Abstract
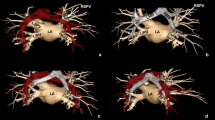
A detailed understanding of the left atrial (LA) anatomy in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) would improve the safety and efficacy of the radiofrequency catheter ablation. The objective of this study was to examine the myocardial thickness under the lines of the circumferential pulmonary vein isolation (CPVI) using 64-slice multidetector computed tomography (MDCT). Fifty-four consecutive symptomatic drug-refractory paroxysmal AF patients (45 men, age 61 ± 12 years) who underwent a primary CPVI guided by a three-dimensional electroanatomic mapping system (Carto XP; Biosense-Webster, Diamond Bar, CA, USA) with CT integration (Cartomerge; Biosense-Webster) were enrolled. Using MDCT, we examined the myocardial thickness of the LA and pulmonary vein (PV) regions in all patients. An analysis of the measurements by the MDCT revealed that the LA wall was thickest in the left lateral ridge (LLR; 4.42 ± 1.28 mm) and thinnest in the left inferior pulmonary vein wall (1.68 ± 0.27 mm). On the other hand, the thickness of the posterior wall in the cases with contact between the esophagus and left PV antrum was 1.79 ± 0.22 mm (n = 30). After the primary CPVI, the freedom from AF without any drugs during a 1-year follow-up period was 78 % (n = 42). According to the multivariate analysis, the thickness of the LLR was an independent positive predictor of an AF recurrence (P = 0.041). The structure of the left atrium and PVs exhibited a variety of myocardial thicknesses in the different regions. Of those, only the measurement of the LLR thickness was associated with an AF recurrence.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kannel WB, Abbott RD, Savage DD, McNamara PM (1982) Epidemiologic features of chronic atrial fibrillation: the Framingham study. N Engl J Med 306:1018–1022
Chen SA, Hsieh MH, Tai CT, Tsai CF, Prakash VS, Yu WC, Hsu TL, Ding YA, Chang MS (1999) Initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating from the pulmonary veins: electrophysiological characteristics, pharmacological responses, and effects of radiofrequency ablation. Circulation 100:1879–1886
Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Quiniou G, Garrigue S, Le Mouroux A, Le Metayer P, Clementy J (1998) Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med 339:659–666
Oral H, Scharf C, Chugh A, Hall B, Cheung P, Good E, Veerareddy S, Pelosi F Jr, Morady F (2003) Catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: segmental pulmonary vein ostial ablation versus left atrial ablation. Circulation 108:2355–2360
Pappone C, Rosanio S, Oreto G, Tocchi M, Gugliotta F, Vicedomini G, Salvati A, Dicandia C, Mazzone P, Santinelli V, Gulletta S, Chierchia S (2000) Circumferential radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary vein ostia: a new anatomic approach for curing atrial fibrillation. Circulation 102:2619–2628
Sumitomo N, Nakamura T, Fukuhara J, Nakai T, Watanabe I, Mugishima H, Hiraoka M (2010) Clinical effectiveness of pulmonary vein isolation for arrhythmic events in a patient with catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Heart Vessels 25:448–452
Mainigi SK, Sauer WH, Cooper JM, Dixit S, Gerstenfeld EP, Callans DJ, Russo AM, Verdino RJ, Lin D, Zado ES, Marchlinski FE (2007) Incidence and predictors of very late recurrence of atrial fibrillation after ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 18:69–74
Hocini M, Sanders P, Jais P, Hsu LF, Takahashi Y, Rotter M, Clementy J, Haissaguerre M (2004) Techniques for curative treatment of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 15:1467–1471
Kato R, Lickfett L, Meininger G, Dickfeld T, Wu R, Juang G, Angkeow P, LaCorte J, Bluemke D, Berger R, Halperin HR, Calkins H (2003) Pulmonary vein anatomy in patients undergoing catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: lessons learned by use of magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 107:2004–2010
Kaseno K, Tada H, Koyama K, Jingu M, Hiramatsu S, Yokokawa M, Goto K, Naito S, Oshima S, Taniguchi K (2008) Prevalence and characterization of pulmonary vein variants in patients with atrial fibrillation determined using 3-dimensional computed tomography. Am J Cardiol 101:1638–1642
Schmidt B, Ernst S, Ouyang F, Chun KR, Broemel T, Bansch D, Kuck KH, Antz M (2006) External and endoluminal analysis of left atrial anatomy and the pulmonary veins in three-dimensional reconstructions of magnetic resonance angiography: the full insight from inside. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 17:957–964
Maeda S, Iesaka Y, Uno K, Otomo K, Nagata Y, Suzuki K, Hachiya H, Goya M, Takahashi A, Fujiwara H, Hiraoka M, Isobe M (2012) Complex anatomy surrounding the left atrial posterior wall: analysis with 3D computed tomography. Heart Vessels 27:58–64
