Abstract
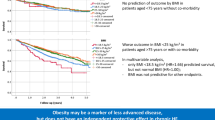
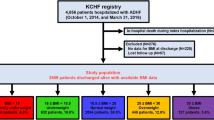
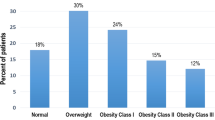
Obesity is known to be associated with the development of heart failure (HF). However, the relationship between the body mass index (BMI) and acute HF (AHF) remains to be elucidated. Eight hundred and eight AHF patients were enrolled in this study. The patients were assigned to four groups according to their BMI values: severely thin (n = 11, BMI <16), normal/underweight (n = 579, 16 ≤ BMI <25), overweight (n = 178, 25 ≤ BMI <30) and obese (n = 40, BMI ≥30). The patients in the severely thin group were more likely to be female, have systolic blood pressure (SBP) <100 mmHg and have valvular disease than normal/underweight patients. The patients in the overweight group were significantly younger than those in the normal/underweight, and those in the overweight group were more likely to have SBP ≥140 mmHg and hypertensive heart disease and less likely to have valvular disease than the patients in the normal/underweight group. The prognosis, including all-cause death, was significantly poorer among patients who were severely thin than those who were normal/underweight, overweight and significantly better among those who were overweight than those who were normal/underweight, severely thin and obese patients. A multivariate Cox regression model identified that severely thin [HR: 3.372, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.362–8.351] and overweight (HR: 0.615, 95% CI 0.391–0.966) were independent predictors of 910-day mortality as the reference of normal/underweight. Overweight patients tended to have SBP ≥140 mmHg and be relatively young, while severely thin patients tended to have SBP <100 mmHg and be female. These factors were associated with a better prognosis of overweight patients and adverse outcomes in severely thin patients. These factors may contribute to the “obesity paradox” in severely decompensated AHF patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Gutierrez HR, Lu Y, Bahalim AN, Farzadfar F, Riley LM, Ezzati M (2011) National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet 377(9765):557–567
Davis GJ (1999) Guidelines for healthy weight. N Engl J Med 341(27):2097–2098
Hubert HB, Feinleib M, McNamara PM, Castelli WP (1983) Obesity as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease: a 26-year follow-up of participants in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 67(5):968–977
Gruberg L, Weissman NJ, Waksman R, Fuchs S, Deible R, Pinnow EE, Ahmed LM, Kent KM, Pichard AD, Suddath WO, Satler LF, Lindsay J Jr (2002) The impact of obesity on the short-term and long-term outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention: the obesity paradox? J Am Coll Cardiol 39(4):578–584
Gurm HS, Whitlow PL, Kip KE (2002) The impact of body mass index on short- and long-term outcomes inpatients undergoing coronary revascularization. Insights from the bypass angioplasty revascularization investigation (BARI). J Am Coll Cardiol 39(5):834–840
Eckel RH (1997) Obesity and heart disease: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Nutrition Committee, American Heart Association. Circulation 96(9):3248–3250
Kenchaiah S, Evans JC, Levy D, Wilson PW, Benjamin EJ, Larson MG, Kannel WB, Vasan RS (2002) Obesity and the risk of heart failure. N Engl J Med 347(5):305–313
De Pergola G, Nardecchia A, Giagulli VA, Triggiani V, Guastamacchia E, Minischetti MC, Silvestris F (2013) Obesity and heart failure. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 13(1):51–57
Beleigoli A, Diniz M, Nunes M, Barbosa M, Fernandes S, Abreu M, Ribeiro A (2011) Reduced brain natriuretic peptide levels in class III obesity: the role of metabolic and cardiovascular factors. Obes Facts 4(6):427–432
Horwich TB, Fonarow GC, Hamilton MA, MacLellan WR, Woo MA, Tillisch JH (2001) The relationship between obesity and mortality in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 38(3):789–795
Koizumi M, Watanabe H, Kaneko Y, Iino K, Ishida M, Kosaka T, Motohashi Y, Ito H (2012) Impact of obesity on plasma B-type natriuretic peptide levels in Japanese community-based subjects. Heart Vessels 27(3):287–294
