Abstract
Background
Arachnoid cysts are a relatively common incidental finding on CT scans of the brain. They most commonly occur in the middle cranial fossa, where familial occurrence has rarely been reported. Posterior fossa arachnoid cysts are more unusual.
Case histories
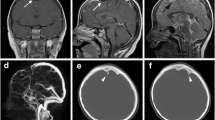
We report the presence of quadrigeminal cistern arachnoid cysts in siblings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen A, Wiegmann TB, MacDougall ML (1986) Arachnoid cyst in a patient with autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis 8:128–130
Go KG, Houthoff HJ, Blaauw EH, Havinga P, Hartsuiker J (1984) Arachnoid cysts of the sylvian fissure. Evidence of fluid secretion. J Neurosurg 60:803–813
Hald JK, Nakstad PH, Skjeldal OH, Stromme P (1991) Bilateral arachnoid cysts of the temporal fossa in four children with glutaric aciduria type I. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 12:407–409
Handa J, Okamoto K, Sato M (1981) Arachnoid cyst of the middle cranial fossa: report of bilateral cysts in siblings. Surg Neurol 16:127–130
Jamjoom ZA, Okamoto E, Jamjoom AH, al-Hajery O, Abu-Melha A (1995) Bilateral arachnoid cysts of the sylvian region in female siblings with glutaric aciduria type I. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 82:1078–1081
Lutcherath V, Waaler PE, Jellum E, Wester K (2000) Children with bilateral temporal arachnoid cysts may have glutaric aciduria type 1 (GAT1); operation without knowing that may be harmful. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:1025–1030
Martinez-Lage JF, Casas C, Fernandez MA, Puche A, Rodriguez Costa T, Poza M (1994) Macrocephaly, dystonia, and bilateral temporal arachnoid cysts: glutaric aciduria type 1. Childs Nerv Syst 10:198–203
Masuno M, Fukushima Y, Sugio Y, Kuroki Y (1987) Partial distal 12q trisomy with arachnoid cyst. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi 32:39–43
Pomeranz S, Constantini S, Lubetzki-Korn I, Amir N (1991) Familial intracranial arachnoid cysts (review). Childs Nerv Syst 7:100–102
Rengachary SS, Watanabe I (1981) Ultrastructure and pathogenesis of intracranial arachnoid cysts. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 40:61–83
Renner C, Razeghi S, Uberall MA, Hartmann P, Lehnert W (1997) Clinically asymptomatic glutaric aciduria type I in a 4 5/12-year-old girl with bilateral temporal arachnoid cysts. J Inherit Metab Dis 20:840–841
Tolmie JL, Day R, Fredericks B, Galea P, Moffett AW (1997) Dominantly inherited cerebral dysplasia: arachnoid cyst associated with mild mental handicap in a mother and her son. J Med Genet 34:1018–1020
Wester K (1999) Peculiarities of intracranial arachnoid cysts: location, sidedness, and sex distribution in 126 consecutive patients. Neurosurgery 45:775–779
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, S., Brown, J.I.M. Familial posterior fossa arachnoid cyst. Childs Nerv Syst 20, 100–103 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-003-0808-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-003-0808-z