Abstract
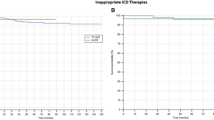
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) are the main therapy to prevent sudden cardiac death in patients with Brugada syndrome (BrS). The subcutaneous ICD (S-ICD) can eliminate lead-associated complications compared with transvenous ICD (TV-ICD). However, S-ICD is susceptible to T-wave oversensing (TWOS) and may result in more frequent inappropriate shocks in patients with BrS. This study aimed to compare inappropriate shocks between TV-ICD and S-ICD in patients with BrS. We enrolled 32 patients with BrS (including one woman; mean age 52 ± 18 years) who were implanted with ICD (23 TV-ICDs and 9 S-ICDs) between January 2002 and November 2018 in Oita University Hospital. We carried out a standard surface electrocardiogram (ECG) screening tests in both supine and standing positions prior to S-ICD implantation. The patients received routine clinical review every month and device monitoring every 4 months. The period of follow-up was 129 ± 51 months. Six patients with BrS and TV-ICDs experienced inappropriate shocks (26%) with their ICD therapy. In contrast, two patients with BrS and S-ICDs experienced inappropriate shocks (22%). There was no significant difference between the two groups (P = 0.82). Although one case in the S-ICD group experienced TWOS-induced inappropriate shock, SMART Pass (new high-pass filter) prevented the subsequent recurrence of inappropriate shocks during ICD therapy. Our results suggest that S-ICD is not inferior to TV-ICD in the incidence of inappropriate shocks. SMART Pass may be a useful tool to prevent inappropriate ICD shocks by TWOS in patients with BrS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Priori SG, Wilde AA, Horie M, Cho Y, Behr ER, Berul C, Blom N, Brugada J, Chiang CE, Huikuri H, Kannankeril P, Krahn A, Leenhardt A, Moss A, Schwartz PJ, Shimizu W, Tomaselli G, Tracy C, Document Reviewers, Ackerman M, Belhassen B, Estes NA 3rd, Fatkin D, Kalman J, Kaufman E, Kirchhof P, Schulze-Bahr E, Wolpert C, Vohra J, Refaat M, Etheridge SP, Campbell RM, Martin ET, Quek SC, Heart Rhythm Society; European Heart Rhythm Association; Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (2013) Executive summary: Hrs/ehra/aphrs expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of patients with inherited primary arrhythmia syndromes. Europace 15:1389–1406
Bardy GH, Smith WM, Hood MA, Crozier IG, Melton IC, Jordaens L, Theuns D, Park RE, Wright DJ, Connelly DT, Fynn SP, Murgatroyd FD, Sperzel J, Neuzner J, Spitzer SG, Ardashev AV, Oduro A, Boersma L, Maass AH, Van Gelder IC, Wilde AA, van Dessel PF, Knops RE, Barr CS, Lupo P, Cappato R, Grace AA (2010) An entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. N Engl J Med 363:36–44
Sueda S, Shinohara T, Takahashi N, Shite J, Shoji T, Akao M, Kijima Y, Masuyama T, Miyaji T, Yamamoto K, Iwasaki Y, Yoshida R, Nakamura S, Ogino Y, Kimura K, Sasai M, Suzuki H, Wakatsuki T, Asajima H, Teragawa H, Ishikawa T, Kitamura K, Oda T, Nakayama T, Kobayashi Y, Sunada D, Yamaki M, Nishizaki F, Tomita Y, Usuda K, Fujinaga H, Kuramitsu S, Andou K, Kiyooka T, Kadota K, Ishii Y, Ohtani H, Maekawa Y, Taguchi E, Nakao K, Kobayashi N, Seino Y, Nakagawa H, Saito Y, Komuro I, Sasaki Y, Ikeda S, Yamaguchi O, Kakutani A, Imanaka T, Ishihara M, Ishii M, Kaikita K, Tsujita K (2020) Questionnaire in patients with aborted sudden cardiac death due to coronary spasm in Japan. Heart Vessels. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-020-01644-7
Guo L, Zhang M, Hu M, Wang B, Wang J, Zuo L, Yang W, Liu B, Liu L (2019) Prevalence of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator based on template ECG screening and ineligible surface ECG predicting factors in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in China. Heart Vessels 34:851–859
Conte G, Kawabata M, de Asmundis C, Taravelli E, Petracca F, Ruggiero D, Caputo ML, Regoli F, Chierchia GB, Chiodini A, Del Bufalo A, Moccetti T, Goya M, Hirao K, Vicentini A, De Ferrari GM, Brugada P, Auricchio A (2018) High rate of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator sensing screening failure in patients with brugada syndrome: a comparison with other inherited primary arrhythmia syndromes. Europace 20:1188–1193
Theuns DAMJ, Brouwer TF, Jones PW, Allavatam V, Donnelley S, Auricchio A, Knops RE, Burke MC (2018) Prospective blinded evaluation of a novel sensing methodology designed to reduce inappropriate shocks by the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm 15:1515–1522
Brouwer TF, Knops RE, Kutyifa V, Barr C, Mondésert B, Boersma LVA, Lambiase PD, Wold N, Jones PW, Healey JS (2018) Propensity score matched comparison of subcutaneous and transvenous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator therapy in the simple and effortless studies. Europace 20:f240–f248
Priori SG, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Mazzanti A, Blom N, Borggrefe M, Camm J, Elliott PM, Fitzsimons D, Hatala R, Hindricks G, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen K, Kuck KH, Hernandez-Madrid A, Nikolaou N, Norekvål TM, Spaulding C, Van Veldhuisen DJ, ESC Scientific Document Group (2015) 2015 esc guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: The task force for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death of the european society of cardiology (esc). Endorsed by: Association for european paediatric and congenital cardiology (aepc). Eur Heart J 36:2793–2867
