Abstract
Purpose
Salmonella intracranial infections, including subdural empyema and brain abscess, are rare clinical manifestations in children. The aim of this study is to investigate the clinical course of Salmonella subdural empyema in infants and children.
Methods
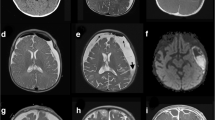
We report a 9-month-old female infant diagnosed as Salmonella subdural empyema with clinical features of prolonged fever for more than 2 months and episodic focal seizures. Literature published between 1986 and 2010 relevant to Salmonella subdural empyema in children were reviewed. The clinical presentations and laboratory findings were analyzed.
Results
Seventeen cases with Salmonella subdural empyema, including our index case, has been reported with detailed clinical presentation. Fever (17/17; 100%), symptoms and signs of increased intracranial pressure (8/17; 47%), seizures (8/17; 47%), and limb paralysis (8/17; 47%) were the most frequent clinical features. Among these cases, unknown causative organism prior to surgery (11/17; 65%) and prolonged fever for more than 3 weeks (5/17; 29%) were also noticed. Sixteen out of 17 patients (94%) required surgical intervention for treatment. The morbidity rate and mortality rate were 29% (5/17) and 6% (1/17), respectively.
Conclusion
Subdural empyema is considered to be a disease with rapid progression. However, the cases caused by Salmonella species may present a slow disease course. Surgical intervention is sometimes the only way to detect the pathogen.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bockova J, Rigamonti D (2000) Intracranial empyema. Pediatr Infect Dis J 19(8):735–737
Osborn MK, Steinberg JP (2007) Subdural empyema and other suppurative complications of paranasal sinusitis. Lancet Infect Dis 7(1):62–67
Darby J, Sheorey H (2008) Searching for Salmonella. Aust Fam Physician 37(10):806–810
Hohmann EL (2001) Nontyphoidal salmonellosis. Clin Infect Dis 32(2):263–269
Drevets DA, Leenen PJM, Greenfield RA (2004) Invasion of the central nervous system by intracellular bacteria. Clin Microbiol Rev 17(2):323–347
Rodriguez RE, Valero V, Watanakunakorn C (1986) Salmonella focal intracranial infections: review of the world literature (1884–1984) and report of an unusual case. Rev Infect Dis 8(1):31–41
Mahapatra AK, Pawar SJ, Sharma RR (2002) Intracranial Salmonella infections: meningitis, subdural collections and brain abscess a series of six surgically managed cases with follow-up results. Pediatr Neurosurg 36(1):8–13
Yen MH, Huang YC, Chou ML (1999) Non-typhoid Salmonella subdural empyema in children: report of two cases. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 32(4):289–291
Jain KC, Mahapatra AK (1998) Subdural empyema due to salmonella infection. Pediatr Neurosurg 28(2):89–90
Mahapatra AK, Bhatia R (1987) Salmonella intracerebral and subdural abscess—report of two cases. Postgrad Med J 63(739):373–375
Intan HI, Zubaidah CD, Norazah A, Norlijah O (2008) Subdural collections due to non-typhi Salmonella infections in two Malaysian children. Singapore Med J 49(7):e186–e189
Dunn DW, McAllister J, Craft JC (1984) Brain abscess and empyema caused by Salmonella. Pediatr Infect Dis 3(1):54–57
Okudera H, Toba Y, Kyoshima K (1989) Bilateral subdural empyema due to Salmonella enteritidis in an infant. Childs Nerv Syst 5(1):45–46
Le Roux PC, Wood M, Campbell RAJ (2007) Subdural empyema caused by an unusual organism following intracranial haematoma. Childs Nerv Syst 23(7):825–827
Hou JW, Teng RJ, Lee CY (1989) Salmonella meningitis complicated with subdural empyema, brain abscess and purpura fulminans: report of one case. Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi 30(6):408–413
