Abstract
Case report
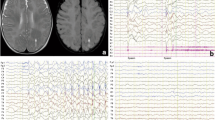
An 11-month-old girl had an onset of oculogyric crisis at 2 months and she presented with epileptic spasms and generalized tonic seizures with series formation at 3 months. Her seizures were medically intractable and her development had gradually regressed after that. MRI showed severe lissencephaly in bilateral hemispheres. Interictal EEG showed hypsarrhythmia periodically and sporadic spike waves in the right hemisphere. The generalized tonic seizures began with bi-frontal polyspikes on EEG. Our diagnosis was lissencephaly presenting with West syndrome and generalized tonic seizures. A total callosotomy was performed at 11 months.
Outcome
Postoperative frequency of seizures decreased prominently and developmental progression was resumed.
Conclusions
This case showed that the corpus callosum may play an important role in some types of symptomatic West syndrome. Corpus callosotomy for treating symptomatic West syndrome should be considered as an option after careful selection and consideration of the timing of surgery.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asarnow RF, LoPresti C, Guthrie D, Elliott T, Cynn V, Shields WD, Shewmon DA, Sankar R, Peacock WJ (1997) Developmental outcomes in children receiving resection surgery for medically intractable infantile spasms. Dev Med Child Neurol 39:430–440
Carmant L, Holmes GL, Lombroso CT (1998) Outcome following corpus callosotomy. J Epilepsy 11:224–228
Cendes F, Ragazzo PC, da Costa V, Martins LF (1993) Corpus callosotomy in treatment of medically resistant epilepsy: preliminary results in a pediatric population. Epilepsia 34:910–917
Chugani HT, Shewmon DA, Shields WD, Sankar R, Comair Y, Vinters HV, Peacock WJ (1993) Surgery for intractable infantile spasms: neuroimaging perspectives. Epilepsia 34:764–771
Enjoji M, Aiya T, Kurikawa T, Nawa A, Nanbu Y, Shinohara S, Harii M (1977) [Analytic developmental schedule for infants] (in Japanese). Keio-Tsushin
Hoffman HJ (2002) Surgery for West’s syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol 497:57–59
Katano H, Nagai H, Aihara N, Yamashita N, Kamiya K, Ishikawa T, Kanayama M (1994) West syndrome associated with porencephaly. Pediatr Neurosurg 21:184–188
Kramer U, Sue WC, Mikati MA (1997) Focal features in West syndrome indicating candidacy for surgery. Pediatr Neurol 16:213–217
Kwan SY, Wong TT, Chang KP, Chi CS, Yang TF, Lee YC, Guo WY, Su MS (2000) Seizure outcome after corpus callosotomy: the Taiwan experience. Childs Nerv Syst 16:87–92
Marchal G, Andermann F, Tampieri D, Robitaille Y, Melanson D, Sinclair B, Olivier A, Silver K, Langevin P (1989) Generalized cortical dysplasia manifested by diffusely thick cerebral cortex. Arch Neurol 46:430–434
Matsuo A, Matsuzaka T, Tsuru A, Moriuchi H, Nakashita Y, Tanaka S, Baba C, Tomimasu K (2001) Epidemiological and clinical studies of West syndrome in Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan. Brain Dev 23:575–579
Matsuzaka T, Baba H, Matsuo A, Tsuru A, Moriuchi H, Tanaka S, Kawasaki C (2001) Developmental assessment-based surgical intervention for intractable epilepsies in infants and young children. Epilepsia 42:6–9
Minguez-Castellanos A, Sanchez-Alvarez JC, Altuzarra A, Serrano-Castro PJ, Hernandez-Ramos EJ, Gomez-Camello A, Garcia-Gomez T (1996) Callosotomy in the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy. Rev Neurol 129:539–548
Ou SF, Chi CS, Shian WJ, Mak SC, Wong TT (1995) Unilateral porencephalic cyst presenting as infantile spasms: a case report. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei) 55:203–208
Pinard JM, Delalande O, Plouin P, Dulac O (1993) Callosotomy in West syndrome suggests a cortical origin of hypsarrhythmia. Epilepsia 34:780–787
Pinard JM, Delalande O, Chiron C, Soufflet C, Plouin P, Kim Y, Dulac O (1999) Callosotomy for epilepsy after West syndrome. Epilepsia 40:1727–1734
Reutens DC, Bye AM, Hopkins IJ, Danks A, Walsh J, Bleasel A, Ouvrier R, MacKenzie RA, Manson JI, Bladin PF, Berkovic SF (1993) Corpus callosotomy for intractable epilepsy: seizure outcome and prognostic factors. Epilepsia 34:904–909
Sorenson JM, Wheless JW, Baumgartner JE, Thomas AB, Brooksire BL, Clifton GL, Willmore LJ (1997) Corpus callosotomy for medically intractable seizures. Pediatr Neurosurg 27:260–267
Spencer SS, Spencer DD, Sass K, Westerveld M, Katz A, Mattson R (1993) Anterior, total, and two-stage corpus callosum section: differential and incremental seizure responses. Epilepsia 34:561–567
Wyllie E, Comair YG, Kotagal P, Raja S, Ruggieri P (1996) Epilepsy surgery in infants. Epilepsia 37:625–637
Yanagaki S, Oguni H, Hayashi K, Imai K, Funatuka M, Tanaka T, Yanagaki M, Osawa M (1999) A comparative study of high-dose and low-dose ACTH therapy for West syndrome. Brain Dev 21:461–467
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamida, T., Maruyama, T., Fujiki, M. et al. Total callosotomy for a case of lissencephaly presenting with West syndrome and generalized seizures. Childs Nerv Syst 21, 1056–1060 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-1081-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-1081-5