Chrysant SG, Chrysant GS (2013) New insights into the true nature of the obesity paradox and the lower cardiovascular risk. J Am Soc Hypertens 7(1):85–94
Curtis JP, Selter JG, Wang Y, Rathore SS, Jovin IS, Jadbabaie F, Kosiborod M, Portnay EL, Sokol SI, Bader F, Krumholz HM (2005) The obesity paradox: body mass index and outcomes in patients with heart failure. Arch Intern Med 165(1):55–61
Oreopoulos A, Padwal R, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Fonarow GC, Norris CM, McAlister FA (2008) Body mass index and mortality in heart failure: a meta-analysis. Am Heart J 156(1):13–22
Yanagisawa S, Inden Y, Yoshida N, Kato H, Miyoshi-Fujii A, Mizutani Y, Ito T, Kamikubo Y, Kanzaki Y, Hirai M, Murohara T (2015) Body mass index is associated with prognosis in Japanese elderly patients with atrial fibrillation: an observational study from the outpatient clinic. Heart Vessels. doi:10.1007/s00380-015-0765-y
Shah R, Gayat E, Januzzi JL Jr, Sato N, Cohen-Solal A, diSomma S, Fairman E, Harjola VP, Ishihara S, Lassus J, Maggioni A, Metra M, Mueller C, Mueller T, Parenica J, Pascual-Figal D, Peacock WF, Spinar J, van Kimmenade R, Mebazaa A (2014) Body mass index and mortality in acutely decompensated heart failure across the world: a global obesity paradox. J Am Coll Cardiol 63(8):778–785
Mebazaa A, Gheorghiade M, Pina IL, Harjola VP, Hollenberg SM, Follath F, Rhodes A, Plaisance P, Roland E, Nieminen M, Komajda M, Parkhomenko A, Masip J, Zannad F, Filippatos G (2008) Practical recommendations for prehospital and early in-hospital management of patients presenting with acute heart failure syndromes. Crit Care Med 36(1 Suppl):S129–S139
Gheorghiade M, Zannad F, Sopko G, Klein L, Pina IL, Konstam MA, Massie BM, Roland E, Targum S, Collins SP, Filippatos G, Tavazzi L (2005) Acute heart failure syndromes: current state and framework for future research. Circulation 112(25):3958–3968
McKee PA, Castelli WP, McNamara PM, Kannel WB (1971) The natural history of congestive heart failure: the Framingham study. N Engl J Med 285(26):1441–1446
Nieminen MS, Harjola VP (2005) Definition and epidemiology of acute heart failure syndromes. Am J Cardiol 96(6A):5G–10G
Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, Ard JD, Comuzzie AG, Donato KA, Hu FB, Hubbard VS, Jakicic JM, Kushner RF, Loria CM, Millen BE, Nonas CA, Pi-Sunyer FX, Stevens J, Stevens VJ, Wadden TA, Wolfe BM, Yanovski SZ, Jordan HS, Kendall KA, Lux LJ, Mentor-Marcel R, Morgan LC, Trisolini MG, Wnek J, Anderson JL, Halperin JL, Albert NM, Bozkurt B, Brindis RG, Curtis LH, DeMets D, Hochman JS, Kovacs RJ, Ohman EM, Pressler SJ, Sellke FW, Shen WK, Smith SC Jr, Tomaselli GF (2014) 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. Circulation 129(25 Suppl 2):S102–S138
McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Bohm M, Dickstein K, Falk V, Filippatos G, Fonseca C, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Jaarsma T, Kober L, Lip GY, Maggioni AP, Parkhomenko A, Pieske BM, Popescu BA, Ronnevik PK, Rutten FH, Schwitter J, Seferovic P, Stepinska J, Trindade PT, Voors AA, Zannad F, Zeiher A, Bax JJ, Baumgartner H, Ceconi C, Dean V, Deaton C, Fagard R, Funck-Brentano C, Hasdai D, Hoes A, Kirchhof P, Knuuti J, Kolh P, McDonagh T, Moulin C, Reiner Z, Sechtem U, Sirnes PA, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Vahanian A, Windecker S, Bonet LA, Avraamides P, Ben Lamin HA, Brignole M, Coca A, Cowburn P, Dargie H, Elliott P, Flachskampf FA, Guida GF, Hardman S, Iung B, Merkely B, Mueller C, Nanas JN, Nielsen OW, Orn S, Parissis JT, Ponikowski P (2012) ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail 14(8):803–869
Davos CH, Doehner W, Rauchhaus M, Cicoira M, Francis DP, Coats AJ, Clark AL, Anker SD (2003) Body mass and survival in patients with chronic heart failure without cachexia: the importance of obesity. J Card Fail 9(1):29–35
Feldman AM, Combes A, Wagner D, Kadakomi T, Kubota T, Li YY, McTiernan C (2000) The role of tumor necrosis factor in the pathophysiology of heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 35(3):537–544
