Abstract
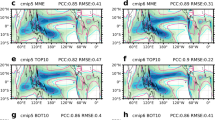
To evaluate the ability of the Predicted Particle Properties (P3) scheme in the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model, we simulated a stratiform rainfall event over northern China on 22 May 2017. WRF simulations with two P3 versions, P3-nc and P3-2ice, were evaluated against rain gauge, radar, and aircraft observations. A series of sensitivity experiments were conducted with different collection efficiencies between ice and cloud droplets. The comparison of the precipitation evolution between P3-nc and P3-2ice suggested that both P3 versions overpredicted surface precipitation along the Taihang Mountains but underpredicted precipitation in the localized region on the leeward side. P3-2ice had slightly lower peak precipitation rates and smaller total precipitation amounts than P3-nc, which were closer to the observations. P3-2ice also more realistically reproduced the overall reflectivity structures than P3-nc. A comparison of ice concentrations with observations indicated that P3-nc underestimated aggregation, whereas P3-2ice produced more active aggregation from the self-collection of ice and ice-ice collisions between categories. Efficient aggregation in P3-2ice resulted in lower ice concentrations at heights between 4 and 6 km, which was closer to the observations. In this case, the total precipitation and precipitation pattern were not sensitive to riming. Riming was important in reproducing the location and strength of the embedded convective region through its impact on ice mass flux above the melting level.
摘 要
本文采用WRF模式可预报冰雪晶特性的P3微物理方案,对2017年5月22日我国北方地区一次积层混合云降水过程进行了数值模拟,并结合地面降水、雷达和飞机探测数据,评估了P3方案两个版本P3-nc(单一类别冰雪晶)和P3-2ice(冰雪晶分为两类)的数值模拟能力。为探讨凇附过程的影响,本文采用不同的冰雪晶-云滴碰并系数开展了数值敏感性试验。对降水演变的分析表明,两个P3版本都高估了太行山沿线的地面降水,而低估了背风面局部地区的降水。当把冰雪晶分为两类时,模拟的小时降雨强度比采用单一类别冰雪晶时稍低,结果更接近观测值,并且雷达回波结构更合理。与飞机观测的冰雪晶数浓度相比,P3-nc低估了聚合过程,而P3-2ice从冰雪晶自身的碰并过程和不同类别冰雪晶之间的碰并过程中产生了更活跃的聚合过程,从而改进了对4–6 km高度冰雪晶浓度的模拟效果。对本次降水过程,地面总降水量和降水分布对凇附过程不敏感,尽管改进凇附过程不能解决WRF模式模拟降水量偏大的问题,完善凇附过程参数化方案仍然对改进对流雨核区位置和强度的模拟效果有重要影响。
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Airborne and radar data will be available on request. The ERA5 reanalysis data came from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) and are available at https://www.ecmwf.int/en/forecasts/datasets.
References
Chen, J. P., and T. C. Tsai, 2016: Triple-moment modal parameterization for the adaptive growth habit of pristine ice crystals. J. Atmos. Sci., 73, 2105–2122, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-15-0220.1.
Cooper, W. A., 1986: Ice initiation in natural clouds. Meteor. Monogr., 21, 29–32, https://doi.org/10.1175/0065-9401-21.43.29.
Dudhia, J., 1989: Numerical study of convection observed during the Winter Monsoon Experiment using a mesoscale two-dimensional model. J. Atmos. Sci., 46, 3077–3107, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1989)046<3077:NSOCOD>2.0.CO;2.
Erfani, E., and D. L. Mitchell, 2017: Growth of ice particle mass and projected area during riming. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 1241–1257, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-1241-2017.
Ek, M. B., and Coauthors, 2003: Implementation of Noah land surface model advances in the National Centers for Environmental Prediction operational mesoscale Eta model. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 108, 8851, https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD003296.
Field, P. R., 1999: Aircraft observations of ice crystal evolution in an altostratus cloud. J. Atmos. Sci., 56, 1925–1941, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1999)056<1925:AO OICE>2.0.CO;2.
Field, P. R., A. J. Heymsfield, and A. Bansemer, 2006: A test of ice self-collection kernels using aircraft data. J. Atmos. Sci., 63, 651–666, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS3653.1.
Garvert, M. F., B. A. Colle, and C. F. Mass, 2005: The 13–14 December 2001 IMPROVE-2 Event. Part I: Synoptic and mesoscale evolution and comparison with a mesoscale model simulation. J. Atmos. Sci., 62, 3474–3492, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS3549.1.
