Abstract
Objectives
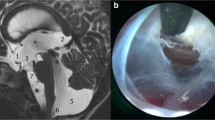
The aims of this study were to describe and analyze the technique of neuroendoscopic foraminal plasty of foramen of Monro (NEFPFMO) in the treatment of isolated unilateral hydrocephalus (IUH) due to membranous occlusion, to evaluate its efficacy and safety, and to define the benefits of neuronavigational guidance of the procedure.
Materials and methods
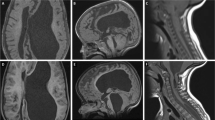
Two symptomatic neonates with IUH, as a result of congenital atresia of foramen of Monro, underwent NEFPFMO plus neuroendoscopic septostomy in the first case and neuronavigational guidance in the second one.
Clinical results were excellent in both neonates. The postoperative ventricular size decreased and the progressive IUH changed to the state of arrested hydrocephalus. The neuronavigation was precise.
Conclusion
NEFPFMO should be the primary treatment option in patients with IUH due to membranous occlusion of foramen of Monro. It reestablishes natural anatomical communication and provides real physiological cerebrospinal fluid flow. Neuronavigation is a useful adjunct of NEFPFMO.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldana PR, Kestle JRW, Brockmeyer, Walker ML (2003) Results of endoscopic septal fenestration in the treatment of isolated ventricular hydrocephalus. Pediatr Neurosurg 38:286–294
Broggi G, Dones I, Ferroli P, Franzini A, Servello D, Duca S (2000) Image-guided neuroendoscopy for third ventriculostomy. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:893–899
Cochrane D, Kestle J, Steinbok P, Evans D, Heron N (1995) Model for the cost analysis of shunted hydrocephalic children. Pediatr Neurosurg 23:14–19
Di Rocco C, Marchese E, Velardi F (1994) A survey of the first complication of newly implanted CSF shunt devices for the treatment of nontumoral hydrocephalus. Cooperative survey of the 1991–1992 Education Committee of the ISPN. Childs Nerv Syst 10:321–327
Drake JM, Prudencio J, Holowaka S, Rutka JT, Hoffman HJ, Humphreys RP (1994) Frameless stereotaxy in children. Pediatr Neurosurg 20:152–159
Drake J, Sainte-Rose C (1995) The Shunt book. Blackwell Science, Cambridge, pp 123–192
Enchev Y, Bozinov O, Miller D, Tirakotai W, Heinze S, Benes L, Bertalanffy, Sure U (2006) Image-guided ultrasonography for recurrent cystic gliomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 14(10):1053–1063
Freudenstein D, Duffner F, Krapf H, Wagner A, Grote E (2002) Neuroendoscopic treatment of idiopathic occlusion of the foramen of Monro in adults. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 42:81–85
Ganslandt O, Behari S, Gralla J, Fahlbusch R, Nimsky C (2002) Neuronavigation: concept, techniques and applications. Neurol India 50:244–255
Grunert P, Hopf N, Perneczky A (1997) Frame-based and frameless endoscopic procedures in the ventricle. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 68:80–89
Gumprecht HK, Widenka DC, Lumenta CB (1999) BrainLab VectorVision neuronavigation system: technology and clinical experiences in 131 cases. Neurosurgery 44:97–105
Hamada H, Hayashi N, Kurimoto M, Umemura K, Hirashima Y, Endo S (2003) Neuroendoscopic septostomy for isolated lateral ventricle. Neurol Med Chir 43:582–588
Javier-Fernandez J, Garcia-Cosamalon PJ, Vinuela J, Ibanez FJ, Mostaza A, Heres S, Ortega F (2001) Endoscopic fenestration as a treatment for asymmetrical hydrocephalus due to obstruction of the foramen of Monro. Neurocirugia (Astur) 12:513–515 (Span)
Kumar R (1999) Unilateral hydrocephalus in paediatric patients, a trial of endoscopic fenestration. Neurol India 47:282–285
Mampalam TJ, Harsh GR 4th, Tien RD, Dillon WP, Wilson CB (1991) Unilateral hydrocephalus in adults. Surg Neurol 35:14–19
Mohanty A, Das BS, Sastry-Kolluri VR, Hedge T (1996) Neuro-endoscopic fenestration of occluded foramen of Monro causing unilateral hydrocephalus. Pediatr Neurosurg 25:248–251
