Abstract
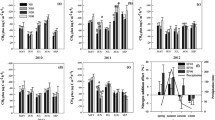
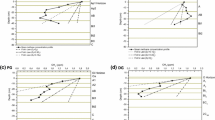
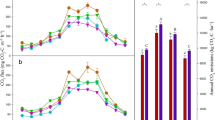
Methane (CH4) is an important greenhouse gas second only to CO2 in terms of its greenhouse effect. Vegetation plays an important role in controlling soil CH4 fluxes, but the spatial variability of soil CH4 fluxes during vegetation restoration in Loess Hilly Region (LHR) is not fully understood. The effects of different plant community types Medicago sativa grassland (MS); Xanthoceras sorbifolium forestland (XS); Caragana korshinskii bushland (CK); Hippophae rhamnoides shrubland (HR); and Stipa bungeana grassland (SB)] on soil CH4 flux in LHR were studied via the static chamber technique. The results showed that the five plant community types were sinks of soil CH4 in LHR, the plant community type significantly affected the soil CH4 flux, and the average CH4 uptake from high to low was in SB, HR, CK, MS, and XS. During the whole study period, the soil CH4 flux showed similar interannual variation. The maximum absorption of soil CH4 appeared in the growing season, while the minimum appeared in winter. Soil CH4 uptake was positively correlated with soil temperature and soil moisture. Soil temperature and moisture are important controlling factors for the temporal variability of soil CH4 flux. In LHR, the Stipa bungeana grassland is the more suitable plant community type for reducing soil CH4 emissions. In the process of vegetation restoration in LHR, the soil CH4 absorption potential of different plant community types should be considered, ecological benefits should be taken into account, and vegetation more suitable for mitigating the greenhouse effect should be selected.
摘要
甲烷(CH4)是一种温室效应仅次于二氧化碳的重要温室气体。植被在控制土壤CH4通量方面起着及其重要的作用,但在黄土丘陵区植被恢复过程中,土壤CH4通量的空间变异性还缺乏认识。本文通过静态箱技术,研究了不同植物群落类型[Medicago sativa草地(MS);Xanthoceras sorbifolium林地(XS);Caragana korshinskii灌丛(CK);Hippophae rhamnoides灌木林(HR);Stipa bungeana草地(SB)]对黄土丘陵区土壤CH4通量的影响。结果表明,五种植物群落类型都是黄土丘陵区土壤CH4的汇,植物群落类型对土壤CH4通量有明显影响,不同植物群落类型下CH4吸收量平均由高到低分别为SB、HR、CK、MS、XS。在整个研究期间,不同植物群落类型下土壤CH4通量呈现类似的年际变化。土壤CH4的最大吸收量出现在生长季节,而最小吸收量出现在冬季。土壤CH4吸收量与土壤温度和土壤湿度呈正相关。土壤温度和水分是土壤CH4通量的时间变化的重要控制因素。在黄土丘陵区,Stipa bungeana草地是比较适合减少土壤CH4排放的植物群落类型。在黄土丘陵区的植被恢复过程中,应考虑不同植物群落类型的土壤CH4吸收潜力,考虑生态效益,并选择更适合缓解温室效应的植被。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai, J., Y. Lyu, Y.-C. Li, X. Zhong, and J. Li, 2021: Methanotrophs bacteria in special environment: A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32, 1509–1517, https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.202104.031. (in Chinese with English abstract)
An, S. S., Y. M. Huang, and B. C. Li, 2006: Characteristics of soil water stable aggregates and relationship with soil properties during vegetation rehablitation in a loess hilly region. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 37, 45–50, https://doi.org/10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2006.01.010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Barrie, L., G. Braathen, J. Butler, E. Dlugokencky, D. J. Hofmann, P. Tans, and Y. Tsutsumi, 2009: WMO Greenhouse Gas Bulletin. Eurpoean Geosciences Union General Assembly 2009,Vienna, Austria. [Available online from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260797073_Annual_Greenhouse_Gas_Bulletin]
Bai, J., and Coauthors, 2017: Relative contribution of photorespiration and antioxidative mechanisms in Caragana korshinskii under drought conditions across the Loess Plateau. Functional Plant Biology, 44, 1111–1123, https://doi.org/10.1071/FP17060.
