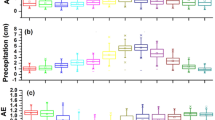
Abstract
Industrial pollution has a significant effect on aerosol properties in Changsha City, a typical city of central China. Therefore, year-round measurements of aerosol optical, radiative and chemical properties from 2012 to 2014 at an urban site in Changsha were analyzed. During the observation period, the energy structure was continuously optimized, which was characterized by the reduction of coal combustion. The aerosol properties have obvious seasonal variations. The seasonal average aerosol optical depth (AOD) at 500 nm ranged from 0.49 to 1.00, single scattering albedo (SSA) ranged from 0.93 to 0.97, and aerosol radiative forcing at the top of the atmosphere (TOA) ranged from −24.0 to 3.8 W m−2. The chemical components also showed seasonal variations. Meanwhile, the scattering aerosol, such as organic carbon, SO42−, NO3−, and NH4+ showed a decrease, and elemental carbon increased. Compared with observation in winter 2012, AOD and TOA decreased by 0.14 and −1.49 W m−2 in winter 2014. The scattering components, SO42−, NO3− and NH4+, decreased by 12.8 µg m−3 (56.8%), 9.2 µg m−3 (48.8%) and 6.4 µg m−3 (45.2%), respectively. The atmospheric visibility and pollution diffusion conditions improved. The extinction and radiative forcing of aerosol were significantly controlled by the scattering aerosol. The results indicate that Changsha is an industrial city with strong scattering aerosol. The energy structure optimization had a marked effect on controlling pollution, especially in winter (strong scattering aerosol).
摘要
工业污染对中国中部典型城市长沙市的气溶胶特性具有很大的影响。2012−14年观测表明, 长沙的气溶胶特性具有明显的季节性变化。冬季各参数明显高于其他季节, 夏季表现出低值。500 nm波段气溶胶光学厚度(AOD)冬季均值为0.90, 夏季为0.75, 大气层顶气溶胶辐射强迫(TOA)冬季的冷却效应比夏季强−18.3 W m−2, PM2.5冬季比夏季高43.5 μg m−3。化学成分也表现出相应的季节性变化。PM2.5中有机碳(OC)、SO42−、NO3−和NH4+散射性气溶胶冬季均值分别比夏季高9.1 μg m−3、6.1 μg m−3、15.8 μg m−3、8.9 μg m−3。不同来向气团气溶胶特性也有较大差异。来源于南方湿润气团的AOD较小(0.54−0.64), PM2.5浓度也较低(32.0−36.1 μg m−3), 对应的TOA呈现加热效应(4.3−4.5 W m−2)。来源于西北方的干燥气团带来粗模态粒子, PM2.5浓度仍相对较低(43.6−79.4 μg m−3), 对应的AOD与TOA分别为0.65−0.84和−16.8至−2.46 W m−2, 表现为弱冷却效应。局地传输气团气溶胶污染最严重, AOD、TOA 和PM2.5可达1.56、−52.9 W m−2和114 μg m−3。随着国家大气污染防治行动计划执行, 2012−14年该地区能源结构不断优化, 燃煤比重显著减小。OC、SO42−、NO3−和NH4+等散射性气溶胶减少。与2012年冬季的观测值相比, 2014年冬季的AOD和TOA分别下降了0.14和−1.49 W m−2。SO42−, NO3−和NH4+这三种散射性成分分别下降了12.8 μg m−3(56.8%), 9.2 μg m−3(48.8%)和6.4 μg m−3(45.2%)。该地区气溶胶的消光和辐射强迫主要受散射性气溶胶的控制, 随着能源结构调整, 散射性气溶胶大幅度减少, 大气能见度和污染扩散条件得到了改善。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, J. J., and Coauthors, 2005: Characterization and source apportionment of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon during fall and winter of 2003 in Xi’an, China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 5(11), 3127–3137, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-5-3127-2005.
Cao, S., D. Wu, L. Z. Chen, J. R. Xia, J. G. Lu, G. Liu, F. Y. Li, and M. Yang, 2016: Characteristics of water-soluble inorganic ions of aerosol in China: A review. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(8), 103–115, https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2016.08.018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Carslaw, K. S., O. Boucher, D. V. Spracklen, G. W. Mann, J. G. L. Rae, S. Woodward, and M. Kulmala, 2010: A review of natural aerosol interactions and feedbacks within the Earth system. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 10, 1701–1737, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-1701-2010.
