Abstract
Purpose
The primary objective of this study was to report the results of author’s 18-year experience of diagnostic stereotactic biopsy procedures in children with intracranial lesions.
Methods and materials
A retrospective analysis was conducted on stereotactic procedures performed on children with brain tumor between 1989 and 2007.
Results
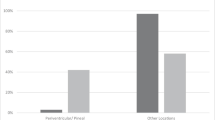
Stereotactic biopsy of intracranial tumors was performed in 172 children (69 girls, and 103 boys) with the mean age of 9.17 ± 3.66 years at the time of diagnosis. The most frequent anatomical location of lesions was brainstem (45.9%). Glioma was the most common diagnosis, represented in 90.7% of patients (156 patients). Other diagnosed tumors (4.7%) were classified as metastatic (1.7%), lymphomas (1.2%), oligodendroglioma (0.6%), craniopharyngioma (0.6%), and pineocytoma (0.6%). Nonneoplastic lesions were revealed in 4.7% of patients.
Conclusion
The most frequent brain pathology of children is glioma, but the incidence of brain lesions other than gliomas and the frequency of brain lesions in the inoperable areas are compelling reasons to establish tissue diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin RT, Preston-Martin S (2004) Epidemiology of brain tumors in childhood—a review. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 199(2):118–131. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2003.12.029
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60(5):277–300. doi:10.3322/caac.20073
Mueller S, Chang S (2009) Pediatric brain tumors: current treatment strategies and future therapeutic approaches. Neurotherapeutics 6(3):570–586. doi:10.1016/j.nurt.2009.04.006
Friedman WA, Sceats DJ Jr, Nestok BR, Ballinger WE Jr (1989) The incidence of unexpected pathological findings in an image-guided biopsy series: a review of 100 consecutive cases. Neurosurgery 25(2):180–184
Lobato RD, Rivas JJ, Cabello A, Roger R (1982) Stereotactic biopsy of brain lesions visualized with computed tomography. Appl Neurophysiol 45(4–5):426–430
Schumacher M, Schulte-Monting J, Stoeter P, Warmuth-Metz M, Solymosi L (2007) Magnetic resonance imaging compared with biopsy in the diagnosis of brainstem diseases of childhood: a multicenter review. J Neurosurg 106(2 Suppl):111–119. doi:10.3171/ped.2007.106.2.111
Wild AM, Xuereb JH, Marks PV, Gleave JR (1990) Computerized tomographic stereotaxy in the management of 200 consecutive intracranial mass lesions. Analysis of indications, benefits and outcome. Br J Neurosurg 4(5):407–415
Bernstein M, Parrent AG (1994) Complications of CT-guided stereotactic biopsy of intra-axial brain lesions. J Neurosurg 81(2):165–168. doi:10.3171/jns.1994.81.2.0165
Gomez H, Barnett GH, Estes ML, Palmer J, Magdinec M (1993) Stereotactic and computer-assisted neurosurgery at the Cleveland Clinic: review of 501 consecutive cases. Cleve Clin J Med 60(5):399–410
Hall WA (1998) The safety and efficacy of stereotactic biopsy for intracranial lesions. Cancer 82(9):1749–1755. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19980501)82
Lunsford LD, Coffey RJ, Cojocaru T, Leksell D (1990) Image-guided stereotactic surgery: a 10-year evolutionary experience. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 54–55:375–387
Greene GM, Hitchon PW, Schelper RL, Yuh W, Dyste GN (1989) Diagnostic yield in CT-guided stereotactic biopsy of gliomas. J Neurosurg 71(4):494–497. doi:10.3171/jns.1989.71.4.0494
Gleason CA, Wise BL, Feinstein B (1978) Stereotactic localization (with computerized tomographic scanning), biopsy, and radiofrequency treatment of deep brain lesions. Neurosurgery 2(3):217–222
Maroon JC, Bank WO, Drayer BP, Rosenbaum AE (1977) Intracranial biopsy assisted by computerized tomography. J Neurosurg 46(6):740–744. doi:10.3171/jns.1977.46.6.0740
Broggi G, Franzini A, Migliavacca F, Allegranza A (1983) Stereotactic biopsy of deep brain tumors in infancy and childhood. Childs Brain 10(2):92–98