Bhandral, R., S. Saggar, N. S. Bolan, and M. J. Hedley, 2007: Transformation of nitrogen and nitrous oxide emission from grassland soils as affected by compaction. Soil and Tillage Research, 94, 482–492, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2006.10.006.
Bhullar, G. S., P. J. Edwards, and H. O. Venterink, 2013a: Variation in the plant-mediated methane transport and its importance for methane emission from intact wetland peat mesocosms. Journal of Plant Ecology, 6(4), 298–304, https://doi.org/10.1093/jpe/rts045.
Bhullar, G. S., M. Iravani, P. J. Edwards, and H. O. Venterink, 2013b: Methane transport and emissions from soil as affected by water table and vascular plants. BMC Ecology, 13, 32, https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6785-13-32.
Billings, W. D., 1952: The environmental complex in relation to plant growth and distribution. The Quarterly Review of Biology, 27, 251–265, https://doi.org/10.1086/399022.
Brummell, M. E., R. E. Farrell, and S. D. Siciliano, 2012: Greenhouse gas soil production and surface fluxes at a high arctic polar oasis. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 52, 1–12, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.03.019.
Bubier, J. L., T. R. Moore, and N. T. Roulet, 1993: Methane emissions from wetlands in the Midboreal region of Northern Ontario, Canada. Ecology, 74, 2240–2254, https://doi.org/10.2307/1939577.
Cao, M. K., S. Marshall, and K. Gregson, 1996: Global carbon exchange and methane emissions from natural wetlands: Application of a process-based model. J. Geophys. Res., 101, 14 399–14 414, https://doi.org/10.1029/96JD00219.
Carmichael, M. J., E. S. Bernhardt, S. L. Bräuer, and W. K. Smith, 2014: The role of vegetation in methane flux to the atmosphere: Should vegetation be included as a distinct category in the global methane budget. Biogeochemistry, 119, 1–24, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-014-9974-1.
Castro, M. S., P. A. Steudler, J. M. Melillo, J. D. Aber, and R. D. Bowden, 1995: Factors controlling atmospheric methane consumption by temperate forest soils. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 9, 1–10, https://doi.org/10.1029/94GB02651.
Chai, L. L., G. Hernandez-Ramirez, D. S. Hik, I. C. Barrio, C. M. Frost, C. C. Soto, and G. Esquivel-Hernández, 2020: A methane sink in the Central American high elevation páramo: Topographic, soil moisture and vegetation effects. Geoderma, 362, 114092, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.114092.
Chen, H. S., 2003: Study on soil water movement and its cycling on a hillslope of the loess plateau. PhD dissertation, Northwest A&F University. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen, M. C., G. Y. Zhang, Y. B. Zou, and H. Min, 2002: Methane oxidation of green-house soils. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture & Life Sciences), 28, 501–506, https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1008-9209.2002.05.008. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen, S. P., 2009: Full utilization of soil and water resources of the Loess Plateau in the middle and Eastern parts of Gansu Province. Technical Supervision in Water Resources, 17, 22–23, https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-1305.2009.05.010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Christiansen, J. R., and P. Gundersen, 2011: Stand age and tree species affect N2O and CH4 exchange from afforested soils. Biogeosciences, 8, 2535–2546, https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-8-2535-2011.
Conrad, R., 1996: Soil microorganisms as controllers of atmospheric trace gases (H2, CO, CH4, OCS, N2O, and NO). Microbiological Reviews, 60, 609–640, https://doi.org/10.1128/MR.60.4.609-640.1996.
