Abstract
Purpose
Certain cytokines play important roles in the pathophysiology of meningitis. The main purpose of this study was to investigate if the levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-12 (IL-12) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) could be diagnostic predictors of bacterial meningitis in children.
Methods
CSF was obtained from 95 patients suspected with meningitis. These cases were classified to the bacterial meningitis (n = 12), aseptic meningitis (n = 41), and nonmeningitis (n = 42) groups. The levels of IL-6 and IL-12 in CSF were measured using the enzyme-linked immmunosorbent assays test.
Results
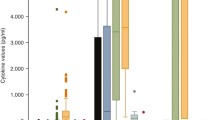
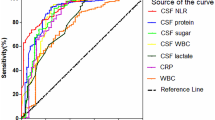
The CSF IL-6 levels in the bacterial meningitis group (45.2 ± 50.0 pg/ml) were significantly higher than those in the aseptic meningitis group (12.9 ± 10.2 pg/ml) and the nonmeningitis group (6.5 ± 7.8 pg/ml; p < 0.05). The CSF IL-12 levels in the bacterial meningitis group (69.8 ± 67.1 pg/ml) were significantly higher than those in the aseptic meningitis group (22.9 ± 10.8 pg/ml) and the nonmeningitis group (15.3 ± 11.2 pg/ml; p < 0.05). With regard to diagnosis, the measurement of CSF IL-6 and IL-12 levels showed sensitivities of 96% and 96%, respectively, and specificities of 51% and 75%, respectively.
Conclusion
It is suggested that the CSF IL-6 and IL-12 levels are useful markers for distinguishing bacterial meningitis from aseptic meningitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kilpi T, Anttila M, Kallio MJ, Peltola H (1991) Severity of childhood bacterial meningitis and duration of illness before diagnosis. Lancet 338:406–409
McCracken GH, Mustafa MM, Ramilo O, Olsen KD, Risser RC (1989) Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin 1-beta and tumor necrosis factor concentrations and outcome from neonatal gram-negative enteric bacillary meningitis. Pediatr Infect Dis 8:155–159
Buke C, Bundschu J, Gallati H, Bartmann P, Pohlandt F (1994) Interleukin-6: a sensitive parameter for the early diagnosis of neonatal bacterial infection. Pediatrics 93:54–58
Okusawa S, Gelfand JA, Ikejima T (1988) Interleukin-1 induces a shock-like state in rabbits: synergism with tumor necorsis factor and the effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitiors. J Clin Invest 81:1162–1172
Harris MC, Costarino AT Jr, Sullivan JS, Dulkerian S, McCawley L, Corcoran L, Butler S, Kilpatrick L (1994) Cytokine elevations in critically ill infants with sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 124:105–111
Helminen M, Vesikari T (1987) Spontaneous and inducible interleukin 1 production from peripheral blood monocytes in bacterial and viral infections in children. Pediatr Infect Dis 6:1102–1106
Waage A, Espevik T (1988) Interleukin-1 potentiates the lethal effect of tumor necrosis factor α/cachectin in mice. J Exp Med 167:1987–1992
Chonmaitree T, Baron S (1991) Bacteria and viruses induce production of interferon in the cerebrospinal fluid of children with acute meningitis: a study of 57 cases and review. Rev Infect Dis 13:106–115
Mastroianni CM, Paoletti F, Rivosecchi RM, Lancella L, Ticca F, Vullo V, Delia S (1994) Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-8 in children with purulent bacterial and tuberculous meningitis. Pediatr Infect Dis 13:1008–1010
Mustafa MM, Lebel MH, Ramilo O, Olsen KD, Reisch JS, Beutler B, McCracken GH Jr (1989) Correlation of interleukin-1β and cachectin concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid and outcome from bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr 15:208–213
Nadal D, leppert D, Frei K, Gallo P, Lamche H, Fontana A (1989) Tumour necrosis factor-α in infectious meningitis. Arch Dis Child 64:1274–1279
Tsai ML, Chen WC, Wang YC, Hung KL (1996) Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-6, interleukin-8 and tumor necrosis factor-α in children with central nervous infections. Acta Ped Sin 37:16–21
Tang RB, Lee BH, Chung RL, Chen SJ, Wong TT (2001) Interelukin 1β and tumor necrosis factor-α in cerebrospinal fluid of children with bacterial meningitis. Childs Nerv Syst 17:453–456
Kishimoto T (1989) The biology of interleukin-6. Blood 74:1–10
Saladino R, Erikson M, Levy N, Bachman D, Siber GR, Fleisher GR (1992) Utility of serum interleukin-6 for diagnosis of invasive bacterial disease in children. Ann Emerg Med 21:1413–1417
Rusconi F, Parizzi F, Garlaschi L, Assael BM, Sironi M, Ghezzi P, Mantovani A (1991) Interleukin 6 activity in infants and children with bacterial meningitis. Pediatr Infect Dis 10:117–121
Torre D, Zeroli C, Ferraro G, Speranza F, Tambini R, Martegani R, Fiori GP (1992) Cerebrospinal fluid levels of IL-6 in patients with acute infections of the central nervous system. Scand J Infect Dis 24:787–791