Han, B., and Coauthors, 2019: Cloud-resolving model intercomparison of an MC3E squall line case: Part II. Stratiform precipitation properties. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 124, 1090–1117, https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD029596.
Hong, S. Y., Y. Noh, and J. Dudhia, 2006: A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Wea. Rev., 134, 2318–2341, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR3199.1.
Hong, S. Y., K. S. S. Lim, Y. H. Lee, J. C. Ha, H. W. Kim, S. J. Ham, and J. Dudhia, 2010: Evaluation of the WRF doublemoment 6-class microphysics scheme for precipitating convection. Advances in Meteorology, 2010, 707253, https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/707253.
Hou, T. J., H. C. Lei, J. F. Yang, Z. X. Hu, and Q. J. Feng, 2016: Investigation of riming within mixed-phase stratiform clouds using weather research and forecasting (WRF) model. Atmospheric Research, 178–179, 291–303, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.04.007.
Hou, T. J., H. C. Lei, Z. X. Hu, J. F. Yang, and X. Y. Li, 2020: Simulations of microphysics and precipitation in a stratiform cloud case over northern China: Comparison of two micro-physics schemes. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 37, 117–129, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-019-8257-0.
Hou, T. J., H. C. Lei, Y. J. He, J. F. Yang, Z. Zhao, and Z. X. Hu, 2021: Aircraft measurements of the microphysical properties of stratiform clouds with embedded convection. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 38, 966–982, https://doi.org/10.1007/s003766-021-0287-8.
Hua, S. F., X. Xu, and B. J. Chen, 2020: Influence of multiscale orography on the initiation and maintenance of a precipitating convective system in North China: A case study. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 125, e2019JD031731, https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD031731.
Iacono, M. J., and Coauthors, 2008: Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 11, D13103, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD009944.
Janjić, Z. I., 1994: The step-mountain eta coordinate model: further developments of the convection, viscous sublayer, and turbulence closure schemes. Mon. Wea. Rev., 122, 927–945, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1994)122%3C0927:TSMECM%3E2.0.CO;2.
Khain, A. P., and Coauthors, 2015: Representation of microphysical processes in cloud-resolving models: Spectral (bin) micro-physics versus bulk parameterization. Rev. Geophys., 5, 247–322, https://doi.org/10.1002/2014RG000468.
Lawson, R. P., and P. Zuidema, 2009: Aircraft microphysical and surface-based radar observations of summertime Arctic clouds. J. Atmos. Sci., 66, 3505–3529, https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JAS3177.1.
Lei, H. C., J. X. Guo, D. Chen, and J. F. Yang, 2020: Systematic bias in the prediction of warm-rain hydrometeors in the WDM6 microphysics scheme and modifications. J. Geo-phys. Res.: Atmos., 125, e2019JD0307564, https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD030756.
Lin, Y. L., R. D. Farley, and H. D. Orville, 1983: Bulk parameterization of the snow field in a cloud model. J. Appl. Meteorol., 22, 1065–1092, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1983)022<1065:BPOTSF>2.0.CO;2.
Locatelli, J. D., and P. V. Hobbs, 1974: Fall speeds and masses of solid precipitation particles. J. Geophys. Res., 79, 2185–2197, https://doi.org/10.1029/JC079i015p02185.
Milbrandt, J. A., and M. K. Yau, 2005: A multimoment bulk micro-physics parameterization. Part II: A proposed three-moment closure and scheme description. J. Atmos. Sci., 62, 3065–3081, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS3535.1.
Milbrandt, J. A., and M. K. Yau, 2006: A multimoment bulk micro-physics parameterization. Part IV: Sensitivity experiments. J. Atmos. Sci., 63, 3137–3159, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS3817.1.
Milbrandt, J. A., and H. Morrison, 2016: Parameterization of cloud microphysics based on the prediction of bulk ice particle properties. Part III: Introduction of multiple free categories. J. Atmos. Sci., 73, 975–995, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-15-0204.1.
Milbrandt, J. A., H. Morrison, D. T. DawsonII, and M. Paukert, 2021: A Triple-moment representation of ice in the Predicted Particle Properties (P3) microphysics scheme. J. Atmos. Sci., 73, 439–458, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-20-0084.1.
Mlawer, E. J., S. J. Taubman, P. D. Brown, M. J. Iacono, and S. A. Clough, 1997: Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the long-wave. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 102, 16 663–16 682. https://doi.org/10.1029/97JD00237.
Molthan, A. L., and B. A. Colle, 2012: Comparisons of single-and double-moment microphysics schemes in the simulation of a synoptic-scale snowfall event. Mon. Wea. Rev., 140, 2982–3002, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-11-00292.1.