Cui, L. J., and Coauthors, 2017: Rewetting decreases carbon emissions from the Zoige Alpine Peatland on the Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability, 9, 948, https://doi.org/10.3390/su9060948.
Curry, C. L., 2007: Modeling the soil consumption of atmospheric methane at the global scale. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 21, GB4012, https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GB002818.
Dalal, R. C., and D. E. Allen, 2008: Greenhouse gas fluxes from natural ecosystems. Australian Journal of Botany, 56, 396–407, https://doi.org/10.1071/BT07128.
De La Bárcena, T. G., L. D’Imperio, P. Gundersen, L. Vesterdal, A. Priemé, and J. R. Christiansen, 2014: Effects of the conversion of cropland to forest on the CH4 oxidation capacity in soils. Applied Soil Ecology, 79, 49–58, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.03.004.
Ding, W. X., Z. C. Cai, and H. Tsuruta, 2004: Methane concentration and emission as affected by methane transport capacity of plants in freshwater marsh. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 158, 99–111, https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000044836.71634.3d.
Do Carmo, J. B., E. R. De Sousa Neto, P. J. Duarte-Neto, J. P. H. B. Ometto, and L. A. Martinelli, 2012: Conversion of the coastal Atlantic forest to pasture: Consequences for the nitrogen cycle and soil greenhouse gas emissions. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 148, 37–43, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.11.010.
Dou, X. L., W. Zhou, Q. F. Zhang, and X. L. Cheng, 2015: Greenhouse gas (CO2, CH4, N2O) emissions from soils following afforestation in central China. Atmos. Environ., 126, 98–106, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.11.054.
Dutta, M. K., R. Ray, R. Mukherjee, T. K. Jana, and S. K. Mukhopadhyay, 2015: Atmospheric fluxes and photo-oxidation of methane in the mangrove environment of the Sundarbans, NE coast of India; A case study from Lothian Island. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 213, 33–41, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.06.010.
Fang, Y. T., P. Gundersen, W. Zhang, G. Y. Zhou, J. R. Christiansen, J. M. Mo, S. F. Dong, and T. Zhang, 2009: Soil-atmosphere exchange of N2O, CO2 and CH4 along a slope of an evergreen broad-leaved forest in southern China. Plant and Soil, 319, 37–48, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9847-2.
FAO, 2010: Global Forest Resources Assessment 2010. FAO, 54 pp.
Fernández-Duque, B., I. A. Pérez, M. Á. García, N. Pardo, and M. L. Sánchez, 2020: Local regressions for decomposing CO2 and CH4 time-series in a semi-arid ecosystem. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 11, 213–223, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2019.10.012.
Frenzel, P., and E. Karofeld, 2000: CH4 emission from a hollow-ridge complex in a raised bog: The role of CH4 production and oxidation. Biogeochemistry, 51, 91–112, https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006351118347.
Gatica, G., M. E. Fernández, M. P. Juliarena, and J. Gyenge, 2020: Environmental and anthropogenic drivers of soil methane fluxes in forests: Global patterns and among — biomes differences. Global Change Biology, 26, 6604–6615, https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15331.
Glatzel, S., N. Basiliko, and T. Moore, 2004: Carbon dioxide and methane production potentials of peats from natural, harvested and restored sites, Eastern Québec, Canada. Wetlands, 24, 261–267, https://doi.org/10.1672/0277-5212(2004)024[0261:CDAMPP]2.0.CO;2.
Gong, Z. T., and Coauthors, 2007: Chinese soil taxonomy. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 21, 36–38.
Harazono, Y., and Coauthors, 2006: Temporal and spatial differences of methane flux at arctic tundra in Alaska. Memoirs of National Institute of Polar Research, 59, 79–95.
Harriss, R. C., and S. E. Frolking, 1992: The sensitivity of methane emissions from Northern Freshwater wetlands to global warming. Global Climate Change and Freshwater Ecosystems, P. Firth and S. G. Fisher, Eds., Springer, 48–67, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-2814-1_3.
