Abstract
Case report
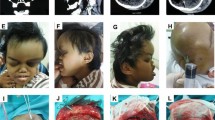
A subgaleal hematoma (SGH) occurred in a young patient with Sturge–Weber syndrome (SWS) who was treated with aspirin after a mild head trauma.
Materials and methods
A 4-year-old child with SWS, who was chronically treated with aspirin at an antiplatelet dosage of 3 mg/kg per day, presented with extensive SGH and significant anemia after a mild head trauma.
Results and conclusion
It is conceivable that the minor head trauma and chronic use of aspirin caused the SGH. Based on this event, the chronic use of aspirin in young patients with SWS, as suggested to prevent stroke-like episodes, is disputable.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anton J, Pineda V, Martin C, Artigas J, Rivera J (1999) Posttraumatic subgaleal hematoma: a case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Emerg Care 15:347–349
Cooling D, Viccellio P (1991) Massive subgaleal hematoma following minor head trauma. J Emerg Med 9(suppl 1):33–35
Fujisawa H, Yonaha H, Oka Y, Uehara M, Nagata Y, Kajiwara K, Fiji M, Kato S, Akimura T, Suzuki M (2005) A marked exophthalmos and corneal ulceration caused by delayed massive expansion of a subgaleal hematoma. Childs Nerv Syst 21:489–492
Guirgis MF, Segal WA, Lueder GT (2002) Subperiosteal orbital hemorrhage as initial manifestation of Christmas disease (factor IX deficiency). Am J Ophthalmol 133:584–585
Israels SJ, Michelson AD (2006) Antiplatelet therapy in children. Thromb Res 118:75–83
Kirkpatrick JS, Gower DJ, Chauvenet A, Kelly D (1986) Subgaleal hematoma in a child, without skull fracture. Dev Med Child Neurol 28:511–514
Kuban K, Winston K, Bresnan M (1983) Childhood subgaleal hematoma following minor head. Am J Dis Child 137:637–640
Maria BL, Neufeld JA, Rosainz LC, Drane WE, Quisling RG, Ben-David K, Hamed LM (1998) Central nervous system structure and function in Sturge–Weber syndrome: evidence of neurologic and radiologic progression. J Child Neurol 13:606–618
Raffini L, Tsarouhas N (2004) Subgaleal hematoma from hair braiding leads to the diagnosis of von Willebrand disease. Pediatr Emerg Care 20:316–318
Seifer D, Puschel K (2006) Subgaleal hematoma in child abuse. Forensic Sci Int 157:131–133
Thomas-Sohl KA, Vaslow DF, Maria BL (2004) Sturge–Weber syndrome: a review. Pediatr Neurol 30:303–310
Udani V, Pujar S, Munot P, Maheshwari S, Mehta N (2007) Natural history and magnetic resonance imaging follow-up in 9 Sturge–Weber Syndrome patients and clinical correlation. J Child Neurol 22:479–483
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greco, F., Fiumara, A., Sorge, G. et al. Subgaleal hematoma in a child with Sturge–Weber syndrome: to prevent stroke-like episodes, is treatment with aspirin advisable?. Childs Nerv Syst 24, 1479–1481 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0662-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0662-0