Changsha Municipal Bureau of Statistics, and Changsha investigation team of National Bureau of Statistics, 2018: Changsha Statistical Yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Charlson, R. J., S. E. Schwartz, J. M. Hales, R. D. Cess, J. A. Coakley Jr., J. E. Hansen, and D. J. Hofmann, 1992: Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Sciences, 255(5043), 423–430, https://doi.org/10.1126/scienc.255.5043.423.
Che, H., and Coauthors, 2015: Ground-based aerosol climatology of China: Aerosol optical depths from the China aerosol remote sensing network (CARSNET) 2002–2013. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15(13), 7619–7652, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-7619-2015.
Che, H. Z., Z. F. Yang, X. Y. Zhang, C. Z. Zhu, Q. L. Ma, H. G. Zhou, and P. Wang, 2009: Study on the aerosol optical properties and their relationship with aerosol chemical compositions over three regional background stations in China. Atmos. Environ., 43(5), 1093–1099, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.11.010.
Chen, J. S., J. Y. Xin, J. L. An, Y. S. Wang, Z. R. Liu, N. Chao, and Z. Meng, 2014: Observation of aerosol optical properties and particulate pollution at background station in the Pearl River Delta region. Atmospheric Research, 143, 216–227, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.02.011.
Chen, Y. X., 2014: Analysis of aerosol types and sources in the typical pollution region of China based on MODIS product. M.S. thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 69 pp. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gong, C. S., 2014: The preliminary research of aerosol climate effect by direct radiative forcing in different ecosystems in mainland China. PhD dissertation, Lanzhou University, 119pp. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gong, C. S., J. Y. Xin, S. G. Wang, Y. S. Wang, P. C. Wang, L. L. Wang, and P. Li, 2014: The aerosol direct radiative forcing over the Beijing metropolitan area from 2004 to 2011. Journal of Aerosol Science, 69, 62–70, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2013.12.007.
Gong, C. S., J. Y. Xin, S. G. Wang, Y. S. Wang, and T. J. Zhang, 2017: Anthropogenic aerosol optical and radiative properties in the typical urban/suburban regions in China. Atmospheric Research, 197, 177–187, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.07.002.
Guo, S., M. Hu, Z. B. Wang, J. Slanina, and Y. L. Zhao, 2010: Size-resolved aerosol water-soluble ionic compositions in the summer of Beijing: Implication of regional secondary formation. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 10(3), 947–959, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-947-2010.
Hu, W. W., M. Hu, W. Hu, C. Chen, and J. F. Peng, 2016: Limitations of EC tracer method in areas with complicated primary sources. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 36(6), 2121–2130, https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2015.0741. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huan, N., L. M. Zeng, and M. Shao, 2005: Review of measurement techniques about organic carbon and elemental carbon in atmospheric particles. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 41(6), 957–964, https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2005.06.017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang, R. J., and Coauthors, 2014: High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature, 514(7521), 218–222, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13774.
Huang, X. J., 2016: Chemical and physical characteristics and source apportionment of atmospheric fine particles in typical cities of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. PhD dissertation, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 137 pp. (in Chinese)
Huang, Y. M., Z. R. Liu, H. Chen, and Y. S. Wang, 2013: Characteristics of mass size distributions of water-soluble inorganic ions during summer and winter haze days of Beijing. Environmental Science, 34(4), 1236–1244, https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.2013.04.017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
IPCC, 2014: Climate Change 2013: the Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Thomas et al., Eds., Cambridge University Press, New York.
Jacobson, M. Z., 2001: Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature, 409, 695–697, https://doi.org/10.1038/35055518.
Jacobson, M. Z., 2002: Control of fossil-fuel particulate black carbon and organic matter, possibly the most effective method of slowing global warming. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 107(D19), ACH 16-1–ACH 16-22, https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JD001376.
Jiang, N., Q. Li, F. C. Su, Q. Wang, X. Yu, P. R. Kang, R. Q. Zhang, and X. Y. Tang, 2018: Chemical characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 between heavily polluted days and other days in Zhengzhou, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 66, 188–198, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.05.006.
Jiang, R., 2017: Concentrations and pollution characteristics of organic carbon and elemental carbon in PM2.5 during the heavy air pollution episodes in Nantong. Environmental Protection Science, 43, 35–38, https://doi.org/10.16803/j.cnki.issn.1004-6216.2017.05.700. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Kaufman, Y. J., 1993: Aerosol optical thickness and atmospheric path radiance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 98(D2), 2677–2692, https://doi.org/10.1029/92JD02427.