Heilman, M. A., and R. G. Carlton, 2001: Methane oxidation associated with submersed vascular macrophytes and its impact on plant diffusive methane flux. Biogeochemistry, 52, 207–224, https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006427712846.
Hong, S., and V. Lakshmi, 2005: Relation between satellite-derived vegetation indices, surface temperature, and vegetation water content. Proc. 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, IEEE, 1118–1122, https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2005.1525312.
Inubushi, K., H. Sugii, S. Nishino, and E. Nishino, 2001: Effect of aquatic weeds on methane emission from submerged paddy soil. American Journal of Botany, 88, 975–979, https://doi.org/10.2307/2657078.
IPCC, 2007: Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press.
IPCC, 2013: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press.
Jespersen, D. N., B. K. Sorrell, and H. Brix, 1998: Growth and root oxygen release by Typha latifolia and its effects on sediment methanogenesis. Aquatic Botany, 61, 165–180, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3770(98)00071-0.
Ji, B., Z. J. Wang, Z. B. Pan, H. Xu, X.-S. Han, and Y. Z. Xie, 2020: Soil carbon storage characteristics of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) Artificial grasslands in the semi-arid hilly gully region of the Loess Plateau, China. Russian Journal of Ecology, 51, 466–476, https://doi.org/10.1134/S1067413620050045.
Joabsson, A., and T. R. Christensen, 2001: Methane emissions from wetlands and their relationship with vascular plants: An Arctic example. Global Change Biology, 7, 919–932, https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1354-1013.2001.00044.x.
Joabsson, A., T. R. Christensen, and B. Wallén, 1999: Vascular plant controls on methane emissions from northern peatforming wetlands. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 14, 385–388, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-5347(99)01649-3.
Jones, W. J., D. P. Nagle Jr., and W. B. Whitman, 1987: Methanogens and the diversity of archaebacteria. Microbiological Reviews, 51, 135–177, https://doi.org/10.1128/mr.51.1.135-177.1987.
Ju, H., G. Z. Shen, M. Z. Ma, J. L. Ge, W. T. Xu, C. M. Zhao, and Q. L. Zhang, 2016: Greenhouse gas fluxes of typical northern subtropical forest soils: Impacts of land use change and reduced precipitation. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40, 1049–1063, https://doi.org/10.17521/cjpe.2016.0069. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Kim, S., S. Lee, M. McCormick, J. G. Kim, and H. Kang, 2016: Microbial community and greenhouse gas fluxes from abandoned rice paddies with different vegetation. Microbial Ecology, 72, 692–703, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0801-1.
Kim, Y. S., 2013: Soil-atmosphere exchange of CO2, CH4 and N2O in Northern temperate forests: Effects of elevated CO2 concentration, N deposition and forest fire. European Journal of Forest Research, 16, 1–43.
Lai, D. Y. F., 2009: Methane dynamics in northern Peatlands: A review. Pedosphere, 19, 409–421, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(09)00003-4.
Lai, D. Y. F., N. T. Roulet, and T. R. Moore, 2014a: The spatial and temporal relationships between CO2 and CH4 exchange in a temperate ombrotrophic bog. Atmos. Environ., 89, 249–259, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.02.034.
Lai, D. Y. F., T. R. Moore, and N. T. Roulet, 2014b: Spatial and temporal variations of methane flux measured by autochambers in a temperate ombrotrophic peatland. J. Geophys. Res., 119, 864–880, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JG002410.
Li, W., J. L. Wang, X. J. Zhang, S. L. Shi, and W. X. Cao, 2018: Effect of degradation and rebuilding of artificial grasslands on soil respiration and carbon and nitrogen pools on an alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Engineering, 111, 134–142, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.10.013.
Lin, X. W., and Coauthors, 2009: Fluxes of CO2, CH4, and N2O in an alpine meadow affected by yak excreta on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau during summer grazing periods. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41, 718–725, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.01.007.