Mohamed-Ali V, Goodrick S, Bulmer K, Holly JM, Yudkin JS, Coppack SW (1999) Production of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors by human subcutaneous adipose tissue in vivo. Am J Physiol 277(6 Pt 1):E971–E975
Fonarow GC, Srikanthan P, Costanzo MR, Cintron GB, Lopatin M (2007) An obesity paradox in acute heart failure: analysis of body mass index and inhospital mortality for 108,927 patients in the Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry. Am Heart J 153(1):74–81
Pozzo J, Fournier P, Lairez O, Vervueren PL, Delmas C, Elbaz M, Carrie D, Galinier M, Roncalli J (2015) Obesity paradox: origin and best way to assess severity in patients with systolic HF. Obesity (Silver Spring) 23(10):2002–2008
Sharma A, Lavie CJ, Borer JS, Vallakati A, Goel S, Lopez-Jimenez F, Arbab-Zadeh A, Mukherjee D, Lazar JM (2015) Meta-analysis of the relation of body mass index to all-cause and cardiovascular mortality and hospitalization in patients with chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol 115(10):1428–1434
Lavie CJ, Alpert MA, Arena R, Mehra MR, Milani RV, Ventura HO (2013) Impact of obesity and the obesity paradox on prevalence and prognosis in heart failure. JACC Heart Fail 1(2):93–102
Vidan MT, Blaya-Novakova V, Sanchez E, Ortiz J, Serra-Rexach JA, Bueno H (2016) Prevalence and prognostic impact of frailty and its components in non-dependent elderly patients with heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 18(7):869–875
Kenchaiah S, Pocock SJ, Wang D, Finn PV, Zornoff LA, Skali H, Pfeffer MA, Yusuf S, Swedberg K, Michelson EL, Granger CB, McMurray JJ, Solomon SD (2007) Body mass index and prognosis in patients with chronic heart failure: insights from the Candesartan in Heart failure: assessment of Reduction in Mortality and morbidity (CHARM) program. Circulation 116(6):627–636
Ajayi AA, Adigun AQ, Ojofeitimi EO, Yusuph H, Ajayi OE (1999) Anthropometric evaluation of cachexia in chronic congestive heart failure: the role of tricuspid regurgitation. Int J Cardiol 71(1):79–84
Levine B, Kalman J, Mayer L, Fillit HM, Packer M (1990) Elevated circulating levels of tumor necrosis factor in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 323(4):236–241
Anker SD, Coats AJ (1999) Cardiac cachexia: a syndrome with impaired survival and immune and neuroendocrine activation. Chest 115(3):836–847
Hasper D, Hummel M, Kleber FX, Reindl I, Volk HD (1998) Systemic inflammation in patients with heart failure. Eur Heart J 19(5):761–765
Doehner W, Frenneaux M, Anker SD (2014) Metabolic impairment in heart failure: the myocardial and systemic perspective. J Am Coll Cardiol 64(13):1388–1400
Anker SD, Chua TP, Ponikowski P, Harrington D, Swan JW, Kox WJ, Poole-Wilson PA, Coats AJ (1997) Hormonal changes and catabolic/anabolic imbalance in chronic heart failure and their importance for cardiac cachexia. Circulation 96(2):526–534
Swan JW, Anker SD, Walton C, Godsland IF, Clark AL, Leyva F, Stevenson JC, Coats AJ (1997) Insulin resistance in chronic heart failure: relation to severity and etiology of heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 30(2):527–532
Doehner W, Pflaum CD, Rauchhaus M, Godsland IF, Egerer K, Cicoira M, Florea VG, Sharma R, Bolger AP, Coats AJ, Anker SD, Strasburger CJ (2001) Leptin, insulin sensitivity and growth hormone binding protein in chronic heart failure with and without cardiac cachexia. Eur J Endocrinol 145(6):727–735
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the staff of the intensive care unit and the medical records office at Chiba Hokusoh Hospital, Nippon Medical School, for their valuable assistance in collecting the medical data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsushita, M., Shirakabe, A., Hata, N. et al. Association between the body mass index and the clinical findings in patients with acute heart failure: evaluation of the obesity paradox in patients with severely decompensated acute heart failure. Heart Vessels 32, 600–608 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-016-0908-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-016-0908-9