Kirkevåg, A., T. Iversen, and A. Dahlback, 1999: On radiative effects of black carbon and sulphate aerosols. Atmos. Environ., 33, 2621–2635, https://doi.org/10.0016/S1352-2310(98)00309-4.
Koepke P., J. Gasteiger, and M. Hess, 2015: Technical note: Optical properties of desert aerosol with non-spherical mineral particles: Data incorporated to OPAC. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15, 5947–5956, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-5947-2015.
Kong, L. B., J. Y. Xin, Z. R. Liu, K. Q. Zhang, G. Q. Tang, W. Y. Zhang, and Y. S. Wang, 2017: The PM2.5 threshold for aerosol extinction in the Beijing megacity. Atmos. Environ., 167, 458–465, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.08.047.
Kong, S. F., and Coauthors, 2014: Ion chemistry for atmospheric size-segregated aerosol and depositions at an offshore site of Yangtze River Delta region, China. Atmospheric Research, 147–148, 205–226, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.05.018.
Koo, J. H., and Coauthors, 2016: Wavelength dependence of Ångström exponent and single scattering albedo observed by skyradiometer in Seoul, Korea. Atmospheric Research, 181, 12–19, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.06.006.
Li, S., W. J. Wang, B. L. Zhang, and Y. Han, 2009: Indirect radiative forcing and climatic effect of the anthropogenic nitrate aerosol on regional climate of China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 26, 543–552, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-0543-9.
Logan, T., B. K. Xi, X. Q. Dong, Z. Li, and M. Cribb, 2013: Classification and investigation of Asian aerosol absorptive properties. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 13(4), 2253–2265, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-2253-2013.
Logan, T., B. K. Xi, and X. Q. Dong, 2014: Aerosol properties and their influences on marine boundary layer cloud condensation nuclei at the ARM mobile facility over the Azores. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 119(8), 4859–4872, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JD021288.
Lohmann, U., and J. Feichter, 2005: Global indirect aerosol effects: A review. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 5, 715–737, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-5-715-2005.
Ma, Y. J., J. Y. Xin, W. Y. Zhang, and Y. S. Wang, 2016: Optical properties of aerosols over a tropical rain forest in Xishuangbanna, South Asia. Atmospheric Research, 178–179, 187–195, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.04.004.
Mukai, S., I. Sano, M. Satoh, and B. N. Holben, 2006: Aerosol properties and air pollutants over an urban area. Atmospheric Research, 82, 643–651, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2006.02.020.
Palancar, G. G., L. E. Olcese, M. Achad, M. L. López, and B. M. Toselli, 2017: A long term study of the relations between erythemal UV-B irradiance, total ozone column, and aerosol optical depth at central Argentina. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 198, 40–47, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2017.05.002.
Pio, C., and Coauthors, 2011: OC/EC ratio observations in Europe: Re-thinking the approach for apportionment between primary and secondary organic carbon. Atmos. Environ., 45, 6121–6132, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.08.045.
Qian, Y., H. Q. Wang, C. B. Fu, and Z. F. Wang, 1998: Seasonal and spatial variation of radiative effects of anthropogenic sulfate aerosol. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 15, 380–392, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-998-0008-6.
Ram, K., and M. M. Sarin, 2010: Spatio-temporal variability in atmospheric abundances of EC, OC and WSOC over Northern India. Journal of Aerosol Science, 41, 88–98, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2009.11.004.
Ram, K., S. Singh, M. M. Sarin, A. K. Srivastava, and S. N. Tripathi, 2016: Variability in aerosol optical properties over an urban site, Kanpur, in the Indo-Gangetic Plain: A case study of haze and dust events. Atmospheric Research, 174–175, 52–61, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.01.014.
Reisen, F., C. P. Meyer, and M. D. Keywood, 2013: Impact of biomass burning sources on seasonal aerosol air quality. Atmos. Environ., 67, 437–447, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.11.004.
Russell, A. G., G. J. McRae, and G. R. Cass, 1983: Mathematical modeling of the formation and transport of ammonium nitrate aerosol. Atmos. Environ., 17, 949–964, https://doi.org/10.1016/0004-6981(83)90247-0.
Seinfeld, J. H., and S. N. Pandis, 1998: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: from Air Pollution to Climate Change. Wiley.