Liu, Y. K., J.-Z. Pang, F. Yi, C.-H. Peng, S. X. Zhang, L. Hou, X. K. Wang, and H.-X. Zhang, 2019: Soil-atmosphere exchange of nitrous oxide, methane and carbon dioxide of different forest types at different elevations in Huoditang forest region of Qinling Mountains. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 34, 1–10, https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2019.01.01.
Lombardi, J. E., M. A. Epp, and J. P. Chanton, 1997: Investigation of the methyl fluoride technique for determining rhizospheric methane oxidation. Biogeochemistry, 36, 153–172, https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005750201264.
Luan, J. W., H. T. Song, C. H. Xiang, D. Zhu, and D. Suolang, 2016: Soil moisture, species composition interact to regulate CO2 and CH4 fluxes in dry meadows on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Engineering, 91, 101–112, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.02.012.
Ma, W. W., A.-R. M. Alhassan, Y. S. Wang, G. Li, H. Wang, and J. M. Zhao, 2018: Greenhouse gas emissions as influenced by wetland vegetation degradation along a moisture gradient on the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of North-West China. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 112, 335–354, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-018-9950-6.
Ma, W. W., G. Li, J. H. Wu, G. R. Xu, and J. Q. Wu, 2020: Respiration and CH4 fluxes in Tibetan peatlands are influenced by vegetation degradation. CATENA, 195, 104789, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104789.
Mills, R. T. E., N. Dewhirst, A. Sowerby, B. A. Emmett, and D. L. Jones, 2013: Interactive effects of depth and temperature on CH4 and N2O flux in a shallow podzol. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 62, 1–4, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.03.003.
Moore, T. R., and M. Dalva, 1993: The influence of temperature and water table position on carbon dioxide and methane emissions from laboratory columns of peatland soils. Journal of Soil Science, 44, 651–664, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1993.tb02330.x.
Nesbit, S. P., and G. A. Breitenbeck, 1992: A laboratory study of factors influencing methane uptake by soils. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 41, 39–54, https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-8809(92)90178-E.
Neubauer, S. C., and J. P. Megonigal, 2015: Moving beyond global warming potentials to quantify the climatic role of ecosystems. Ecosystems, 18, 1000–1013, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-015-9879-4.
Oertel, C., J. Matschullat, K. Zurba, F. Zimmermann, and S. Erasmi, 2016: Greenhouse gas emissions from soils—A review. Geochemistry, 76, 327–352, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2016.04.002.
Olefeldt, D., M. R. Turetsky, P. M. Crill, and A. D. McGuire, 2013: Environmental and physical controls on northern terrestrial methane emissions across permafrost zones. Global Change Biology, 19, 589–603, https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12071.
Pihlatie, M., A. J. Kieloaho, E. Halmeenmäki, K. Ryhti, and J. Heinonsalo, 2017: Ground vegetation reduces forest floor net CH4 uptake in a boreal upland forest. Preprints, Egu General Assembly Conf, 4945, https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017EGUGA..19.4945P.
Plain, C., F.-K. Ndiaye, P. Bonnaud, J. Ranger, and D. Epron, 2019: Impact of vegetation on the methane budget of a temperate forest. The New Phytologist, 221, 1447–1546, https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15452.
Robertson, G. P., 1989: Nitrification and denitrification in humid tropical ecosystems: potential controls on nitrogen retention. Mineral nutrients in tropical forest and savanna ecosystems, 9, 55–69.
Rusch, H., and H. Rennenberg, 1998: Black alder (Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn.) trees mediate methane and nitrous oxide emission from the soil to the atmosphere. Plant and Soil, 201, 1–7, https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004331521059.
Schimel, J. P., 1995: Plant transport and methane production as controls on methane flux from arctic wet meadow tundra. Biogeochemistry, 28, 183–200, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02186458.
