Abstract
Background and purpose
Based on the time until treatment failure, we retrospectively analyzed 389 children to compare the long-term effectiveness of first-line antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) in children with generalized onset or unclassified epileptic seizures.
Methods
Analyses were based on time until treatment failure and time until remission.
Results
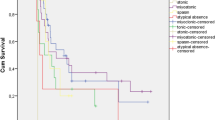
In terms of time until treatment failure, the failure rates of topiramate and carbamazepine were higher than that of sodium valproate (p < 0.05). For time until 1-year remission, sodium valproate was found to be significantly better than either topiramate or carbamazepine (p < 0.05). For the subgroup with generalized onset epilepsy, sodium valproate was much better than either topiramate or carbamazepine (p < 0.05). No significant differences were found between topiramate and carbamazepine (p = 0.319). For unclassified epileptic seizures, no significant differences were found among the three AEDs.
Conclusion
Sodium valproate should be the drug of choice for patients with children with generalized onset, and no significant differences were found among the three AEDs in unclassified epileptic seizures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkovic SF (2005) Treatment with anti-epileptic drugs. Aust Fam Physician 34:1017–1020
Bondareva IB, Jelliffe RW, Gusev EI, Guekht AB, Melikyan EG, Belousov YB (2006) Population pharmacokinetic modelling of carbamazepine in epileptic elderly patients: implications for dosage. J Clin Pharm Ther 31:211–221
Coppola G, Capovilla G, Montagnini A, Romeo A, Spano M, Tortorella G, Veggiotti P, Viri M, Pascotto A (2002) Topiramate as add-on drug in severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy: an Italian multicenter open trial. Epilepsy Res 49:45–48
French JA, Kanner AM, Bautista J, Abou-Khalil B, Browne T, Harden CL, Theodore WH, Bazil C, Stern J, Schachter SC, Bergen D, Hirtz D, Montouris GD, Nespeca M, Gidal B, Marks WJ Jr, Turk WR, Fischer JH, Bourgeois B, Wilner A, Faught RE Jr, Sachdeo RC, Beydoun A, Glauser TA (2004) Efficacy and tolerability of the new antiepileptic drugs I: treatment of new onset epilepsy: report of the therapeutics and technology assessment subcommittee and quality standards subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Epilepsy Society. Neurology 62:1252–1260
Gerstner T, Bauer MO, Longin E, Bell N, Koenig SA (2007) Reversible hepatotoxicity, pancreatitis, coagulation disorder and simultaneous bone marrow suppression with valproate in a 2-year-old girl. Seizure 16:554–556
Gilliam FG, Santos JM (2006) Adverse psychiatric effects of antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsy Res 68:67–69
Grosso S, Galimberti D, Farnetani MA, Cioni M, Mostardini R, Vivarelli R, Di Bartolo RM, Bernardoni E, Berardi R, Morgese G, Balestri P (2005) Efficacy and safety of topiramate in infants according to epilepsy syndromes. Seizure 14:183–189
Hanssens Y, Al-Asmi A, Al-Busaidi I, Deleu D (2006) Efficacy and tolerability of antiepileptic drugs in an Omani epileptic population. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 108:532–538
Iinuma K, Morimoto K, Akiyama T, Ikeda A, Kurihara M (2006) Proposed diagnostic scheme for the classification of epileptic seizures and epilepsies (ILAE, 2001): proposal from Japan Epilepsy Society. Epilepsia 47:1588–1589, discussion 1590–1581
Klein KM, Hamer HM, Reis J, Schmidtke J, Oertel WH, Theisen FM, Hebebrand J, Rosenow F (2005) Weight change in monozygotic twins treated with valproate. Obes Res 13:1330–1334