Gendrel D, Raymond J, Coste J, Moulin F, Lorrot M, Guerin S, Ravilly S, Lefevre H, Royer C, Lacombe C, Palmer P, Bohuon C (1999) Comparison of procalcitonin with C-reactive protein, interleukin 6 and interferon-alpha for differentiation of bacterial vs. viral infections. Pediatr Infect Dis 18:875–881
Sheldon J, Riches P, Gooding R, Soni N, Hobbs JR (1993) C-reactive protein and its cytokine mediators in intensive-care patients. Clin Chem 39:147–50
Stearman M, Southgate HJ (1994) The use of cytokine and C-reactive protein measurements in cerebrospinal fluid during acute infective meningitis. Ann Clin Biochem 31:255–261
Tatara R, Imai H (2000) Serum C-reactive protein in the differential diagnosis of childhood meningitis. Pediatr Int 42:541–546
Hashim IA, Walsh A, Hart A, Hart CA, Shenkin A (1995) Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-6 and its diagnostic value in the investigation of meningitis. Ann Clin Biochem 32:289–296
Kanoh Y, Ohtani H (1997) Levels of interleukin-6, CRP and alpha 2 macroglobulin in cerebrospinal fluid and serum as indicator of blood-CSF barrier damage. Biochem Mol Biol Int 43:269–278
Kornelisse RF, Hack CE, Savelkoul HF, van der Pouw Kraan TC, Hop WC, van Mierlo G, Suur MH, Neijens HJ, de Groot R (1997) Intrathecal production of interleukin-12 and gamma interferon in patients with bacterial meningitis. Infect Immun 65:877–881
Tauber MG, Moser B (1999) Cytokines and chemokines in meningeal inflammation: biology and clinical implications. Clin Infect Dis 28:1–12
Tang RB, Chen SJ, Wu KK, Lee BH, Chen PY (1997) Interferon γ in cerebrospinal fluid of children with aseptic meningitis. J Chin Med Assoc 59:248–253
Azuma H, Tsuda N, Sasaki K, Okuno A (1997) Clinical significance of cytokine measurement for detection of meningitis. J Pediatr 131:463–465
Sundgren-Andersson AK, Ostlund P, Bartfai T (1998) IL-6 is essential in TNF-alpha-induced fever. Am J Physiol 275:2028–2034
Dulkerian SJ, Kilpatrick L, Costarino AT Jr, McCawley L, Fein J, Corcoran L, Zirin S, Harris MC (1995) Cytokine elevations in infants with bacterial and aseptic meningitis. J Pediatr 126:872–876
Chavanet P, Bonnotte B, Guiguet M, Zeller V, Solary E, Maurice L, Casasnovas O, Caillot D, Waldner A, Kisterman JP et al (1992) High concentrations of intrathecal interleukin-6 in human bacterial and nonbacterial meningitis. J Infect Dis 166:428–431
López-Cortés LF, Marquez-Arbizu R, Jimenez-Jimenez LM, Jimenez-Mejías E, Caballero-Granado FJ, Rey-Romero C, Polaina M, Pachón J (2000) Cerebrospinal fluid tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and interleukin-8 as diagnostic markers of cerebrospinal fluid infection in neurosurgical patients. Crit Care Med 28:215–219
Rea IM, McNerlan SE, Alexander HD (2000) Total serum IL-12 and IL-12p40, but not IL-12p70, are increased in the serum of older subjects; relationship to CD3(+) and NK subsets. Cytokine 12:156–159
Stahel PF, Kossmann T, Joller H, Trentz O, Morganti-Kossmann MC (1998) Increased interleukin-12 levels in human cerebrospinal fluid following severe head trauma. Neurosci Lett 249:123–126
Mastroianni CM, Paoletti F, Lichtner M, D'Agostino C, Vullo V, Delia S (1997) Cerebrospinal fluid cytokines in patients with tuberculous meningitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 84:171–176
Turrin NP, Rivest S (2004) Innate immune reaction in response to seizures: implications for the neuropathology associated with epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 16:321–334
Hazelzet JA, Kornelisse RF, van der Pouw Kraan TC, Joosten KF, van der Voort E, van Mierlo G, Suur MH, Hop WC, de Groot R, Hack CE (1997) Interleukin 12 levels during the initial phase of septic shock with purpura in children: relation to severity of disease. Cytokine 9:711–716
Bidarkundi GK, Wig JD, Bhatnagar A, Majumdar S (2002) Clinical relevance of intracellular cytokines IL-6 and IL-12 in acute pancreatitis, and correlation with APACHE III score. Brit J Biomed Sci 59:85–89
Leal IS, Smedegard B, Andersen P, Appelberg R (1999) Interleukin-6 and interleukin-12 participate in induction of a type 1 protective T-cell response during vaccination with a tuberculosis subunit vaccine. Infect Immun 67:5747–5754
Acknowledgment
The study was supported by grants from the Taipei Veterans General Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsieh, CC., Lu, JH., Chen, SJ. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-12 in children with meningitis. Childs Nerv Syst 25, 461–465 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0715-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0715-4