Sebacher, D. I., R. C. Harriss, and K. B. Bartlett, 1985: Methane emissions to the atmosphere through aquatic plants. Journal of Environmental Quality, 14, 40–46, https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1985.00472425001400010008x.
Shannon, R. D., J. R. White, J. E. Lawson, and B. S. Gilmour, 1996: Methane efflux from emergent vegetation in peatlands. Journal of Ecology, 84, 239–246, https://doi.org/10.2307/2261359.
Shi, R. A., L. J. Li, M. Y. You, J. Ding, S. Wang, and X. Z. Han, 2013: Impact of soil temperature and moisture on Soil N2O emission from mollisols under different land-use types. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 32, 2286–2292, https://doi.org/10.11654/jaes.2013.11.026. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Simpson, I. J., G. C. Edwards, G. W. Thurtell, G. Den Hartog, H. H. Neumann, and R. M. Staebler, 1997: Micrometeorological measurements of methane and nitrous oxide exchange above a boreal aspen forest. J. Geophys. Res., 102, 29 331–29 341, https://doi.org/10.1029/97JD03181.
Singh, B. K., R. D. Bardgett, P. Smith, and D. S. Reay, 2010: Microorganisms and climate change: Terrestrial feedbacks and mitigation options. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 8, 779–790, https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2439.
Solomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, M. Marquis, K. Averyt, M. M. B. Tignor, and J. H. L. Miller, 2007: Climate change 2007: The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. ed. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (United Kingdom).
Song, C. C., X. F. Xu, H. Q. Tian, and Y. Y. Wang, 2009: Ecosystem-atmosphere exchange of CH4 and N2O and ecosystem respiration in wetlands in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeastern China. Global Change Biology, 15, 692–705, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01821.x.
Ström, L., A. Ekberg, M. Mastepanov, and T. R. Christensen, 2003: The effect of vascular plants on carbon turnover and methane emissions from a tundra wetland. Global Change Biology, 9, 1185–1192, https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00655.x.
Ström, L., M. Mastepanov, and T. R. Christensen, 2005: Species-specific effects of vascular plants on carbon turnover and methane emissions from wetlands. Biogeochemistry, 75, 65–82, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-6124-1.
Sun, J. X., D. Liu, L. Qin, X. N. Zhang, X. M. He, and G. H. Lv, 2012: Research on Soil CH4 flux of cotton fields and abandoned lands in Ebinur Lake Area. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 49, 1489–1496, https://doi.org/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2012.08.019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tang, K. L., Q. C. Hou, B. K. Wang, and P. C. Zhang, 1993: The environment background and administration way of wind-water erosion crisscross region and Shenmu Experimental Area on the loess Plateau. Memoir of NISWC, Academia Sinica and Ministry of Water Resources, 18, 2–15, http://stbcyj.paperonce.org/oa/darticle.aspx?id=19930202. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Thompson, A. M., K. B. Hogan, and J. S. Hoffman, 1992: Methane reductions: Implications for global warming and atmospheric chemical change. Atmospheric Environment. Part A. General Topics, 26, 2665–2668, https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-1686(92)90118-5.
Von Fischer, J. C., and L. O. Hedin, 2007: Controls on soil methane fluxes: Tests of biophysical mechanisms using stable isotope tracers. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 21, GB2007, https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GB002687.
Von Fischer, J. C., R. C. Rhew, G. M. Ames, B. K. Fosdick, and P. E. Von Fischer, 2010: Vegetation height and other controls of spatial variability in methane emissions from the Arctic coastal tundra at Barrow, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res., 115, G00I03, https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JG001283.
Wang, H. X., 2014: Artificial grass grazing CH4 fluxes characteristics of different semi-arid region of region of inner Mongolia. M.S. thesis, School of Resources and Environment. Inner Mongolia University. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang, H. Y., J. Q. Wu, G. Li, and L. J. Yan, 2020: Changes in soil carbon fractions and enzyme activities under different vegetation types of the northern Loess Plateau. Ecology and Evolution, 10, 12 211–12 223, https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.6852.