Alvarez Sastre C, Villarejo F, Lopez Robledillo JC, Martin-Gamero AP, Perez Diaz C (2002) Subdural empyema with extension to vertebral canal secondary to salmonellosis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Childs Nerv Syst 18(9–10):528–531
Ghais A, Armano R, Menten R, Mathot M, Zech F, Nassogne MC (2009) Meningitis with subdural empyema due to non-typhoid Salmonella in a 9-month-old girl. Eur J Pediatr 168(12):1537–1540
Tabarani CM, Bennett NJ, Kiska DL, Riddell SW, Botash AS, Domachowske JB (2010) Empyema of preexisting subdural hemorrhage caused by a rare salmonella species after exposure to bearded dragons in a foster home. J Pediatr 156:322–323
Wu T-J, Chiu N-C, Huang F-Y (2008) Subdural empyema in children–20-year experience in a medical center. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 41(1):62–67
Sirinavin S, Chiemchanya S, Vorachit M (2001) Systemic nontyphoidal Salmonella infection in normal infants in Thailand. Pediatr Infect Dis J 20(6):581–587
Lee WS, Puthucheary SD, Omar A (1999) Salmonella meningitis and its complications in infants. J Paediatr Child Health 35(4):379–382
Farmer TW, Wise GR (1973) Subdural empyema in infants, children and adults. Neurology 23(3):254–261
Yilmaz N, Kiymaz N, Yilmaz C, Bay A, Yuca SA, Mumcu C et al (2006) Surgical treatment outcome of subdural empyema: a clinical study. Pediatr Neurosurg 42(5):293–298
Banerjee AD, Pandey P, Devi BI, Sampath S, Chandramouli BA (2009) Pediatric supratentorial subdural empyemas: a retrospective analysis of 65 cases. Pediatr Neurosurg 45(1):11–18
Feuerman T, Wackym PA, Gade GF, Dubrow T (1989) Craniotomy improves outcome in subdural empyema. Surg Neurol 32(2):105–110
Dill SR, Cobbs CG, McDonald CK (1995) Subdural empyema: analysis of 32 cases and review. Clin Infect Dis 20(2):372–386
Osman Farah J, Kandasamy J, May P, Buxton N, Mallucci C (2009) Subdural empyema secondary to sinus infection in children. Childs Nerv Syst 25(2):199–205
American Academy of Pediatrics, Subcommittee on Management of S, Committee on Quality I (2001) Clinical practice guideline: management of sinusitis. Pediatrics 108(3):798–808
Hanel RA, Araujo JC, Antoniuk A, da Silva Ditzel LF, Flenik Martins LT, Linhares MN (2000) Multiple brain abscesses caused by Salmonella typhi: case report. Surg Neurol 53(1):86–90
Pasic S, Minic A, Djuric P, Micic D, Kuzmanovic M, Sarjanovic L et al (2006) Fever of unknown origin in 185 paediatric patients: a single-centre experience. Acta Paediatr 95(4):463–466
Chantada G, Casak S, Plata JD, Pociecha J, Bologna R (1994) Children with fever of unknown origin in Argentina: an analysis of 113 cases. Pediatr Infect Dis J 13(4):260–263
Salcedo SP, Noursadeghi M, Cohen J, Holden DW (2001) Intracellular replication of Salmonella typhimurium strains in specific subsets of splenic macrophages in vivo. Cell Microbiol 3(9):587–597
Richter-Dahlfors A, Buchan AM, Finlay BB (1997) Murine salmonellosis studied by confocal microscopy: Salmonella typhimurium resides intracellularly inside macrophages and exerts a cytotoxic effect on phagocytes in vivo. J Exp Med 186(4):569–580
Alpuche-Aranda CM, Racoosin EL, Swanson JA, Miller SI (1994) Salmonella stimulate macrophage macropinocytosis and persist within spacious phagosomes. J Exp Med 179(2):601–608
Karim M, Islam N (2002) Salmonella meningitis: report of three cases in adults and literature review. Infection 30(2):104–108
Bok AP, Peter JC (1993) Subdural empyema: burr holes or craniotomy? A retrospective computerized tomography-era analysis of treatment in 90 cases. J Neurosurg 78(4):574–578
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, KM., Lee, HF., Chi, CS. et al. Obscure manifestations of Salmonella subdural empyema in children: case report and literature review. Childs Nerv Syst 27, 591–595 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1274-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1274-z