Abstract
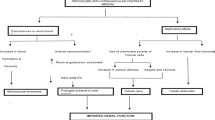
Renal congestion is caused by elevated central venous pressure (CVP), and decreases glomerular filtration in patients with congestive heart failure. Since real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) using microbubble-based contrast agents can visualize the perfused microvascular bed, we sought to evaluate the impairment of renal perfusion during acute renal congestion with CEUS. In Wister rats, CEUS of kidney was performed with the direct monitoring of CVP and intra-renal pressure (IRP). When CVP was elevated to 10 and 15 mmHg after the bolus injection of normal saline via the femoral vein, peak intensity (PI, dB) and time to PI (TTP) in the renal cortex and medulla were compared with control rats. There was a strong correlation between IRP and CVP (r = 0.95, p < 0.0001). In the congestion model, more time was required for enhancement of the parenchyma, especially in the medulla compared to control; TTP of the medulla and cortex at 15 mmHg CVP (CVP15) was significantly prolonged compared with controls (medulla, 4351 ± 98 vs. 1415 ± 267 ms, p = 0.003; cortex, 3219 ± 106 vs. 1335 ± 264 ms, p = 0.005). In addition, medullary PI at CVP15 decreased, but not significantly, compared to those of controls and at 10 mmHg CVP (20.1 ± 0.9, 22.8 ± 1.6, 21.6 ± 0.2 dB). In contrast, cortical PIs at CVP15 were significantly lower than that of control (24.6 ± 1.0 vs. 31.4 ± 1.0 dB, p = 0.007). CEUS revealed that impaired renal parenchymal flow in an acute congestion model is accompanied with increased renal interstitial pressure.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mullens W, Abrahams Z, Francis GS, Sokos G, Taylor DO, Starling RC, Young JB, Tang WH (2009) Importance of venous congestion for worsening of renal function in advanced decompensated heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 53:589–596
Damman K, van Deursen VM, Navis G, Voors AA, van Veldhuisen DJ, Hillege HL (2009) Increased central venous pressure is associated with impaired renal function and mortality in a broad spectrum of patients with cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 53:582–588
Joles JA, Bongartz LG, Gaillard CA, Braam B (2009) Renal venous congestion and renal function in congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 54:1632–1633
Burnett JC Jr, Knox FG (1980) Renal interstitial pressure and sodium excretion during renal vein constriction. Am J Physiol 238:F279–F282
Cosgrove D, Lassau N (2010) Imaging of perfusion using ultrasound. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:S65–S85
Fan L, Lianfang D, Jinfang X, Yijin S, Ying W (2008) Diagnostic efficacy of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in solid renal parenchymal lesions with maximum diameters of 5 cm. J Ultrasound Med 27:875–885
Xu ZF, Xu HX, Xie XY, Liu GJ, Zheng YL, Lu MD (2010) Renal cell carcinoma and renal angiomyolipoma: differential diagnosis with real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med 29:709–717
Schwenger V, Korosoglou G, Hinkel UP, Morath C, Hansen A, Sommerer C, Dikow R, Hardt S, Schmidt J, Kücherer H, Katus HA, Zeier M (2006) Real-time contrast-enhanced sonography of renal transplant recipients predicts chronic allograft nephropathy. Am J Transplant 6:609–615
Fischer T, Filimonow S, Dieckhöfer J, Slowinski T, Mühler M, Lembcke A, Budde K, Neumayer HH, Ebeling V, Giessing M, Thomas A, Morgera S (2006) Improved diagnosis of early kidney allograft dysfunction by ultrasound with echo enhancer—a new method for the diagnosis of renal perfusion. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21(10):2921–2929
Ciccone MM, Cortese F, Fiorella A, Scicchitano P, Cito F, Quistelli G, Pertosa G, D’Agostino R, Guida P, Favale S (2011) The clinical role of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the evaluation of renal artery stenosis and diagnostic superiority as compared to traditional echo-color-Doppler flow imaging. Int Angiol 30:135–139
Valentino M, Serra C, Zironi G, De Luca C, Pavlica P, Barozzi L (2006) Blunt abdominal trauma: emergency contrast-enhanced sonography for detection of solid organinjuries. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:1361–1367
Regine G, Atzori M, Miele V, Buffa V, Galluzzo M, Luzietti M, Adami L (2007) Second-generation sonographic contrast agents in the evaluation of renal trauma. Radiol Med 112:581–587
Garber J, Barbee R, Bielitzki J, Clayton LA, Donovan J, Hendriksen C, Kohn D, Lipman N, Locke P, Melcher J, Quimby F, Turner P, Wood G, Wurbel H (2008) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, 8th edn. National Academy Press, Washington, DC, pp 1–220
