cytogenet Cell Genet 91(1–4):138–140
Kini U, Hurst JA, Byren JC, Wall SA, Johnson D, Wilkie AOM (2010) Etiological heterogeneity and clinical characteristics of metopic synostosis: evidence from a tertiary craniofacial unit. Am J Med Genet 152(6):1383–1389
Lajeunie E, Barcik U, Thorne JA, El Ghouzzi V, Bourgeois M, Renier D (2001) Craniosynostosis and fetal exposure to sodium valproate. J Neurosurg 95(5):778–782
Azimi C, Kennedy SJ, Chitayat D, Chakraborty P, Clarke JTR, Forrest C, Teebi AS (2003) Clinical and genetic aspects of trigonocephaly: a study of 25 cases. Am J Med Genet A 117A(2):127–135
Johnston JJ, Olivos-Glander I, Killoran C, Elson E, Turner JT, Peters KF, Abbott MH, Aughton DJ, Aylsworth AS, Bamshad MJ, Booth C, Curry CJ, David A, Dinulos MB, Flannery DB, Fox MA, Graham JM, Grange DK, Guttmacher AE, Hannibal MC, Henn W, Hennekam RC, Holmes LB, HoymeHE LKA, Lin AE, Macleod P, Manchester DK, Marcelis C, Mazzanti L, McCann E, McDonald MT, Mendelsohn NJ, Moeschler JB, Moghaddam B, Neri G, Newbury-Ecob R, Pagon RA, Phillips JA III, Sadler LS, Stoler JM, Tilstra D, Walsh Vockley CM, Zackai EH, Zadeh TM, Brueton L, Black GC, Biesecker LG (2005) Molecular and clinical analyses of Greig cephalopolysyndactyly and Pallister-Hall syndromes: robust phenotype prediction from the type and position of GLI3 mutations. Am J Hum Genet 76(4):609–622
Jehee FS, Alonso LG, Cavalcanti DP, Kim C, Wall SA, Mulliken JB, Sun M, Jabs EW, Boyadjiev SA, Wilkie AO, Passos-Bueno MR (2006) Mutational screening of FGFR1, CER1, and CDON in a large cohort of trigonocephalic patients. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J 43(2):148–151
Komori T (2011) Signaling networks in RUNX2-dependent bone development. J Cell Biochem 112(3):750–755
Cohen MM Jr (2009) Perspectives on RUNX genes: an update. Am J Med Genet A 149A(12):2629–46
Fryburg JS, Hwang V, Lin KY (1995) Recurrent lambdoid synostosis within two families. Am J Med Genet 58(3):262–266
Rogers GF, Edwards PD, Robson CD, Mulliken JB (2005) Concordant contralateral lambdoidal synostosis in dizygotic twins. J Craniofac Surg 16(3):435–439
Kadlub N, Persing JA, da Silva FR, Shin JH (2008) Familial lambdoid craniosynostosis between father and son. J Craniofac Surg 19(3):850–4
Johson D, Horsley SW, Moloney DM, Oldridge M, Twigg SR, Walsh S, Barrow M, Njølstad PR, Kunz J, Ashworth GJ, Wall SA, Kearney L, Wilkie AO (1998) A comprehensive screen for TWIST mutations in patients with craniosynostosis identifies a new microdeletion syndrome of chromosome band 7p21.1. Am J Hum Genet 63(5):1282–1293
Karteszi J, Kress W, Szasz M, Czako M, Melegh B, Kosztolanyi GY, Morava E (2004) Partial craniosynostosis in a patient with deletion 22q11. Genet Couns 15(4):481–483
McDonald-McGinn DM, Gripp KW, Kirschner RE, Maisenbacher MK, Hustead V, Schauer GM, Keppler-Noreuil KM, Ciprero KL, Pasquariello P Jr, LaRossa D, Bartlett SP, Whitaker LA, Zackai EH (2005) Craniosynostosis: another feature of the 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 136A(4):358–362
Yamamoto T, Sameshima K, Sekido K-i, Aida N, Matsumoto N, Naritomi K, Kurosawa K (2006) Trigonocephaly in a boy with paternally inherited deletion 22q11.2 syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 140A(12):1302–1304
Jehee FS, Bertola DR, Yelavarthi KK, Krepischi-Santos AC, Kim C, Vianna-Morgante AM, Vermeesch JR, Passos-Bueno MR (2007) An 11q11–q13.3 duplication, including FGF3 and FGF4 genes, in a patient with syndromic multiple craniosynostoses. Am J Med Genet A 143A(16):1912–1918
Gajecka M, Yu W, Ballif BC, Glotzbach CD, Bailey KA, Shaw CA, Kashork CD, Heilstedt HA, Ansel DA, Theisen A, Rice R, Rice DP, Shaffer LG (2005) Delineation of mechanisms and regions of dosage imbalance in complex rearrangements of 1p36 leads to a putative gene for regulation of cranial suture closure. Eur J Hum Genet 13(2):139–149
