Abstract
Background
Diabetes mellitus is a highly prevalent and growing chronic disease that is associated with increased risk of recurrence among several stroke subtypes. However, evidence on the prognostic role of diabetes in the setting of cryptogenic stroke (CS) remains scarce.
Methods
From April 2019 to November 2021, we recruited prospectively 78 consecutive patients with CS. Patients were classified according to the presence of diabetes. Main outcome was the composite of stroke recurrence and death. Secondary outcome was stroke recurrence.
Results
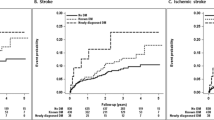
Mean age of the cohort was 78 ± 7.7 years and 18 patients (23%) had diabetes. After a median clinical follow-up of 23 months the incidence of stroke recurrence and mortality [HR 5.8 (95% CI 1.9–19), p = 0.002] and the incidence of stroke recurrence [HR 16.6 (95% CI 1.8–149), p = 0.012], were higher in patients with diabetes. After adjusting for potential confounders diabetes was identified as an independent predictor of stroke recurrence and death in patients with CS [HR 33.8 (95% CI 2.1–551), p = 0.013]. Other independent predictors of stroke recurrence and mortality were hypertension [HR 31.4 (95% CI 1.8–550), p = 0.018], NTproBNP [HR 1.002 (95% CI 1.001–1.004), p = 0.013] and chronic kidney disease (CKD) [HR 27.4 (95% CI 1.4–549) p = 0.03]. Furthermore, diabetes was an independent predictor of stroke recurrence [HR 103 (95% CI 1.3–8261), p = 0.038].
Conclusion
Diabetic patients with CS are at higher risk of stroke recurrence and death. Hypertension CKD and NTproBNP are also independent predictors of stroke recurrence and death after CS.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Zhang L, Li X, Wolfe CDA, O’Connell MDL, Wang Y (2021) Diabetes as an independent risk factor for stroke recurrence in ischemic stroke patients: an updated meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology 55(6):427–435
Kim JS, Nah HW, Park SM, Kim SK, Cho KH, Lee J, Lee YS, Kim J, Ha SW, Kim EG, Kim DE, Kang DW, Kwon SU, Yu KH, Lee BC (2012) Risk factors and stroke mechanisms in atherosclerotic stroke. Intracranial compared with extracranial and anterior compared with posterior circulation disease. Stroke 43(12):3313–3318
Regenhardt RW, Das AS, Ohtomo R, Lo EH, Ayata C, Gurol ME (2019) Pathophysiology of lacunar stroke: history’s mysteries and modern interpretations. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 28(8):2079–2097
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, Biller J, Brown M, Demaerschalk BM, Hoh B, Jauch EC, Kidwell CS, Leslie-Mazwi TM, Ovbiagele B, Scott PA, Sheth KN, Southerland AM, Summers DV, Tirschwell DL (2019) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 50:e344–e418
Guzik A, Bushnell C (2017) Stroke epidemiology and risk factor management. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 23:15–39
Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Boriani G, Castella M, Dan GA, Dilaveris PE, Fauchier L, Filippatos G, Kalman JM, La Meir M, Lane DA, Lebeau JP, Lettino M, Lip GYH, Pinto FJ, Thomas GN, Valgimigli M, Van Gelder IC, Van Putte BP, Watkins CL (2021) ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J 42(5):373–498
Kleindorfer DO, Towfighi A, Chaturvedi S, Cockroft KM, Gutierrez J, Lombardi-Hill D, Kamel H, Kernan WN, Kittner SJ, Leira EC, Lennon O, Meschia JF, Nguyen TN, Pollak PM, Santangeli P, Sharrief AZ, Smith SC Jr, Turan TN, Williams LS (2021) 2021 guideline for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 52(7):e364–e467
Sanna T, Diener HC, Passman RS, Di Lazzaro V, Bernstein RA, Morillo CA, Rymer MM, Thijs V, Rogers T, Beckers F, Lindborg K, Brachmann J (2014) Cryptogenic stroke and underlying atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 370(26):2478–2486
Vera A, Cecconi A, Ximénez-Carrillo Á, Ramos C, Martínez-Vives P, Lopez-Melgar B, Sanz-García A, Ortega G, Aguirre C, Vivancos J, Jiménez-Borreguero LJ, Alfonso F (2022) A comprehensive model to predict atrial fibrillation in cryptogenic stroke: the decryptoring score. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.106161
Easton JD, Saver JL, Albers GW, Alberts MJ, Chaturvedi S, Feldmann E, Hatsukami TS, Higashida RT, Johnston SC, Kidwell CS, Lutsep HL, Miller E, Sacco RL (2009) Definition and evaluation of transient ischemic attack: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this statement as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke 40(6):2276–2293
Johnston SC, Rothwell PM, Nguyen-Huynh MN, Giles MF, Elkins JS, Bernstein AL, Sidney S (2007) Validation and refinement of scores to predict very early stroke risk after transient ischaemic attack. Lancet 369(9558):283–292
Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA, Kuznetsova T, Lancellotti P, Muraru D, Picard MH, Rietzschel ER, Rudski L, Spencer KT, Tsang W, Voigt JU (2015) Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American society of echocardiography and the European association of cardiovascular imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 28:1–39