Wang, X. H., and J. Bennett, 2008: Policy analysis of the conversion of cropland to forest and grassland program in China. Environmental Economics and Policy Studies, 9, 119–143, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03353986.
Wang, Y. F., and Coauthors, 2014: Soil methane uptake by grasslands and forests in China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 74, 70–81, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.02.023.
Wang, Y. S., and Y. H. Wang, 2003: Quick measurement of CH4, CO2 and N2O emissions from a short-plant ecosystem. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 20, 842–844, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02915410.
Wang, Z. T., L. Yang, G. Li, C. S. Chai, Y. D. Zhang, R. Chen, and J. Q. Zhang, 2019: Effects of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) degradation on herbage distribution and diversity in the semi-arid Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 3720–3729, https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201805181099. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wei, E. W., R. Yang, H. P. Zhao, P. H. Wang, S. Q. Zhao, W. C. Zhai, Y. Zhang, and H. L. Zhou, 2019: Microwave-assisted extraction releases the antioxidant polysaccharides from seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berries. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 123, 280–290, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.074.
Werner, C., R. Kiese, and K. Butterbach-Bahl, 2007: Soil-atmosphere exchange of N2O, CH4, and CO2 and controlling environmental factors for tropical rain forest sites in western Kenya. J. Geophys. Res., 112, D03308, https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD007388.
Werner, C., X. H. Zheng, J. W. Tang, B. H. Xie, C. Y. Liu, R. Kiese, and K. Butterbach-Bahl, 2006: N2O, CH4 and CO2 emissions from seasonal tropical rainforests and a rubber plantation in Southwest China. Plant and Soil, 289, 335–353, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-9143-y.
Whalen, S. C., 2005: Biogeochemistry of methane exchange between natural wetlands and the atmosphere. Environmental Engineering Science, 22, 73–94, https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2005.22.73.
Whalen, S. C., and W. S. Reeburgh, 1990: Consumption of atmospheric methane by tundra soils. Nature, 346, 160–162, https://doi.org/10.1038/346160a0.
Wilson, K. S., and E. R. Humphreys, 2010: Carbon dioxide and methane fluxes from Arctic mudboils. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 90, 441–449, https://doi.org/10.4141/CJSS09073.
WMO, 2020: WMO greenhouse gas bulletin: The state of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere based on global observations through 2019.
Wu, B., and C. C. Mu, 2019: Effects on greenhouse gas (CH4, CO2, N2O) emissions of conversion from over-mature forest to secondary forest and Korean pine plantation in northeast China. Forests, 10, 788, https://doi.org/10.3390/f10090788.
Wu, J. Q., H. Y. Wang, G. Li, W. W. Ma, J. H. Wu, Y. Gong, and G. R. Xu, 2020: Vegetation degradation impacts soil nutrients and enzyme activities in wet meadow on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Scientific Reports, 10, 21271, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78182-9.
Wu, J. Q., W. W. Ma, G. Li, and G. P. Chen, 2018: Effects of four vegetation types on soil physical characteristics and permeability in Loess Plateau. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 3, 133–138, https://doi.org/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2018.04.021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu, X., Z. Yao, N. Brüggemann, Z. Y. Shen, B. Wolf, M. Dannenmann, X. Zheng, and K. Butterbach-Bahl, 2010: Effects of soil moisture and temperature on CO2 and CH4 soil-atmosphere exchange of various land use/cover types in a semiarid grassland in Inner Mongolia, China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 42, 773–787, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.01.013.
Xia, J. J., Z. W. Yan, G. S. Jia, H. Q. Zeng, P. D. Jones, W. Zhou, and A. Z. Zhang, 2015: Projections of the advance in the start of the growing season during the 21st century based on CMIP5 simulations. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 33, 831–838, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-014-4125-0.