Hiraki Y, Fujita H, Yamamori S, Ohashi H, Eguchi M, Harada N, Mizuguchi T, Matsumoto N (2006). Mild craniosynostosis with 1p36.3 trisomy and 1p36.3 deletion syndrome caused by familial translocation t(Y;1). Am J Med Genet A 140(16):1773–1777
Shur N, Cowan J, Wheeler PG (2003) Craniosynostosis and congenital heart anomalies associated with a maternal deletion of 15q15-22.1. Am J Med Genet A 120A(4):542–546
Shiihara T, Kato M, Kimura T, Hayasaka K, Yamamori S, Ogata T (2004) Craniosynostosis with extra copy of MSX2 in a patient with partial 5q-trisomy. Am J Med Genet A 128A(2):214–216
Wang JC, Steinraths M, Dang L, Lomax B, Eydoux P, Stockley T, Yong SY, Van Allen MI (2007) Craniosynostosis associated with distal 5q-trisomy: further evidence that extra copy of MSX2 gene leads to craniosynostosis. Am J Med Genet A 143A(24):2931–2936
Villa O, Del Campo M, Salido M, Gener B, Astier L, Del Valle J, Gallastegui F, Pérez-Jurado LA, Solé F (2007) Small supernumerary marker chromosome causing partial trisomy 6p in a child with craniosynostosis. Am J Med Genet A 43A(10):1108–1113
Jehee FS, Krepischi-Santos AC, Rocha KM, Cavalcanti DP, Kim CA, Bertola DR, Alonso LG, D'Angelo CS, Mazzeu JF, Froyen G, Lugtenberg D, Vianna-Morgante AM, Rosenberg C, Passos-Bueno MR (2008) High frequency of submicroscopic chromosomal imbalances in patients with syndromic craniosynostosis detected by a combined approach of microsatellite segregation analysis, multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification and array-based comparative genome hybridisation. J Med Genet 45(7):447–450
Veltman IM, Veltman JA, Arkesteijn G, Janssen IM, Vissers LE, de Jong PJ, van Kessel AG, Schoenmakers EF (2003) Chromosomal breakpoint mapping by array CGH using flow-sorted chromosomes. Biotechniques 35(5):1066–1070
Gribble SM, Prigmore E, Burford DC, Porter KM, Ng BL, Douglas EJ, Fiegler H, Carr P, Kalaitzopoulos D, Clegg S, Sandstrom R, Temple IK, Youings SA, Thomas NS, Dennis NR, Jacobs PA, Crolla JA, Carter NP (2005) The complex nature of constitutional de novo apparently balanced translocations in patients presenting with abnormal phenotypes. J Med Genet 42(1):8–16
Harvard C, Malenfant P, Koochek M, Creighton S, Mickelson EC, Holden JJ, Lewis ME, Rajcan-Separovic E (2005) A variant Cri du Chat phenotype and autism spectrum disorder in a subject with de novo cryptic microdeletions involving 5p15.2 and 3p24.3e25 detected using whole genomic array CGH. Clin Genet 67(4):341–351
Rosenberg C, Knijnenburg J, Chauffaille Mde L, Brunoni D, Catelani AL, Sloos W, Szuhai K, Tanke HJ (2005) Array CGH detection of a cryptic deletion in a complex chromosome rearrangement. Hum Genet 116(5):390–394
De Gregori M, Ciccone R, Magini P, Pramparo T, Gimelli S, Messa J, Novara F, Vetro A, Rossi E, Maraschio P, Bonaglia MC, Anichini C, Ferrero GB, Silengo M, Fazzi E, Zatterale A, Fischetto R, Previderé C, Belli S, Turci A, Calabrese G, Bernardi F, Meneghelli E, Riegel M, Rocchi M, Guerneri S, Lalatta F, Zelante L, Romano C, Fichera M, Mattina T, Arrigo G, Zollino M, Giglio S, Lonardo F, Bonfante A, Ferlini A, Cifuentes F, Van Esch H, Backx L, Schinzel A, Vermeesch JR, Zuffardi O (2007) Cryptic deletions are a common finding in “balanced” reciprocal and complex chromosome rearrangements: a study of 59 cases. J Med Genet 44(12):750–762
Hoffer MJ, Hilhorst-Hofstee Y, Knijnenburg J, Hansson KB, Engelberts AC, Laan LA, Bakker E, Rosenberg C (2007) A 6 Mb deletion in band 2q22 due to a complex chromosome rearrangement associated with severe psychomotor retardation, microcephaly and distinctive dysmorphic facial features. Eur J Med Genet 50(2):149–154
Schluth-Bolard C, Till M, Labalme A, Rey C, Banquart E, Fautrelle A, Martin-Denavit T, Le Lorc'h M, Romana SP, Lazar V, Edery P, Sanlaville D (2008) TWIST microdeletion identified by array CGH in a patient presenting SaethreeChotzen phenotype and a complex rearrangement involving chromosomes 2 and 7. Eur J Med Genet 51(2):156–164