Badano L, Kolias T, Muraru D (2018) Standardization of left atrial, right ventricular and right atrial deformation imaging using two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography: a consensus document of the EACVI/ASE/Industry task force to standardize deformation imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 19(6):591–600
Tsang W, Salgo IS, Medvedofsky D (2016) Transthoracic 3D echocardiographic left heart chamber quantification using an automated adaptive analytics algorithm. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 9(7):769–782
Draznin B, Aroda VR, Bakris G, Benson G, Brown FM, Freeman R, Green J, Huang E, Isaacs D, Kahan S, Leon J, Lyons SK, Peters AL, Prahalad P, Reusch JEB, Young-Hyman D (2022) Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 45(Suppl 1):S17–S38
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, Clement DL, Coca A, de Simone G, Dominiczak A, Kahan T, Mahfoud F, Redon J, Ruilope L, Zanchetti A, Kerins M, Kjeldsen SE, Kreutz R, Laurent S, Lip GYH, McManus R, Narkiewicz K, Ruschitzka F, Schmieder RE, Shlyakhto E, Tsioufis C, Aboyans V, Desormais I (2018) 2018 ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens 36(10):1953–2041
Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, Koskinas KC, Casula M, Badimon L, Chapman MJ, De Backer GG, Delgado V, Ference BA, Graham IM, Halliday A, Landmesser U, Mihaylova B, Pedersen TR, Riccardi G, Richter DJ, Sabatine MS, Taskinen MR, Tokgozoglu L, Wiklund O, ESC Scientific Document Group (2020) 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J 41:111–188
Hart RG, Diener HC, Coutts SB, Easton JD, Granger CB, O’Donnell MJ, Sacco RL, Connolly SJ (2014) Embolic strokes of undetermined source: the case for a new clinical construct. Lancet Neurol 13(4):429–438
Diener HC, Sacco RL, Easton JD, Granger CB, Bernstein RA, Uchiyama S, Kreuzer J, Cronin L, Cotton D, Grauer C, Brueckmann M, Chernyatina M, Donnan G, Ferro JM, Grond M, Kallmünzer B, Krupinski J, Lee BC, Lemmens R, Masjuan J, Odinak M, Saver JL, Schellinger PD, Toni D, Toyoda K (2019) Dabigatran for prevention of stroke after embolic stroke of undetermined source. N Engl J Med 380:1906–1917
Hart RG, Sharma M, Mundl H, Kasner SE, Bangdiwala SI, Berkowitz SD, Swaminathan B, Lavados P, Wang Y, Wang Y, Davalos A, Shamalov N, Mikulik R, Cunha L, Lindgren A, Arauz A, Lang W, Czlonkowska A, Eckstein J, Gagliardi RJ, Amarenco P, Ameriso SF, Tatlisumak T, Veltkamp R, Hankey GJ, Toni D, Bereczki D, Uchiyama S, Ntaios G, Yoon BW, Brouns R, Endres M, Muir KW, Bornstein N, Ozturk S, O’Donnell MJ, De Vries Basson MM, Pare G, Pater C, Kirsch B, Sheridan P, Peters G, Weitz JI, Peacock WF, Shoamanesh A, Benavente OR, Joyner C, Themeles E, Connolly SJ (2018) Rivaroxaban for stroke prevention after embolic stroke of undetermined source. N Engl J Med 378(23):2191–2201
Fuentes B, Gutiérrez-Zúñiga R, Díez-Tejedor E (2020) It’s time to say goodbye to the ESUS construct. Front Neurol 11:653
Sagris D, Perlepe K, Leventis I, Samara S, Manios E, Korompoki E, Makaritsis K, Milionis H, Vemmos K, Ntaios G (2021) Statin treatment and outcomes after embolic stroke of undetermined source. Intern Emerg Med 16(5):1261–1266
Palacio S, McClure LA, Benavente OR, Bazan C 3rd, Pergola P, Hart RG (2014) Lacunar strokes in patients with diabetes mellitus: risk factors, infarct location, and prognosis: the secondary prevention of small subcortical strokes study. Stroke 45(9):2689–2694
Redgrave JN, Lovett JK, Syed AB, Rothwell PM (2008) Histological features of symptomatic carotid plaques in patients with impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes (Oxford plaque study). Cerebrovasc Dis 26(1):79–86
Ueno Y, Yamashiro K, Tanaka R, Kuroki T, Hira K, Kurita N, Urabe T, Hattori N (2016) Emerging risk factors for recurrent vascular events in patients with embolic stroke of undetermined source. Stroke 47(11):2714–2721
Hart RG, Veltkamp RC, Sheridan P, Sharma M, Kasner SE, Bangdiwala SI, Ntaios G, Shoamanesh A, Ameriso SF, Toni D, Czlonkowska A, Lindgren A, Hankey GJ, Perera KS, Shuaib A, Coutts SB, Gagliardi RJ, Berkowitz SD, Mundl H, Peters G, Connolly SJ (2019) Predictors of recurrent ischemic stroke in patients with embolic strokes of undetermined source and effects of rivaroxaban versus aspirin according to risk status: the NAVIGATE ESUS trial. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 28(8):2273–2279
Ntaios G, Lip GYH, Lambrou D, Michel P, Perlepe K, Eskandari A, Nannoni S, Sirimarco G, Strambo D, Vemmos K, Koroboki E, Manios E, Vemmou A, Rodríguez-Campello A, Cuadrado-Godia E, Roquer J, Arnao V, Caso V, Paciaroni M, Diez-Tejedor E, Fuentes B, Rodríguez Pardo J, Arauz A, Ameriso SF, Pertierra L, Gómez-Schneider M, Hawkes MA, Bandini F, Chavarria Cano B, Mohedano AMI, García Pastor A, Gil-Núñez A, Putaala J, Tatlisumak T, Barboza MA, Karagkiozi E, Makaritsis K, Papavasileiou V (2018) Renal function and risk stratification of patients with embolic stroke of undetermined source. Stroke 49(12):2904–2909