Koenig SA, Buesing D, Longin E, Oehring R, Haussermann P, Kluger G, Lindmayer F, Hanusch R, Degen I, Kuhn H, Samii K, Jungck A, Bruckner R, Seitz R, Boxtermann W, Weber Y, Knapp R, Richard HH, Weidner B, Kasper JM, Haensch CA, Fitzek S, Hartmann M, Borusiak P, Muller-Deile A, Degenhardt V, Korenke GC, Hoppen T, Specht U, Gerstner T (2006) Valproic acid-induced hepatopathy: nine new fatalities in Germany from 1994 to 2003. Epilepsia 47:2027–2031
Kwan P, Brodie MJ (2000) Early identification of refractory epilepsy. N Engl J Med 342:314–319
Kwan P, Brodie MJ (2001) Effectiveness of first antiepileptic drug. Epilepsia 42:1255–1260
Lloyd A, McIntosh E, Price M (2005) The importance of drug adverse effects compared with seizure control for people with epilepsy: a discrete choice experiment. Pharmacoeconomics 23:1167–1181
Lossius MI, Clench-Aas J, van Roy B, Mowinckel P, Gjerstad L (2006) Psychiatric symptoms in adolescents with epilepsy in junior high school in Norway: a population survey. Epilepsy Behav 9:286–292
Lyseng-Williamson KA, Yang LP (2007) Topiramate: a review of its use in the treatment of epilepsy. Drugs 67:2231–2256
Marson AG, Al-Kharusi AM, Alwaidh M, Appleton R, Baker GA, Chadwick DW, Cramp C, Cockerell OC, Cooper PN, Doughty J, Eaton B, Gamble C, Goulding PJ, Howell SJ, Hughes A, Jackson M, Jacoby A, Kellett M, Lawson GR, Leach JP, Nicolaides P, Roberts R, Shackley P, Shen J, Smith DF, Smith PE, Smith CT, Vanoli A, Williamson PR (2007) The SANAD study of effectiveness of valproate, lamotrigine, or topiramate for generalised and unclassifiable epilepsy: an unblinded randomised controlled trial. Lancet 369:1016–1026
McVicar KA, Ballaban-Gil K, Rapin I, Moshe SL, Shinnar S (2005) Epileptiform EEG abnormalities in children with language regression. Neurology 65:129–131
Neligan A, Shorvon SD (2009) The history of status epilepticus and its treatment. Epilepsia 50(Suppl 3):56–68
Schiller Y, Najjar Y (2008) Quantifying the response to antiepileptic drugs: effect of past treatment history. Neurology 70:54–65
Trojnar MK, Wierzchowska-Cioch E, Krzyzanowski M, Jargiello M, Czuczwar SJ (2004) New generation of valproic acid. Pol J Pharmacol 56:283–288
Tuchman R, Rapin I (2002) Epilepsy in autism. Lancet Neurol 1:352–358
Tudur Smith C, Marson AG, Chadwick DW, Williamson PR (2007) Multiple treatment comparisons in epilepsy monotherapy trials. Trials 8:34
Velez A, Eslava-Cobos J (2006) Epilepsy in Colombia: epidemiologic profile and classification of epileptic seizures and syndromes. Epilepsia 47:193–201
Wilby J, Kainth A, Hawkins N, Epstein D, McIntosh H, McDaid C, Mason A, Golder S, O'Meara S, Sculpher M, Drummond M, Forbes C (2005) Clinical effectiveness, tolerability and cost-effectiveness of newer drugs for epilepsy in adults: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 9:1–157, iii–iv
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the patients who participated in this study. This research was supported by grant nos. 30770747 and 30801249 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the grant nos. 7042024 and 7081002 from the National Natural Science Foundation of Beijing, and grant no. 2003–2037 from the Capital Development Foundation of Beijing and Hygiene Industry-specific Research Projects of China (No. 200802074). The sponsors of the research had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, YX., Zou, LP., Ma, MS. et al. Retrospective analysis of the effectiveness of first-line antiepileptic drugs for generalized onset and unclassified epileptic seizures in Chinese children. Childs Nerv Syst 27, 279–284 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1255-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1255-2