Heading
Abstract
Introduction. Subdural empyema is an uncommon but serious complication of sinusitis. Despite the use of advanced imaging facilities, modern antibiotic therapy and aggressive neurosurgical protocols, this condition still carries significant morbidity and mortality.
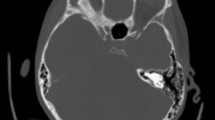
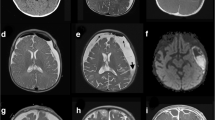
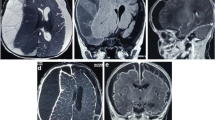
Case report. We report an unusual case of sinusitis-associated acute subdural empyema in a 13-year-old patient, presenting in a catastrophic manner with acutely raised intracranial pressure. Emergency bifrontal decompressive craniectomy was necessary both to reduce the intracranial pressure and to drain the subdural empyema.
Results. The full range of intracranial complications subsequently occurred, including brain abscesses, recurrent subdural empyema and ventriculitis. Despite this, the patient's outcome was good, with minimal intellectual deficits.
Conclusion. In cases of severe intracranial infection, we therefore advocate an aggressive surgical approach coupled with appropriate antibiotics to ensure a good outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ong, Y., Goh, K. & Chan, C. Bifrontal decompressive craniectomy for acute subdural empyema. Childs Nerv Syst 18, 340–343 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-002-0597-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-002-0597-9