Abstract
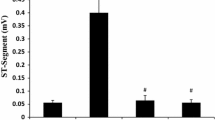
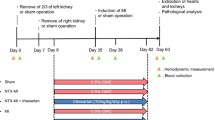
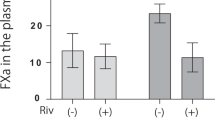
The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of irbesartan, carvedilol, and irbesartan plus carvedilol on the expression of tissue factor (TF) and tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) mRNA and protein in rat myocardium after myocardial infarction (MI). MI was induced in male Wistar rats by ligation of the anterior descending branch of the left coronary artery. Irbesartan at 50 mg/kg/day, carvedilol at 1 mg/kg/day, irbesartan plus carvedilol, or placebo was administered intragastrically; expression of TF and TFPI mRNA and protein was determined by RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. The relative left ventricle weights were lower in all three treatment groups than in the placebo group, with the lowest relative weight in the irbesartan plus carvedilol group (P < 0.001). The size of the infarcted area was lower in the carvedilol and the combined groups than in the placebo group (P < 0.001). The levels of expression of TF and TFPI mRNA and protein were lower in the combined group than in the placebo group or the carvedilol group (P < 0.001). Treatment with irbesartan plus carvedilol reduced the expression of TF and TFPI mRNA and protein after MI in rats, and combined treatment with both agents had greater effects than the single agents alone. These findings suggest that the beneficial effects of these drugs may include anticoagulation and that combined therapy with both agents is an option that should be evaluated further.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doughty RN, Whalley GA, Gamble G, MacMahon S, Sharpe N (1997) Left ventricular remodeling with carvedilol in patients with congestive heart failure due to ischemic heart disease. Australia-New Zealand Heart Failure Research Collaborative Group. J Am Coll Cardiol 29:1060–1066
Senior R, Basu S, Kinsey C, Schaeffer S, Lahiri A (1999) Carvedilol prevents remodeling in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 137:646–652
Yang YJ, Zhang P, Ruan YM (2000) Comparison of losartan, enalapril and their combination in preventing ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in rats. Eur Heart J 21(Suppl):72
Yang YJ, Tang YD, Zhang P, Ruan YM, Xu XL, Zhou YW, Tian Y, Gao RL, Chen JL, Chen ZJ (2001) Effects of different doses of carvedilol for prevention and treatment of left ventricular remodeling in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Chin J Med 81:927–930
Richer C, Fomes P, Cazaubon C, Domergue V, Nisato D, Giudicelli JF (1999) Effects of long-term angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockade on survival, hemodynamics and cardiac remodeling in chronic heart failure in rats. Cardiovasc Res 41:100–108
Fernandes-Santos C, Mendonca L, Mandarin-de-Lacerda CA (2009) Favorable cardiac and aortic remodeling in olmesartan-treated spontaneously hypertensive rats. Heart Vessels 24:219–227
Tsuda M, Iwai M, Li J-M, Li H-G, Min L-J, Ide A, Okumura M, Suzuki J, Mogi M, Suzuki H, Horiuchi M (2005) Inhibitory effect of AT1 receptor blocker, olmesartan, and estrogen on atherosclerosis via anti-oxidative stress. Hypertension 45:545–551
Steppich BA, Braun SL, Stein A, Demetz G, Groha P, Schömig A, von Beckerath N, Kastrati A, Ott I (2009) Plasma TF activity predicts cardiovascular mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Thromb J 7:11. doi:10.1186/1477-9560-7-11
Zaman AG, Helft G, Worthley SG, Badimon JJ (2000) The role of plaque rupture and thrombosis in coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 149:251–266
Steppich B, Mattisek C, Sobczyk D, Kastrati A, Schömig A, Ott I (2005) Tissue factor pathway inhibitor on circulating microparticles in acute myocardial infarction. Thromb Haemost 93:35–39
Koh KK, Chung WJ, Ahn JY, Han SH, Kang WC, Seo YH, Ahn TH, Choi IS, Shin EK (2004) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers reduce tissue factor activity and plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 antigen in hypertensive patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Atherosclerosis 177:155–160
Yang QF, Li CL, Chen J, Liu J, Liu H, Hu FC, Hu YC, Zhang YZ (2003) Effects of carvedilol on blood viscosity and platelet aggregation in patients with essential hypertension. Henan Univ Trans Med Sci Ed 22:20–22
Zang RY, Sun YH, Huang YL (2002) Effects of fosinopril, irbesartan and combined treatment on ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Chin J Cardiol 30(10):626–629
Nishiyama M, Park IS, Yoshikawa T, Hatai Y, Ando M, Takahashi Y, Mori K, Murakami Y (2009) Efficacy and safety of carvedilol for heart failure in children and patients with congenital heart disease. Heart Vessels 24:187–192
Schneider MP, Klingbeil AU, Delles C, Ludwig M, Kolloch RE, Krekler M, Stumpe KO, Schmieder RE (2004) Effect of irbesartan versus atenolol on left ventricular mass and voltage: results of the cardiovascular irbesartan project. Hypertension 44:61–66
Toda N (2003) Vasodilating beta-adrenoceptor blockers as cardiovascular therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther 100:215–234
Doughty RN, Whalley GA, Walsh HA, Gamble GD, López-Sendón J, Sharpe N, CAPRICORN Echo Substudy Investigators (2004) Effects of carvedilol on left ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial iinfarction: the CAPRICORN Echo Substudy. Circulation 109:201–206
Frishman WH, Henderson LS, Lukas MA (2008) Controlled-release carvedilol in the management of systemic hypertension and myocardial dysfunction. Vasc Health Risk Manag 4:1387–1400
