Abstract
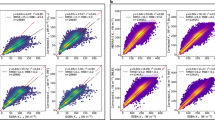
Long-term, ground-based daily global solar radiation (DGSR) at Zhongshan Station in Antarctica can quantitatively reveal the basic characteristics of Earth’s surface radiation balance and validate satellite data for the Antarctic region. The fixed station was established in 1989, and conventional radiation observations started much later in 2008. In this study, a random forest (RF) model for estimating DGSR is developed using ground meteorological observation data, and a high-precision, long-term DGSR dataset is constructed. Then, the trend of DGSR from 1990 to 2019 at Zhongshan Station, Antarctica is analyzed. The RF model, which performs better than other models, shows a desirable performance of DGSR hindcast estimation with an R2 of 0.984, root-mean-square error of 1.377 MJ m−2, and mean absolute error of 0.828 MJ m−2. The trend of DGSR annual anomalies increases during 1990–2004 and then begins to decrease after 2004. Note that the maximum value of annual anomalies occurs during approximately 2004/05 and is mainly related to the days with precipitation (especially those related to good weather during the polar day period) at this station. In addition to clouds and water vapor, bad weather conditions (such as snowfall, which can result in low visibility and then decreased sunshine duration and solar radiation) are the other major factors affecting solar radiation at this station. The high-precision, long-term estimated DGSR dataset enables further study and understanding of the role of Antarctica in global climate change and the interactions between snow, ice, and atmosphere.
摘 要
自1989年起, 中国在东南极拉斯曼丘陵建立中山站, 并开始地面常规气象要素业务观测, 但辐射观测始于2008年. 长期地面辐射资料的缺失, 为定量揭示极区地表辐射特征、 长期趋势变化和极区卫星产品验证带来挑战. 本研究基于南极中山站地面气象观测数据结合随机森林(RF)模型, 构建了1989年以来高精度的长时间序列日太阳总辐射 (DGSR) 历史数据集. 本文采用的RF模型具有超高的历史估算性能, 其精度指标R2为0.984, 均方根误差为1.377 MJ m-2, 平均绝对误差为0.828 MJ m-2. 此外, 对DGSR历史数据集进行长期趋势变化及其影响因子研究的结果表明: DGSR年异常值在1990 ~ 2004年呈增加趋势, 于2005年开始下降, 且年最大年异常值出现在2004/05年, 这主要与该站的降水日数变化有关. 除了云层和水汽外, 恶劣的天气条件(如降雪, 导致能见度低, 日照时间和太阳辐射减少)也是影响该站太阳辐射变化的主因之一.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai, S. T., S. S. Wang, Y. S. Li, G. Moholdt, C. X. Zhou, L. B. Liu, and Y. D. Yang, 2019: High-precision ice-flow velocities from ground observations on Dalk Glacier, Antarctica. Polar Science, 19, 13–23, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polar.2018.09.003.
Aun, M., and Coauthors, 2020: Solar UV radiation measurements in Marambio, Antarctica, during years 2017–2019. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 20, 6037–6054, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-20-6037-2020.
Bian, L. G., L. H. Lu, C. G. Lu, Z. F. Xue, P. Q. Jia, and Y. Wang, 1998: A study of radiative features at the Great Wall and Zhongshan Stations of Antarctica. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorology, 9, 160–168. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Bintanja, R., 1995: The local surface energy balance of the ecology glacier, King George Island, Antarctica: Measurements and modelling. Antarctic Science, 7(3), 315–325, https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954102095000435.
Braun, M., and R. Hock, 2004: Spatially distributed surface energy balance and ablation modelling on the ice cap of King George Island (Antarctica). Global and Planetary Change, 42, 45–58, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2003.11.010.
Che, H. Z., G. Y. Shi, X. Y. Zhang, R. Arimoto, J. Q. Zhao, L. Xu, B. Wang, and Z. H. Chen, 2005: Analysis of 40 years of solar radiation data from China, 1961–2000. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L06803, https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL022322.
Che, H. Z., and Coauthors, 2019: Large contribution of meteorological factors to inter-decadal changes in regional aerosol optical depth. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 19, 10497–10523, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-2019-360.
Chen, C., Q. M. Zhang, Q. Ma, and B. Yu, 2019: LightGBM-PPI: Predicting protein-protein interactions through LightGBM with multi-information fusion. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 191, 54–64, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2019.06.003.
Chen, G., Y. C. Wang, S. S. Li, W. Cao, H. Y. Ren, L. D. Knibbs, M. J. Abramson, and Y. M. Guo, 2018: Spatiotemporal patterns of PM10 concentrations over China during 2005–2016: A satellite-based estimation using the random forests approach. Environmental Pollution, 242, 605–613, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.012.
Chen, J.-L., G.-S. Li, and S.-J. Wu, 2013: Assessing the potential of support vector machine for estimating daily solar radiation using sunshine duration. Energy Conversion and Management, 75, 311–318, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2013.06.034.