Watanabe R, Matsumura M, Chen CJ, Kaneda Y, Ishihara M, Fujimaki M (2003) Gray-scale liver enhancement with Sonazoid (NC100100), a novel ultrasound contrast agent; detection of hepatic tumors in a rabbit model. Biol Pharm Bull 26:1272–1277
Wakui N, Takayama R, Kamiyama N, Kobayashi K, Matsui D, Matsukiyo Y, Kanekawa T, Ikehara T, Ishii K, Sumino Y (2013) Arrival time parametric imaging using Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography is useful for the detection of spoke-wheel patterns of focal nodular hyperplasia smaller than 3 cm. Exp Ther Med 5(6):1551–1554
Wakui N, Sumino Y, Kamiyama N (2010) A case of high-flow hepatic hemangioma: analysis by parametoric imaging using Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography. J Med Ultrason (2001) 37(2):87–90
Sugimoto Katsutoshi, Moriyasu Fuminori, Kamiyama Naohisa, Yamada Masahiko, Iijima Hiroko (2008) Correlation between parametric imaging using contrast ultrasound and the histological differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res 38:273–280
Ross EA (2012) Congestive renal failure: the pathophysiology and treatment of renal venous hypertension. J Card Fail 18:930–938
Damman K, Voors AA, Navis G, van Veldhuisen DJ, Hillege HL (2011) The cardiorenal syndrome in heart failure. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 54:144–153
Lang RM, Feinstein SB, Powsner SM, McCoy CE, Frederickson ED, Neumann A, Goldberg LI, Borow KM (1987) Contrast ultrasonography of the kidney: a new method for evaluation of renal perfusion in vivo. Circulation 75:229–234
Aronson S, Wiencek JG, Feinstein SB, Heidenreich PA, Zaroff JG, Walker R, Roizen MF (1993) Assessment of renal blood flow with contrast ultrasonography. Anesth Analg 76:964–970
Okayama S, Hirai T, Yamashita N, Somekawa S, Iwano M, Uemura S, Kanauchi M, Saito Y (2008) Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with Sonazoid for evaluation of renal microcirculation. J Med Ultrason (2001) 35(4):183–189
Hvattum E, Normann PT, Oulie I, Uran S, Ringstad O, Skotland T (2001) Determination of perfluorobutane in rat blood by automatic headspace capillary gas chromatography and selected ion monitoring mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 24:487–494
Wei K, Le E, Bin JP, Coggins M, Thorpe J, Kaul S (2001) Quantification of renal blood flow with contrast-enhanced ultrasound. J Am Coll Cardiol 37:1135–1140
McArthur C, Baxter GM (2012) Current and potential renal applications of contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Clin Radiol 67:909–922
Kay DH, Mazonakis M, Geddes C, Baxter G (2009) Ultrasonic microbubble contrast agents and the transplant kidney. Clin Radiol 64:1081–1087
Zöllner FG, Zimmer F, Klotz S, Hoeger S, Schad LR (2015) Functional imaging of acute kidney injury at 3 Tesla: investigating multiple parameters using DCE-MRI and a two-compartment filtration model. Z Med Phys 25:58–65
Gennisson JL, Grenier N, Combe C, Tanter M (2012) Supersonic shear wave elastography of in vivo pig kidney: influence of blood pressure, urinary pressure and tissue anisotropy. Ultrasound Med Biol 38:1559–1567
Young LS, Regan MC, Barry MK, Geraghty JG, Fitzpatrick JM (1996) Methods of renal blood flow measurement. Urol Res 24:149–160
Cowley AW, Roman RJ, Fenoy FJ, Mattson DL (1992) Effect of renal medullary circulation on arterial pressure. J Hypertens Suppl 10:S187–S193
Fallick C, Sobotka PA, Dunlap ME (2011) Sympathetically mediated changes in capacitance: redistribution of the venous reservoir as a cause of decompensation. Circ Heart Fail 4:669–675
Lerman LO, Bentley MD, Fiksen-Olsen MJ, Strick DM, Ritman EL, Romero JC (1995) Pressure dependency of canine intrarenal blood flow within the range of autoregulation. Am J Physiol 268:F404–F409
Leithe ME, Margorien RD, Hermiller JB, Unverferth DV, Leier CV (1984) Relationship between central hemodynamics and regional blood-flow in normal subjects and in patients with congestive heart-failure. Circulation 69:57–64
Kilcoyne MM, Schmidt DH, Cannon PJ (1973) Intrarenal blood flow in congestive heart failure. Circulation 47:786–797
Funding sources
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relationships that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komuro, K., Seo, Y., Yamamoto, M. et al. Assessment of renal perfusion impairment in a rat model of acute renal congestion using contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Heart Vessels 33, 434–440 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-017-1063-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-017-1063-7