Swinkels ME, Simons A, Smeets DF, Vissers LE, Veltman JA, Pfundt R, de Vries BB, Faas BH, Schrander-Stumpel CT, McCann E, Sweeney E, May P, Draaisma JM, Knoers NV, van Kessel AG, van Ravenswaaij-Arts CM (2008) Clinical and cytogenetic characterization of 13 dutch patients with deletion 9p syndrome: delineation of the critical region for a consensus phenotype. Am J Med Genet A 146A(11):1430–1438
Tagariello A, Heller R, Greven A, Kalscheuer VM, Molter T, Rauch A, Kress W, Winterpacht A (2006) Balanced translocation in a patient with craniosynostosis disrupts the SOX6 gene and an evolutionarily conserved non-transcribed region. J Med Genet 43(6):534–540
Bastepe M (2007) The GNAS locus: quintessential complex gene encoding Gsα, XLαs, and other imprinted transcripts. Curr Genomics 8(6):398–414
Turleau C, de Grouchy J, Chabrolle JP (1978) Intercalary deletions of 9q. Ann Genet 21(4):234–236
Bastepe M, Lane AH, Jüppner H (2001) Paternal uniparental isodisomy of chromosome 20q–and the resulting changes in GNAS1 methylation–as a plausible cause of pseudohypoparathyroidism. Am J Hum Genet 68(5):1283–1289
Christ LA, Crowe CA, Micale MA, Conroy JM, Schwartz S (1999) Chromosome breakage hotspots and delineation of the critical region for the 9p-deletion syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 65(5):1387–1395
Dawson AJ, Chernos J, McGowan-Jordan J, Lavoie J, Shetty S, Steinraths M, Wang JC, Xu J, Canadian College of Medical Geneticists Committees (2011) CCMG guidelines: prenatal and postnatal diagnostic testing for uniparental disomy. Clin Genet 79(2):118–124
Velissariou V, Antoniadi T, Gyftodimou J, Bakou K, Grigoriadou M, Christopoulou S, Hatzipouliou A, Donoghue J, Karatzis P, Katsarou E, Petersen MB (2002) Maternal uniparental isodisomy 20 in a foetus with trisomy 20 mosaicism: clinical, cytogenetic and molecular analysis. Eur J Hum Genet 10(11):694–698
Massimi L, Tamburrini G, Caldarelli M, Di Rocco C (2007) Effectiveness of a limited invasive scalp approach in the correction of sagittal craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 23(12):1389–401
Chieffo D, Tamburrini G, Massimi L, Di Giovanni S, Giansanti C, Caldarelli M, Di Rocco C (2010) Long-term neuropsychological development in single-suture craniosynostosis treated early. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5(3):232–7
Lajeunie E, Crimmins DW, Arnaud E, Renier D (2005) Genetic considerations in nonsyndromic midline craniosynostoses: a study of twins and their families. J Neurosurg 103(4 Suppl):353–6
Opitz JM, Johnson RC, McCreadie SR, Smith DN (1969) The C syndrome of multiple congenital anomalies. Birth Defects Orig Art Ser V(2):161–166
Say B, Meyer J (1981) Familial trigonocephaly associated with short stature and developmental delay. Am J Dis Child 135(8):711–712
Frydman M, Kauschansky A, Elian E (1984) Trigonocephaly: a new familial syndrome. Am J Med Genet 18(1):55–59
Hennekam RCM, Van Den Boogaard MJ (1990) Autosomal dominant craniosynostosis of the sutura metopica. Clin Genet 38(5):374–377
Jovanović-Privrodski JD, Kavecan II, Obrenović MR, Buonadonna LA, Bukvić NM (2009) Autism and hypoplastic corpus callosum in a case of monocentric marker chromosome 15. Pediatr Neurol 41(1):65–67
Bukvic N, Delli Carri V, Di Cosola ML, Pustorino G, Cesarano C, Chetta M, Santacroce R, Sarno M, Sessa F, Longo V, Novelli A, Gentile M, Margaglione M (2010) Familial X;Y translocation with distinct phenotypic consequences: characterization using FISH and array CGH. Am J Med Genet A 152A(7):1730–1734
Dixon MJ, Marazita ML, Beaty TH, Murray JC (2011) Cleft lip and palate: understanding genetic and environmental influences. Nat Rev Genet 12(3):167–78
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lattanzi, W., Bukvic, N., Barba, M. et al. Genetic basis of single-suture synostoses: genes, chromosomes and clinical implications. Childs Nerv Syst 28, 1301–1310 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1781-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1781-1