Xia, N., E. Z. Du, X. H. Wu, Y. Tang, Y. Wang, and W. De Vries, 2020: Effects of nitrogen addition on soil methane uptake in global forest biomes. Environmental Pollution, 264, 114751, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114751.
Yan, L. J., G. Li, J. Q. Wu, W. W. Ma, and H. Y. Wang, 2019: Effects of four typical vegetations on soil active organic carbon and soil carbon in Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 5546–5554, https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201805091031. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang, G., and Coauthors, 2014: Effects of soil warming, rainfall reduction and water table level on CH4 emissions from the Zoige peatland in China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 78, 83–89, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.07.013.
Yang, G., and Coauthors, 2019: Peatland degradation reduces methanogens and methane emissions from surface to deep soils. Ecological Indicators, 106, 105488, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105488.
Yang, J. J., S. S. An, H. Zhang, Y. N. Chen, T. H. Dang, and J. Y. Jiao, 2015: Effect of erosion on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity in the loess hills. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 5666–5674, https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201310302611. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang, J., M. Y. Liu, M. M. Zhang, J. H. Yang, and R. S. Cao, 2019: Characteristics of soil greenhouse gas fluxes under different forest types in the Loess Plateau tableland, China. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38, 944–956, https://doi.org/10.11654/jaes.2018-0826. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao, G. Q., M. Y. Liu, J. H. Yang, H. Liu, J. Zhang, M. M. Zhang, and X. R. Li, 2018: Spatial variations and environmental interpretations of soil greenhouse gases fluxes under different land-use types in the tableland of the Loess Plateau. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 49, 461–468, https://doi.org/10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2018.02.29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou, Q. Y., and Q. Cai, 2021: Role of ethylene in the regulatory mechanism underlying the abortion of ovules after fertilization in Xanthoceras sorbifolium. Plant Molecular Biology, 106, 67–84, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-021-01130-2.
Zhu, X. X., and Coauthors, 2015b: Effects of warming, grazing/cutting and nitrogen fertilization on greenhouse gas fluxes during growing seasons in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 214–215, 506–514, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.09.008.
Zhu, X. Y., C. C. Song, C. M. Swarzenski, Y. D. Guo, X. H. Zhang, and J. Y. Wang, 2015a: Ecosystem-atmosphere exchange of CO2 in a temperate herbaceous Peatland in the Sanjiang Plain of northeast China. Ecological Engineering, 75, 16–23, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.11.035.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the people who were involved in the field and laboratory work. This study was financially supported by the Gansu Province Key Research and Development Program (Grant No. 20YF8NA135), the Gansu Province Financial Special Project (Grant No. GSCZZ 20160909), and the Industrial Support Program Project (Grant No. 2021CYZC-15, No.2022CYZC-41). The authors would like to thank Director Jin CHEN, Xiaoping WANG, and other staff from the Soil and Water Conservation Research Institute in Dingxi City, Gansu Province, for their support with the management of the experimental field, and Bin WU of the Ecological Research Center of Northeast Forestry University for his advice on the experimental data in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Article Highlights
• The five plant community types studied are sinks of soil CH4 in LHR.
• Plant community type significantly affects soil CH4 flux, and the largest average soil CH4 uptake flux is in Stipa bungeana grassland.
• Max (min) soil CH4 uptake is in the growing season (winter); soil temperature and moisture control the temporal variation of soil CH4 flux.
• Stipa bungeana grassland is the ideal plant community type to reduce soil CH4 emissions in LHR.
This paper is a contribution to the special issue on Carbon Neutrality: Important Roles of Renewable Energies, Carbon Sinks, NETs, and non-CO2 GHGs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Li, G., Yan, L. et al. Effects of Plant Community Type on Soil Methane Flux in Semiarid Loess Hilly Region, Central Gansu Province, China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 39, 1360–1374 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-022-1169-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-022-1169-4