Wen H, Jiang H, Lu Z, He B, Hu X, Chen J, Zhao D (2009) Carvedilol ameliorates the decreases in connexin 43 and ventricular fibrillation threshold in rats with myocardial infarction. Tohoku J Exp Med 218:121–127
Ardissino D, Merlini PA, Ariëns R, Coppola R, Bramucci E, Mannucci PM (1997) Tissue factor antigen and activity in human coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Lancet 349:769–771
Carter AM (2005) Inflammation, thrombosis and acute coronary syndromes. Diab Vasc Dis Res 2:113–121
Golino P, Ragni M, Cirillo P, Scognamiglio A, Ravera A, Buono C, Guarino A, Piro O, Lambiase C, Botticella F, Ezban M, Condorelli M, Chiariello M (2000) Recombinant human, active site-blocked factor VIIa reduces infarct size and no-reflow phenomenon in rabbits. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278:H1507–H1516
Erlich JH, Boyle EM, Labriola J, Kovacich JC, Santucci RA, Fearns C, Morgan EN, Yun W, Luther T, Kojikawa O, Martin TR, Pohlman TH, Verrier ED, Mackman N (2000) Inhibition of the tissue factor-thrombin pathway limits infarct size after myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury by reducing inflammation. Am J Pathol 157:1849–1862
Napoleone E, Di Santo A, Camera M, Tremoli E, Lorenzet R (2000) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors downregulate tissue factor synthesis in monocytes. Circ Res 86:139–143
Muller DN, Mervaala EM, Schmidt F, Park JK, Dechend R, Genersch E, Breu V, Löffler BM, Ganten D, Schneider W, Haller H, Luft FC (2000) Effect of bosentan on NF-kappaB, inflammation, and tissue factor in angiotensin II-induced end-organ damage. Hypertension 36:282–290
Napoleone E, Di Santo A, Camera M, Tremoli E, Lorenzet R (2000) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors downregulate tissue factor synthesis in monocytes. Circ Res 86:139–143
Koh KK, Chung WJ, Ahn JY, Han SH, Kang WC, Seo YH, Ahn TH, Choi IS, Shin EK (2004) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers reduce tissue factor activity and plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 antigen in hypertensive patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Atherosclerosis 177:155–160
Li N, Zhu W, Chen L, Ke Y (2006) Effects of valsartan and captopril on expression and activity of rabbit vascular smooth muscle cell tissue factors and tissue factor pathway inhibitors. Chin J Cardiol 34:922
Soeda S, Tsunoda T, Kurokawa Y, Shimeno H (1998) Tumor necrosis factor-α induced release of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 from human umbilical vein endothelial cells: involvement of intracellular ceramide signaling event. Biochim Biophys Acta 1448:37–45
Birgel M, Gottschling-Zeller H, Röhrig K, Hauner H (2000) Role of cytokines in the regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression and secretion in newly differentiated subcutaneous human adipocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1682–1687
Rössig L, Haendeler J, Mallat Z, Hugel B, Freyssinet JM, Tedgui A, Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM (2000) Congestive heart failure induces endothelial cell apotosis: protective role of carvedilol. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:2081–2089
Polte T, Oberle S, Schder H (1997) Nitric oxide protects endothelial cells from tumor necrosis factor-α mediated cytotoxicity: possible involvement of cyclic GMP. FEBS Lett 409:46–48
Castro P, Vukasovic JL, Chiong M, Díaz-Araya G, Alcaino H, Copaja M, Valenzuela R, Greig D, Pérez O, Corbalan R, Lavandero S (2005) Effects of carvedilol on oxidative stress and chronotropic response to exercise in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 7:1033–1039
Verma S (2004) Angiotensin receptor blockers and myocardial infarction. BMJ 329:1248–1249
Kveiborg B, Major-Petersen A, Christiansen B, Torp-Pedersen C (2007) Carvedilol in the treatment of chronic heart failure: lessons from the Carvedilol or Metroprolol European Trial. Vasc Health Risk Manag 3:31–37
McDonald MA, Simpson SH, Ezedowits JA, Gyenes G, Tsuyuki RT (2005) Angiotensin receptor blockers and risk of myocardial infarction: systematic review. BMJ doi:10.1136/bmj.38595.518542.3A
Wang J, Zhu TB, Yang ZJ, Wang LS, Ma WZ (2005) Study of free tissue factor pathway inhibitors in acute coronary syndrome. Nanjing Med Univ Trans Nat Sci Ed 25:259–261
Falciani M, Gori AM, Fedi S, Chiarugi L, Simonetti I, Dabizzi RP, Prisco D, Pepe G, Abbate R, Gensini GF, Neri Serneri GG (1998) Elevated tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor circulating levels in ischemic heart diseases patients. Thromb Haemost 79:495–499
Wu Y, Sun B, Dai Q, Wang W (2006) Changes in plasma tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor levels in patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing anticoagulant therapy. Chin J Med 41(6):35–36
Soejima H, Ogawa H, Yasue H, Kaikita K, Nishiyama K, Misumi K, Takazoe K, Miyao Y, Yoshimura M, Kugiyama K, Nakamura S, Tsuji I, Kumeda K (1999) Heightened tissue factor associated with tissue factor pathway inhibitor and prognosis in patients with unstable angina. Circulation 22:2908–2913
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by research project of Heilongjiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (D2007-74), funded by Heilongjiang Provincial Department of Education (11511152) and Heilongjiang Provincial Department of Health (2005235).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Zhao, J., Liu, W. et al. Combined effects of irbesartan and carvedilol on expression of tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor in rats after myocardial infarction. Heart Vessels 26, 646–653 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-010-0106-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-010-0106-0