Tops LF, Bax JJ, Zeppenfeld K, Jongbloed MR, Lamb HJ, van der Wall EE, Schalij MJ (2005) Fusion of multislice computed tomography imaging with three-dimensional electroanatomic mapping to guide radiofrequency catheter ablation procedures. Heart Rhythm 2:1076–1081
Calkins H, Brugada J, Packer DL, Cappato R, Chen SA, Crijns HJ, Damiano RJ Jr, Davies DW, Haines DE, Haissaguerre M, Iesaka Y, Jackman W, Jais P, Kottkamp H, Kuck KH, Lindsay BD, Marchlinski FE, McCarthy PM, Mont JL, Morady F, Nademanee K, Natale A, Pappone C, Prystowsky E, Raviele A, Ruskin JN, Shemin RJ (2007) HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for personnel, policy, procedures and follow-up. A report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Task Force on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 4:816–861
Tsao HM, Hu WC, Wu MH, Tai CT, Chang SL, Lin YJ, Lo LW, Hu YF, Wu TJ, Sheu MH, Chang CY, Chen SA (2011) Characterization of the dynamic function of the pulmonary veins before and after atrial fibrillation ablation using multi-detector computed tomographic images. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 27:1049–1058
Corradi D, Maestri R, Macchi E, Callegari S (2011) The atria: from morphology to function. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 22:223–235
Tsao HM, Wu MH, Huang BH, Lee SH, Lee KT, Tai CT, Lin YK, Hsieh MH, Kuo JY, Lei MH, Chen SA (2005) Morphologic remodeling of pulmonary veins and left atrium after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: insight from long-term follow-up of three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 16:7–12
Yamada T, Yoshida Y, Tsuboi N, Murakami Y, Okada T, McElderry HT, Yoshida N, Doppalapudi H, Epstein AE, Plumb VJ, Inden Y, Murohara T, Kay GN (2008) Efficacy of pulmonary vein isolation in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation patients with a Brugada electrocardiogram. Circ J 72:281–286
Maeda S, Iesaka Y, Otomo K, Uno K, Nagata Y, Suzuki K, Hachiya H, Goya M, Takahashi A, Fujiwara H, Isobe M (2011) No severe pulmonary vein stenosis after extensive encircling pulmonary vein isolation: 12-month follow-up with 3D computed tomography. Heart Vessels 26:440–448
Schwartzman D, Lacomis J, Wigginton WG (2003) Characterization of left atrium and distal pulmonary vein morphology using multidimensional computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 41:1349–1357
Chang SL, Lin YJ, Tai CT, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Udyavar AR, Hu YF, Chiang SJ, Wongcharoen W, Tsao HM, Ueng KC, Higa S, Lee PC, Chen SA (2009) Induced atrial tachycardia after circumferential pulmonary vein isolation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: electrophysiological characteristics and impact of catheter ablation on the follow-up results. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 20:388–394
Cabrera JA, Ho SY, Climent V, Sanchez-Quintana D (2008) The architecture of the left lateral atrial wall: a particular anatomic region with implications for ablation of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J 29:356–362
Yokoyama K, Nakagawa H, Shah DC, Lambert H, Leo G, Aeby N, Ikeda A, Pitha JV, Sharma T, Lazzara R, Jackman WM (2008) Novel contact force sensor incorporated in irrigated radiofrequency ablation catheter predicts lesion size and incidence of steam pop and thrombus. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 1:354–362
Kuck KH, Reddy VY, Schmidt B, Natale A, Neuzil P, Saoudi N, Kautzner J, Herrera C, Hindricks G, Jais P, Nakagawa H, Lambert H, Shah DC (2012) A novel radiofrequency ablation catheter using contact force sensing: Toccata study. Heart Rhythm 9:18–23
Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen SA, Davies W, Iesaka Y, Kalman J, Kim YH, Klein G, Packer D, Skanes A (2005) Worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circulation 111:1100–1105
Cummings JE, Schweikert RA, Saliba WI, Burkhardt JD, Kilikaslan F, Saad E, Natale A (2006) Brief communication: atrial–esophageal fistulas after radiofrequency ablation. Ann Intern Med 144:572–574
Pappone C, Oral H, Santinelli V, Vicedomini G, Lang CC, Manguso F, Torracca L, Benussi S, Alfieri O, Hong R, Lau W, Hirata K, Shikuma N, Hall B, Morady F (2004) Atrio-esophageal fistula as a complication of percutaneous transcatheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 109:2724–2726
Han J, Good E, Morady F, Oral H (2004) Images in cardiovascular medicine. Esophageal migration during left atrial catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Circulation 110:e528
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Masao Kiguchi, R.T., Department of Radiology, for his excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suenari, K., Nakano, Y., Hirai, Y. et al. Left atrial thickness under the catheter ablation lines in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: insights from 64-slice multidetector computed tomography. Heart Vessels 28, 360–368 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-012-0253-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-012-0253-6