Colombo F, Casentini L, Zanusso M, Danieli D, Benedetti A (1988) Validity of stereotactic biopsy as a diagnostic tool. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 42:152–156
Kreth FW, Muacevic A, Medele R, Bise K, Meyer T, Reulen HJ (2001) The risk of haemorrhage after image guided stereotactic biopsy of intra-axial brain tumours—a prospective study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 143(6):539–545, discussion 545–536
Lee T, Kenny BG, Hitchock ER, Teddy PJ, Palividas H, Harkness W, Meyer CH (1991) Supratentorial masses: stereotactic or freehand biopsy? Br J Neurosurg 5(4):331–338
St George EJ, Walsh AR, Sgouros S (2004) Stereotactic biopsy of brain tumours in the paediatric population. Childs Nerv Syst 20(3):163–167. doi:10.1007/s00381-003-0897-8
Voges J, Schroder R, Treuer H, Pastyr O, Schlegel W, Lorenz WJ, Sturm V (1993) CT-guided and computer assisted stereotactic biopsy. Technique, results, indications. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 125(1–4):142–149
Wen DY, Hall WA, Miller DA, Seljeskog EL, Maxwell RE (1993) Targeted brain biopsy: a comparison of freehand computed tomography-guided and stereotactic techniques. Neurosurgery 32(3):407–412, discussion 412–403
Yu X, Liu Z, Tian Z, Li S, Huang H, Xiu B, Zhao Q, Liu L, Jing W (2000) Stereotactic biopsy for intracranial space-occupying lesions: clinical analysis of 550 cases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 75(2–3):103–108
Apuzzo ML, Chandrasoma PT, Cohen D, Zee CS, Zelman V (1987) Computed imaging stereotaxy: experience and perspective related to 500 procedures applied to brain masses. Neurosurgery 20(6):930–937
Kelly PJ (1986) Computer-assisted stereotaxis: new approaches for the management of intracranial intra-axial tumors. Neurology 36(4):535–541
Kelly PJ, Ft E, Kall BA, Goerss SJ, Scheithauer B (1985) Surgical options for patients with deep-seated brain tumors: computer-assisted stereotactic biopsy. Mayo Clin Proc 60(4):223–229
Sawin PD, Hitchon PW, Follett KA, Torner JC (1998) Computed imaging-assisted stereotactic brain biopsy: a risk analysis of 225 consecutive cases. Surg Neurol 49(6):640–649
Thomas DG, Nouby RM (1989) Experience in 300 cases of CT-directed stereotactic surgery for lesion biopsy and aspiration of haematoma. Br J Neurosurg 3(3):321–325
Cartmill M, Punt J (1999) Diffuse brain stem glioma. A review of stereotactic biopsies. Childs Nerv Syst 15(5):235–237, discussion 238
Chico-Ponce de Leon F, Perezpena-Diazconti M, Castro-Sierra E, Guerrero-Jazo FJ, Gordillo-Dominguez LF, Gutierrez-Guerra R, Salamanca T, Sosa-Sainz G, Santana-Montero BL, DeMontesinos-Sampedro A (2003) Stereotactically-guided biopsies of brainstem tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 19(5–6):305–310. doi:10.1007/s00381-003-0737-x
Perez-Gomez JL, Rodriguez-Alvarez CA, Marhx-Bracho A, Rueda-Franco F (2010) Stereotactic biopsy for brainstem tumors in pediatric patients. Childs Nerv Syst 26(1):29–34. doi:10.1007/s00381-009-1000-x
Pincus DW, Richter EO, Yachnis AT, Bennett J, Bhatti MT, Smith A (2006) Brainstem stereotactic biopsy sampling in children. J Neurosurg 104(2 Suppl):108–114. doi:10.3171/ped.2006.104.2.108
Roujeau T, Machado G, Garnett MR, Miquel C, Puget S, Geoerger B, Grill J, Boddaert N, Di Rocco F, Zerah M, Sainte-Rose C (2007) Stereotactic biopsy of diffuse pontine lesions in children. J Neurosurg 107(1 Suppl):1–4. doi:10.3171/PED-07/07/001
Valdes-Gorcia J, Espinoza-Diaz DM, Paredes-Diaz E (1998) Stereotactic biopsy of brain stem and posterior fossa lesions in children. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140(9):899–903
Choux MDRC, Hockley AD, Walker ML (1999) Pediatric neurosurgery. Brainstem tumors, 1st edn. Churchill Livingstone, London
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meshkini, A., Shahzadi, S., Zali, A. et al. Computed tomography-guided stereotactic biopsy of intracranial lesions in pediatric patients. Childs Nerv Syst 27, 2145–2148 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1534-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1534-6