Chen, Y. M., C. X. Zhou, S. T. Ai, Q. Liang, L. Zheng, R. X. Liu, and H. B. Lei, 2020: Dynamics of Dalk Glacier in East Antarctica derived from multisource satellite observations since 2000. Remote Sensing, 12, 1809, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111809.
Choi, T. I., S.-J. Kim, J. H. Kim, H. Kwon, and M. A. Lazzara, 2019: Characteristics of surface meteorology at Lindsey Islands, Amundsen Sea, West Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res., 124, 6294–6306, https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD029556.
Cortes, C., and V. Vapnik, 1995: Support-vector networks. Machine Learning, 20, 273–297, https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022627411411.
Ding, M. H., D. Y. Yang, M. R. Van Den Broeke, I. Allison, C. D. Xiao, D. H. Qin, and B. J. Huai, 2020: The surface energy balance at Panda 1 station, Princess Elizabeth Land: A typical katabatic wind region in East Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res., 125, e2019JD030378, https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD030378.
Dou, Y. K., G. Y. Zuo, X. M. Chang, and Y. Chen, 2019: A study of a standalone renewable energy system of the Chinese Zhongshan station in Antarctica. Applied Sciences, 9, 1968, https://doi.org/10.3390/app9101968.
Garbe, J., T. Albrecht, A. Levermann, J. F. Donges, and R. Winkelmann, 2020: The hysteresis of the Antarctic Ice Sheet. Nature, 585, 538–544, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2727-5.
Gui, K., and Coauthors, 2019: Satellite-derived PM2.5 concentration trends over Eastern China from 1998 to 2016: Relationships to emissions and meteorological parameters. Environmental Pollution, 247, 1125–1133, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.056.
Gui, K., and Coauthors, 2020: Construction of a virtual PM2.5 observation network in China based on high-density surface meteorological observations using the Extreme Gradient Boosting model. Environment International, 141, 105801, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105801.
Guo, J. P., and Coauthors, 2017: Declining frequency of summertime local-scale precipitation over eastern China from 1970 to 2010 and its potential link to aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett., 44, 5700–5708, https://doi.org/10.1022/2017GL073533.
He, Y. Y., and K. C. Wang, 2020: Variability in direct and diffuse solar radiation across China from 1958 to 2017. Geophys. Res. Lett., 47, e2019GL084570, https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL084570.
He, Y. Y., K. C. Wang, C. L. Zhou, and M. Wild, 2018: A revisit of global dimming and brightening based on the sunshine duration. Geophys. Res. Lett., 45, 4281–4289, https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL077424.
Huang, G. H., M. G. Ma, S. L. Liang, S. M. Liu, and X. Li, 2011: A LUT-based approach to estimate surface solar irradiance by combining MODIS and MTSAT data. J. Geophys. Res., 116(D22), D22201, https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JD016120.
Jaross, G., and J. Warner, 2008: Use of Antarctica for validating reflected solar radiation measured by satellite sensors. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D16S34, https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD008835.
Jiang, Y. N., 2009: Computation of monthly mean daily global solar radiation in China using artificial neural networks and comparison with other empirical models. Energy, 44, 1276–1283, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2009.05.009.
Ke, G. L., Q. Meng, T. Finley, T. F. Wang, W. Chen, W. D. Ma, Q. W. Ye, and T.-Y. Liu, 2017: LightGBM: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. Proc. 31st Int. Conf. on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, NIPS, 3146–3154.
Lacelle, D., C. Lapalme, A. F. Davila, W. Pollard, M. Marinova, J. Heldmann, and C. P. McKay, 2016: Solar radiation and air and ground temperature relations in the cold and hyperarid Quartermain Mountains, McMurdo Dry Valleys of Antarctica. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes, 27, 163–176, https://doi.org/10.1002/ppp.1859.
Ohmura, A., 2009: Observed decadal variations in surface solar radiation and their causes. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D00D05, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD011290.
Park, S.-J., T.-J. Choi, and S.-J. Kim, 2013: Heat flux variations over sea ice observed at the coastal area of the sejong station, Antarctica. Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 49, 443–450, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-013-0040-z.
Qin, J., Z. Q. Chen, K. Yang, S. L. Liang, and W. J. Tang, 2011: Estimation of monthly-mean daily global solar radiation based on MODIS and TRMM products. Applied Energy, 88, 2480–2489, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.01.018.
Quinlan, J., 1986: Induction of decision trees. Machine Learning, 1, 81–106, https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022643204877.
Scott, R. C., D. Lubin, A. M. Vogelmann, and S. Kato, 2017: West Antarctic ice sheet cloud cover and surface radiation budget from NASA A-Train satellites. J. Climate, 30, 6151–6170, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0644.1.
Soares, J., M. Alves, F. N. D. Ribeiro, and G. Codato, 2019: Surface radiation balance and weather conditions on a non-glaciated coastal area in the Antarctic region. Polar Science, 23, 117–128, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polar.2019.04.001.
Stanhill, G., and S. Cohen, 1997: Recent changes in solar irradiance in Antarctica. J. Climate, 10, 2078–2086, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1997)010<2078:RCISII>2.0.CO;2.