Molthan, A. L., B. A. Colle, S. E. Yuter, and D. Stark, 2016: Comparisons of modeled and observed reflectivities and fall speeds for snowfall of varied riming degrees during winter storms on Long Island, New York. Mon. Wea. Rev., 144, 4327–4347, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-15-0397.1.
Morrison, H., and W. W. Grabowski, 2008: A novel approach for representing ice microphysics in models: Description and tests using a kinematic framework. J. Atmos. Sci., 65, 1528–1548, https://doi.org/10.1175/2007JAS249L1.
Morrison, H., and J. A. Milbrandt, 2015: Parameterization of cloud microphysics based on the prediction of bulk ice particle properties. Part I: Scheme description and idealized tests. J. Atmos. Sci., 72, 287–311, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-14-0065.1.
Morrison, H., J. A. Curry, and V. I. Khvorostyanov, 2005: A new double-moment microphysics parameterization for application in cloud and climate models. Part I: Description. J. Atmos. Sci., 64, 1665–1677, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS3446.1.
Morrison, H., and Coauthors, 2020: Confronting the challenge of modeling cloud and precipitation microphysics. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 12, e2019MS001689, https://doi.org/10.1029/2019MS001689.
Naeger, A. R., B. A. Colle, and A. Molthan, 2017: Evaluation of cloud microphysical schemes for a warm frontal snowband during the GPM Cold Season Precipitation Experiment (GCPEx). Mon. Wea. Rev., 145, 4627–4650, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-17-0081.1.
Naeger, A. R., B. A. Colle, N. Zhou, and A. Molthan, 2020: Evaluating warm and cold rain processes in cloud microphysical schemes using OLYMPEX field measurements. Mon. Wea. Rev., 148, 2163–2190, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-19-0092.1.
Reisner, J., R. M. Rasmussen, and R. T. Bruintjes, 1998: Explicit forecasting of supercooled liquid water in winter storms using the MM5 mesoscale model. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 124, 1071–1107, https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49712454804.
Rutledge, S. A., and P. V. Hobbs, 1984: The mesoscale and microscale structure and organization of clouds and precipitation in midlatitude cyclones. XII: A diagnostic modeling study of precipitation development in narrow cold-frontal rainbands. J. Atmos. Sci., 41, 2949–2972, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1984)041<2949:TMAMSA>2.0.CO;2.
Stoelinga, M. T., and Coauthors, 2003: Improvement of microphysical parameterization through observational verification experiment. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 84, 1807–1826, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-84-12-1807.
Thompson, G., and T. Eidhammer, 2014: A study of aerosol impacts on clouds and precipitation development in a large winter cyclone. J. Atmos. Sci., 71, 3636–3658, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-13-0305.1.
Thompson, G., P. R. Field, R. M. Rasmussen, and W. D. Hall, 2008: Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme. Part II: Implementation of a new snow parameterization. Mon. Wea. Rev., 136, 5095–5115, https://doi.org/10.1175/2008MWR2387.1.
Tsai, T. C., and J. P. Chen, 2020: Multimoment ice bulk micro-physics scheme with consideration for particle shape and apparent density. Part I: Methodology and idealized simulation. J. Atmos. Sci., 77, 1821–1850, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-19-0125.1.
Vitart, F., G. Balsamo, J. R. Bidlot, S. Lang, I. Tsonevsky, D. Richardson, and M. Balmaseda, 2019: Use of ERA5 reanalysis to initialise re-forecasts proves beneficial. ECMWF Newsletter, 161, 26–31, https://doi.org/10.21957/g71fv083lm.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments that helped strengthen the manuscript. This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFC1510305) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41705119 and 41575131). Baojun CHEN also acknowledges support from the CMA Key Innovation Team (CMA2022ZD10). Qiujuan FENG was supported by the General Project of Natural Science Research in Shanxi Province (20210302123358) and the Key Projects of Shanxi Meteorological Bureau (SXKZDDW20217104). The airborne data were obtained from Hebei Provincial Weather Modification Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Article Highlights
• Active riming and aggregation occurred within the embedded convective region.
• Compared with P3-nc, P3-2ice produced more efficient aggregation and more realistic radar structures.
• The simulated embedded convective region was affected by the ice mass flux associated with riming.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, T., Chen, B., Lei, H. et al. Evaluation of the Predicted Particle Properties (P3) Microphysics Scheme in Simulations of Stratiform Clouds with Embedded Convection. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 40, 1859–1876 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-023-2178-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-023-2178-7