Nonaka Y, Oi S, Samii A, Paterno V, Feigl GC, Lüdemann W, Samii M (2006) Neuronavigational neuroendoscopic surgery. Frameless free-hand maneuvering of a handy rigid-rod neuroendoscope on visualized three-dimensional computerized image guidance: trajectory to the prepontine cistern in cadaver study. Childs Nerv Syst 22:18–27
Oi S, Matsumoto S (1985) Slit ventricles as a cause of isolated ventricles after shunting. Childs Nerv Syst 1:189–193
Oi S, Matsumoto S (1985) Pathophysiology of nonneoplastic obstruction of the foramen of Monro and progressive unilateral hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 17:891–896
Oi S, Yamada H, Sasaki K, Matsumoto S (1985) Atresia of the foramen of Monro resulting in severe unilateral hydrocephalus with subfalcial herniation and infratentorial diverticulum. Neurosurgery 16:103–106
Oi S (1996) Recent advances in neuroendoscopic surgery: the realistic indication and clinical achievement. Crit Rev Neurosurg 6:64–72
Oi S, Honda Y, Hidaka M, Sato O, Matsumoto S (1998) Intrauterine high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging in fetal hydrocephalus and prenatal estimation of postnatal outcomes with “perspective classification”. J Neurosurg 88:685–694
Oi S, Hidaka M, Honda Y, Togo K, Shinoda M, Shimoda M, Tsugane R, Sato O (1999) Neuroendoscopic surgery for specific forms of hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst 15:56–68
Oi S, Abbott R (2004) Loculated ventricles and isolated compartments in hydrocephalus: their pathophysiology and the efficacy of neuroendoscopic surgery. Neurosurg Clin N Am 15:77–87
Oi S, Samii A, Samii M (2005) Frameless free-hand maneuvering of a small-diameter rigid-rod neuroendoscope with a working channel used during high-resolution imaging. J Neurosurg 102(1):113–118
Piatt J, Carlson C (1993) A search for determinants of cerebrospinal fluid shunt survival: retrospective analysis of a 14-year institutional experience. Pediatr Neurosurg 19:233–242
Rhoten RLP, Luciano MG, Barnett GH (1997) Computer-assisted endoscopy for neurosurgical procedures: technical note. Neurosurgery 40:632–638
Sainte-Rose C, Piatt J, Renier D, Pierre-Kahn A, Hirsch J, Hoffman H, Humphreys R, Hendrick E (1991) Mechanical complications in shunts. Pediatr Neurosurg 17:2–9
Schroeder HW, Wagner W, Tschiltschke W, Gaab M (2001) Frameless neuronavigation in intracranial endoscopic neurosurgery. J Neurosurg 94:72–79
Schroeder HW, Oertel J, Gaab M (2007) Endoscopic treatment of cerebrospinal fluid pathway obstructions. Neurosurgery 60(ONS Suppl 1):44–52
Spennato P, Cinalli G, Ruggiero C, Aliberti F, Trischitta V, Cianciulli E, Maggi G (2007) Neuroendoscopic treatment of multiloculated hydrocephalus in children. J Neurosurg 106(1 Suppl):29–35
Surchev JK, Georgiev KD, Enchev Y, Avramov RS (2002) Ventriculoperitoneal shunts in children—our 14-year experience. Childs Nerv Syst 18:259 (Abstract)
Surchev J, Georgiev K, Enchev Y, Avramov R (2002) Extremely rare complications in cerebrospinal fluid shunt operations. J Neurosurg Sci 46:100–102
Wong TT, Lee LS (2000) Membranous occlusion of the foramen of Monro following ventriculoperitoneal shunt insertion: a role for endoscopic foraminoplsaty. Childs Nerv Syst 16:213–217
Acknowledgment
Dr. Yavor Enchev, Ph.D. is a neurosurgeon in the Department of Neurosurgery, Medical University-Sofia, Bulgaria. During the period of elaboration of the manuscript, he was a holder of “Prof. Oi Neuroendoscopy Fellowship”, supported by “Karl Storz-Japan” Scholarship.
Disclosure
The first author was involved in the design of the aforementioned endoscope. He was not involved in the economic exploitation of the instrument.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oi, S., Enchev, Y. Neuroendoscopic foraminal plasty of foramen of Monro. Childs Nerv Syst 24, 933–942 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0627-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0627-3