Tang, W. J., K. Yang, J. He, and J. Qin, 2010: Quality control and estimation of global solar radiation in China. Solar Energy, 84, 466–475, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2010.01.006.
Tang, W.-J., K. Yang, J. Qin, C. C. K. Cheng, and J. He, 2011: Solar radiation trend across China in recent decades: A revisit with quality-controlled data. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11, 393–406, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-393-2011.
Tang, W. J., K. Yang, J. Qin, and M. Min, 2013: Development of a 50-year daily surface solar radiation dataset over China. Science China Earth Sciences, 56, 1555–1565, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-012-4542-9.
Tang, W. J., K. Yang, J. Qin, M. Min, and X. L. Niu, 2018: First effort for constructing a direct solar radiation data set in china for solar energy applications. J. Geophys. Res., 123, 1724–1734, https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD028005.
Wang, G. C., and X. Z. Xiong, 1991: Analysis of some characteristics of solar radiation at Zhongshan Station, Antarctica. Antarctic Research, 3, 64–68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang, L. C., O. Kisi, M. Zounemat-Kermani, G. A. Salazar, Z. M. Zhu, and W. Gong, 2016: Solar radiation prediction using different techniques: Model evaluation and comparison. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 61, 384–397, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.04.024.
Wang, R. H., 2012: AdaBoost for feature selection, classification and its relation with SVM, a review. Physics Procedia, 25, 800–807, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2012.03.160.
Wang, Y. W., and M. Wild, 2016: A new look at solar dimming and brightening in China. Geophys. Res. Lett., 43, 11777–11785, https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL071009.
Wen, J., J. L. Zhao, S. W. Luo, and Z. Han, 2002: The improvements of BP neural network learning algorithm. Proc. 5th Int. Conf. on Signal Processing Proceedings. 16th World Computer Congress 2000, Beijing, IEEE, 1647–1649, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICOSP.2000.893417.
Wild, M., 2009: Global dimming and brightening: A review. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D00D16, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD011470.
Wild, M., and Coauthors, 2005: From dimming to brightening: Decadal changes in solar radiation at Earth’s surface. Science, 308, 847–850, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1103215.
Xue, W. T., and Coauthors, 2019: Declining diurnal temperature range in the North China Plain related to environmental changes. Climate Dyn., 52, 6109–6119, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4505-8.
Yang, Y. K., S. P. Palm, A. Marshak, D. L. Wu, H. B. Yu, and Q. Fu, 2014: First satellite-detected perturbations of outgoing longwave radiation associated with blowing snow events over Antarctica. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 730–735, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013GL058932.
Yu, L., and Coauthors, 2019: The variability of surface radiation fluxes over landfast sea ice near Zhongshan Station, east Antarctica during austral spring. International Journal of Digital Earth, 12, 860–877, https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2017.1304458.
Zelterman, D., 2015: Applied Multivariate Statistics with R. Springer, 393 pp, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14093-3.
Zeng, Z. L., and Coauthors, 2020: Daily global solar radiation in china estimated from high-density meteorological observations: A random forest model framework. Earth and Space Science, 7, e2019EA001058, https://doi.org/10.1029/2019EA001058.
Zhang, T., C. X. Zhou, and L. Zheng, 2019: Analysis of the temporal-spatial changes in surface radiation budget over the Antarctic sea ice region. Science of the Total Environment, 666, 1134–1150, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.264.
Zhang, X. T., S. L. Liang, G. X. Wang, Y. J. Yao, B. Jiang, and J. Cheng, 2016: Evaluation of the reanalysis surface incident shortwave radiation products from NCEP, ECMWF, GSFC, and JMA using satellite and surface observations. Remote Sensing, 8, 225, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030225.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41941010, 41771064 and 41776195), the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFC1400303), and the Basic Fund of the Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences (Grant No. 2018Z001). We greatly appreciate the help from the Polar Research Institute of China and the Antarctic expeditioners at the Chinese Zhongshan Station. The long-term (March 1989-February 2020) estimated DGSR dataset can be acquired in the Mendeley data repository (data identification number: https://doi.org/10.17632/2y2mmhzvcx.1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Article Highlights
• A thirty-year DGSR dataset, which was produced by combining in situ meteorological observation records with a random forest model, is presented.
• The RF model shows the best performance for estimating historical DGSR with an R2 of 0.984, root-mean-square error of 1.377 MJ m−2, and mean absolute error of 0.828 MJ m−2.
• The long-term DGSR trend generally increases during 1990–2004 and then begins to decrease after 2004 at Zhongshan Station.
• Clouds, water vapor, and abnormal weather events in Antarctica are major factor affecting solar radiation.
Electronic Supplementary Material to
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Z., Wang, Z., Ding, M. et al. Estimation and Long-term Trend Analysis of Surface Solar Radiation in Antarctica: A Case Study of Zhongshan Station. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 38, 1497–1509 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-021-0386-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-021-0386-6