Shao, P., J. Y. Xin, J. L. An, L. B. Kong, B. Y. Wang, J. X. Wang, Y. S. Wang, and D. Wu, 2017: The empirical relationship between PM2.5 and AOD in Nanjing of the Yangtze River Delta. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 8(2), 233–243, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2016.09.001.
Sheng, P. X., J. T. Mao, J. G. Li, Z. M. Ge, A. C. Zhang, J. G. Sang, N. X. Pan, and H. S. Zhang, 2013: Atmospheric Physic. Peking University Press, 551 pp. (in Chinese)
Singh, A., and S. Dey, 2012: Influence of aerosol composition on visibility in megacity Delhi. Atmos. Environ., 62, 367–373, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.08.048.
Srinivas, B., and M. M. Sarin, 2014: PM2.5, EC and OC in atmospheric outflow from the Indo-Gangetic plain: Temporal variability and aerosol organic carbon-to-organic mass conversion factor. Science of the Total Environment, 487, 196–205, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.002.
Su, H. J., and Coauthors, 2018: Effects of transport on aerosols over the eastern slope of the Tibetan Plateau: Synergistic contribution of Southeast Asia and the Sichuan Basin. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 11(5), 425–431, https://doi.org/10.1080/16742834.2018.1512832.
Su, H. J., 2018: Observation and extinction characteristics of PM2.5 in typical urban areas of North China. M.S. thesis, Chengdu University of Information Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tang, B. Y., and Coauthors, 2018: Characteristics of complex air pollution in typical cities of North China. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 11(1), 29–36, https://doi.org/10.1080/16742834.2018.1394158.
Tian, H. W., Y. F. Zheng, H. L. Chen, W. Deng, and Z. X. Du, 2010: Inversion and analysis of aerosol optical depth in Zhengzhou. Meteorological Science and Technology, 38(4), 515–520, https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2010.04.023. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tian, S. L., Y. P. Pan, and Y. S. Wang, 2016: Size-resolved source apportionment of particulate matter in urban Beijing during haze and non-haze episodes. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16, 1–19, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-1-2016.
Wang, L. C., W. Gong, X. G. Xia, J. Zhu, J. Li, and Z. M. Zhu, 2015: Long-term observations of aerosol optical properties at Wuhan, an urban site in Central China. Atmos. Environ., 101, 94–102, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.11.021.
Wang, M. X., R. J. Zhang, and Y. F. Pu, 2001: Recent researches on aerosol in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18(4), 576–586, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-001-0046-9.
Wang, P., H. Z. Che, X. C. Zhang, Q. L. Song, Y. Q. Wang, Z. H. Zhang, X. Dai, and D. J. Yu, 2010: Aerosol optical properties of regional background atmosphere in Northeast China. Atmos. Environ., 44, 4404–4412, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.07.043.
Wang, T., 2016: Research on the spatial and temporal distribution of PM2.5 in Changsha, Zhuzhou and Xiangtan. M.S. thesis, Hunan University of Science and Technology, 79 pp. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang, Y. Q., X. Y. Zhang, and R. R. Draxler, 2009: TrajStat: GIS-based software that uses various trajectory statistical analysis methods to identify potential sources from long-term air pollution measurement data. Environmental Modelling & Software, 24, 938–939, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2009.01.004.
Watson, J. G., J. C. Chow, F. W. Lurmann, and S. P. Musarra, 1994: Ammonium nitrate, nitric acid, and ammonia equilibrium in wintertime Phoenix, Arizona. Air & Waste, 44(4), 405–412, https://doi.org/10.1080/1073161X.1994.10467262.
Xia, X. G., H. B. Chen, P. Goloub, X. M. Zong, W. X. Zhang, and P. C. Wang, 2013: Climatological aspects of aerosol optical properties in north china plain based on ground and satellite remote-sensing data. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 127, 12–23, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2013.06.024.
Xin, J. Y., and Coauthors, 2007: Aerosol optical depth (AOD) and Ångström exponent of aerosols observed by the Chinese Sun Hazemeter Network from August 2004 to September 2005. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 112(D5), D05203, https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD007075.
Xin, J. Y., and Coauthors, 2015: The campaign on atmospheric aerosol research network of China: CARE-China. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 96(7), 1137–1155, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-14-00039.1.
Xin, J. Y., and Coauthors, 2016a: The observation-based relationships between PM2.5 and AOD over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 121, 10 701–10 716, https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD024655.