Bahit MC, Sacco RL, Easton JD, Meyerhoff J, Cronin L, Kleine E, Grauer C, Brueckmann M, Diener HC, Lopes RD, Brainin M, Lyrer P, Wachter R, Segura T, Granger CB (2021) Predictors of atrial fibrillation development in patients with embolic stroke of undetermined source: an analysis of the RE-SPECT ESUS trial. Circulation 144(22):1738–1746
Pagola J, Juega J, Francisco-Pascual J, Bustamante A, Penalba A, Pala E, Rodriguez M, De Lera-Alfonso M, Arenillas JF, Cabezas JA, Moniche F, de Torres R, Montaner J, González-Alujas T, Alvarez-Sabin J, Molina CA (2020) Predicting atrial fibrillation with high risk of embolization with atrial strain and NT-proBNP. Transl Stroke Res 12(5):735–741
Fonseca AC, Brito D, Pinho e Melo T, Geraldes R, Canhão P, Caplan LR, Ferro JM (2014) N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide shows diagnostic accuracy for detecting atrial fibrillation in cryptogenic stroke patients. Int J Stroke 9(4):419–425
Acknowledgements
Alberto Vera, Alberto Cecconi, Martínez-Vives, Beatriz Lopez-Melgar, Álvaro Montes, Luis Jesús Jiménez-Borreguero, Fernando Alfonso: Cardiology Department, Hospital Universitario de La Princesa, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, IIS-IP, CIBER-CV, c/ Diego de León 62, Madrid 28006, Madrid, Spain. Álvaro Ximénez-Carrillo, Carmen Ramos, Clara Aguirre, José Vivancos: Stroke Center. Neurology Department, Hospital Universitario de La Princesa, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. IIS-IP, Madrid, Spain. Ancor Sanz-García, Guillermo Ortega: Data Analysis Unit, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria, Hospital Universitario de la Princesa, Madrid, Spain.
Funding
Authors received a research grant from Spanish Society of Cardiology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
AV has made substantial contributions to conception, design and acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. He has been involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. AC has made substantial contributions to conception, design and acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. He has been involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. AXC has made substantial contributions to conception, design and acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. He has been involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. CR: has made substantial contributions to conception, design and acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. He has been involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. PMV has made substantial contributions to conception, design and acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. He has been involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. BLM has made substantial contributions to conception, design and acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. He has been involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. ASG has made substantial contributions to analysis and interpretation of data. He has been involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. GO has made substantial contributions to analysis and interpretation of data. He has been involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. CA agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. AM agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. JV has made substantial contributions to conception, design and acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. He has been involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. He has given final approval of the version to be published. LJJB has made substantial contributions to conception, design and acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. He has been involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. He has given final approval of the version to be published. FA has made substantial contributions to conception, design and acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. He has been involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. He has given final approval of the version to be published. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any conflict of interest in relation with this work.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by Ethical Committee of Hospital Universitario de la Princesa (7-02-19, acta CEIm 03/19).
Informed consent
All patients or their relatives provided written informed consent.
Guaranties
AC, LJJB and FA are guarantors of this paper.
Patient and public involvement statement
Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vera, A., Cecconi, A., Ximénez-Carrillo, Á. et al. Risk of recurrent stroke and mortality after cryptogenic stroke in diabetic patients. Heart Vessels 38, 817–824 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-023-02235-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-023-02235-y