Antzelevitch C, Brugada P, Borggrefe M, Brugada J, Brugada R, Corrado D, Gussak I, LeMarec H, Nademanee K, Perez Riera AR, Shimizu W, Schulze-Bahr E, Tan H, Wilde A (2005) Brugada syndrome: report of the second consensus conference: endorsed by the heart rhythm society and the european heart rhythm association. Circulation 111:659–670
Priori SG, Wilde AA, Horie M, Cho Y, Behr ER, Berul C, Blom N, Brugada J, Chiang CE, Huikuri H, Kannankeril P, Krahn A, Leenhardt A, Moss A, Schwartz PJ, Shimizu W, Tomaselli G, Tracy C (2013) Executive summary: Hrs/ehra/aphrs expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of patients with inherited primary arrhythmia syndromes. Heart Rhythm 10:e85–108
Maisel WH, Kramer DB (2008) Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator lead performance. Circulation 117:2721–2723
Hauser RG, Hayes DL (2009) Increasing hazard of sprint fidelis implantable cardioverter-defibrillator lead failure. Heart Rhythm 6:605–610
Basu-Ray I, Liu J, Jia X, Gold M, Ellenbogen K, DiNicolantonio J, Komócsi A, Vorobcsuk A, Kim J, Afshar H, Lam W, Mathuria N, Razavi M, Rasekh A, Saeed M (2017) Subcutaneous versus transvenous implantable defibrillator therapy: a meta-analysis of case-control studies. JACC Clin Electrophysiol 3:1475–1483
Kooiman KM, Knops RE, Olde Nordkamp L, Wilde AA, de Groot JR (2014) Inappropriate subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shocks due to T-wave oversensing can be prevented: implications for management. Heart Rhythm 11:426–434
Afzal MR, Evenson C, Badin A, Patel D, Godara H, Essandoh M, Okabe T, Tyler J, Houmsse M, Augostini R, Hummel J, Kalbfleisch S, Daoud EG, Weiss R (2017) Role of exercise electrocardiogram to screen for T-wave oversensing after implantation of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm 14:1436–1439
Kamakura T, Wada M, Ishibashi K, Inoue YY, Miyamoto K, Okamura H, Nagase S, Noda T, Aiba T, Yasuda S, Kusano K (2017) Impact of electrocardiogram screening during drug challenge test for the prediction of T-wave oversensing by a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator in patients with Brugada syndrome. Heart Vessels 32:1277–1283
Olde Nordkamp LR, Conte G, Rosenmöller BR, Warnaars JL, Tan HL, Caputo ML, Regoli F, Moccetti T, Auricchio A, Knops RE, Wilde AA (2016) Brugada syndrome and the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. J Am Coll Cardiol 68:665–666
Miwa N, Nagata Y, Yamaguchi T, Nagase M, Sasaki T, Nozato T, Ashikaga T, Goya M, Hirao K (2019) Effect of diurnal variations in the QRS complex and T waves on the eligibility for subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. Heart Rhythm 16:913–920
Lambiase PD, Barr C, Theuns DA, Knops R, Neuzil P, Johansen JB, Hood M, Pedersen S, Kääb S, Murgatroyd F, Reeve HL, Carter N, Boersma L, EFFORTLESS Investigators (2014) Worldwide experience with a totally subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: early results from the effortless s-icd registry. Eur Heart J 35:1657–1665
Tachibana M, Nishii N, Banba K, Fujita S, Ikeda E, Okawa K, Morita H, Ito H (2019) Smart pass will prevent inappropriate operation of s-icd. J Arrhythm 35:86–91
Sarkozy A, Boussy T, Kourgiannides G, Chierchia GB, Richter S, De Potter T, Geelen P, Wellens F, Spreeuwenberg MD, Brugada P (2007) Long-term follow-up of primary prophylactic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator therapy in brugada syndrome. Eur Heart J 28:334–344
Sacher F, Probst V, Maury P, Babuty D, Mansourati J, Komatsu Y, Marquie C, Rosa A, Diallo A, Cassagneau R, Loizeau C, Martins R, Field ME, Derval N, Miyazaki S, Denis A, Nogami A, Ritter P, Gourraud JB, Ploux S, Rollin A, Zemmoura A, Lamaison D, Bordachar P, Pierre B, Jaïs P, Pasquié JL, Hocini M, Legal F, Defaye P, Boveda S, Iesaka Y, Mabo P, Haïssaguerre M (2013) Outcome after implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator in patients with Brugada syndrome: a multicenter study-part 2. Circulation 128:1739–1747
Conte G, Sieira J, Ciconte G, de Asmundis C, Chierchia GB, Baltogiannis G, Di Giovanni G, La Meir M, Wellens F, Czapla J, Wauters K, Levinstein M, Saitoh Y, Irfan G, Julià J, Pappaert G, Brugada P (2015) Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator therapy in Brugada syndrome: a 20-year single-center experience. J Am Coll Cardiol 65:879–888
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Masae Hayashi for her excellent secretarial assistance.
Funding
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid (grant number 18K06856 from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Science and Culture [T. Shinohara]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinohara, T., Abe, I., Hirota, K. et al. Usefulness of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator therapy in patients with Brugada syndrome. Heart Vessels 36, 260–266 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-020-01683-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-020-01683-0