Xin, J. Y., C. S. Gong, S. G. Wang, and Y. S. Wang, 2016b: Aerosol direct radiative forcing in desert and semi-desert regions of northwestern China. Atmospheric Research, 171, 56–65, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2015.12.004.
Xu, G. J., Y. Gao, Q. Lin, W. Li and L. Q. Chen, 2013: Characteristics of water-soluble inorganic and organic ions in aerosols over the Southern Ocean and coastal East Antarctica during austral summer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 118, 13 303–13 318, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JD019496.
Zhang, C. X., and Coauthors, 2019: Satellite UV-Vis spectroscopy: Implications for air quality trends and their driving forces in China during 2005–2017. Light, Science & Applications, 8, 100, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-019-0210-6.
Zhang, F., Z. W. Wang, H. R. Cheng, X. P. Lv, W. Gong, X. M. Wang, and G. Zhang, 2015: Seasonal variations and chemical characteristics of PM2.5 in Wuhan, central China. Science of the Total Environment, 518–519, 97–105, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.054.
Zhang, J. H., J. T. Mao, and M. H. Wang, 2002: Analysis of the aerosol extinction characteristics in different areas of China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 19(1), 136–152, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-002-0040-x.
Zhang, K. Q., and Coauthors, 2018: The aerosol optical properties and PM2.5 components over the world’s largest industrial zone in Tangshan, North China. Atmospheric Research, 201, 226–234, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.10.025.
Zhang, K., Y. S. Wang, T. X. Wen, G. R. Liu, B. Hu, and Y. N. Zhao, 2008: On-line analysis and mass concentration characters of the Alkali Metal Ions of PM10 in Beijing. Environmental Science, 29(1), 246–252, https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.01.041. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang, T. H., and H. Liao, 2016: Aerosol absorption optical depth of fine-mode mineral dust in eastern China. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 9(1), 7–14, https://doi.org/10.1080/16742834.2015.1126154.
Zhang, X. Y., Y. Q. Wang, T. Niu, X. C. Zhang, S. L. Gong, Y. M. Zhang, and J. Y. Sun, 2012: Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12, 779–799, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-779-2012.
Zhao, D. D., J. Y. Xin, C. S. Gong, X. Wang, Y. J. Ma, and Y. N. Ma, 2018: Trends of aerosol optical properties over the heavy industrial zone of northeastern Asia in the past decade (2004–2015). J. Atmos. Sci., 75(6), 1741–1754, https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-17-0260.1.
Zhao, H. J., and Coauthors, 2013b: Aerosol optical properties over urban and industrial region of Northeast China by using ground-based sun-photometer measurement. Atmos. Environ., 75, 270–278, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.04.048.
Zhao, H. J., H. Z. Che, Y. J. Ma, X. G. Xia, Y. F. Wang, P. Wang, and X. C. Wu, 2015: Temporal variability of the visibility, particulate matter mass concentration and aerosol optical properties over an urban site in Northeast China. Atmospheric Research, 166, 204–212, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2015.07.003.
Zhao, P. S., F. Dong, D. He, X. J. Zhao, X. L. Zhang, W. Z. Zhang, Q. Yao, and H. Y. Li, 2013a: Characteristics of concentrations and chemical compositions for PM2.5 in the region of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei, China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 13, 4631–4644, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-4631-2013.
Zheng, X. Y., X. D. Liu, F. H. Zhao, F. K. Duan, T. Yu, and H. Cachier, 2005: Seasonal characteristics of biomass burning contribution to Beijing aerosol. Science in China Series B: Chemistry, 48(5), 481–488, https://doi.org/10.1360/042005-15.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFC0202001), the Chinese Academy of Sciences Strategic Priority Research Program(Grant No. XDA23020301), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 42061130215 and 41605119). The authors are grateful for the MODIS services provided by the NASA EOSDIS Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC). Researchers are welcome to email the Corresponding Author (Prof. Jinyuan XIN: xjy@mail.iap.ac.cn) and share the data in manuscript by a bilateral cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Article Highlights
• High-concentration industrial aerosol strongly cooled the atmosphere-surface system.
• Inorganic ions and carbonaceous aerosol were the main constituents of particulate matter.
• Extinction and radiative forcing of aerosol were significantly controlled by the scattering aerosol.
• Adjustment of the energy structure played a clear role in the control of atmospheric pollution.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Xin, J., Zhang, W. et al. Optical, Radiative and Chemical Characteristics of Aerosol in Changsha City, Central China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 37, 1310–1322 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-020-0076-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-020-0076-9