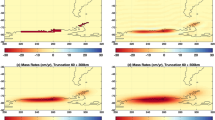
Abstract
Accurate atmospheric temperature and moisture information with high temporal/spatial resolutions are two of the key parameters needed in regional numerical weather prediction (NWP) models to reliably predict high-impact weather events such as local severe storms (LSSs). High spectral resolution or hyperspectral infrared (HIR) sounders from geostationary orbit (GEO) provide an unprecedented source of near time-continuous, three-dimensional information on the dynamic and thermodynamic atmospheric fields—an important benefit for nowcasting and NWP-based forecasting. In order to demonstrate the value of GEO HIR sounder radiances on LSS forecasts, a quick regional OSSE (Observing System Simulation Experiment) framework has been developed, including high-resolution nature run generation, synthetic observation simulation and validation, and impact study on LSS forecasts. Results show that, on top of the existing LEO (low earth orbit) sounders, a GEO HIR sounder may provide value-added impact [a reduction of 3.56% in normalized root-mean-square difference (RMSD)] on LSS forecasts due to large spatial coverage and high temporal resolution, even though the data are assimilated every 6 h with a thinning of 60 km. Additionally, more frequent assimilations and smaller thinning distances allow more observations to be assimilated, and may further increase the positive impact from a GEO HIR sounder. On the other hand, with denser and more frequent observations assimilated, it becomes more difficult to handle the spatial error correlation in observations and gravity waves due to the limitations of current assimilation and forecast systems (such as a static background error covariance). The peak reduction of 4.6% in normalized RMSD is found when observations are assimilated every 3 h with a thinning distance of 30 km.
摘 要
具有高时空间分辨率的精确的大气温度和湿度信息, 是利用区域数值天气预报模式, 准确预报局地强风暴天气的两个关键参数. 来自地球静止轨道的高光谱分辨率红外探测仪, 能提供大气的动力和热力的近乎连续的三维信息. 这些前所未有的关于大气垂直结构的信息, 对临近预报和基于数值天气模式的预报具有重要意义. 为了展示地球静止轨道高光谱红外探测仪对局地强风暴预报的价值, 我们开发了一个快速的区域观测系统模拟试验框架, 包括高分辨率的自然大气场景(nature run)的生成, 观测的模拟和验证, 以及对局地强风暴预报的影响研究. 结果表明, 与现有的低地球轨道大气探测仪的相比, 地球静止轨道高光谱红外探测仪对区域模式具有更大的空间覆盖率和更高的时间分辨率. 在目前的每6小时一次, 稀疏距离为60公里的业务同化设置下, 能够改进局地强风暴预报, 减少整体分析和预报误差3.56%. 此外, 更频繁的同化和更小的数据稀疏距离能使更多的观测数据被同化, 从而进一步增加地球静止轨道高光谱红外探测仪的正影响效果.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atlas, R., 1997: Atmospheric observations and experiments to assess their usefulness in data assimilation (gtSpecial Issuelt-Data assimilation in meteology and oceanography: Theory and practice). J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 75, 111–130, https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj1965.75.1B111.
Atlas, R., L. Bucci, B. Annane, R. Hoffman, and S. Murillo, 2015: Observing system simulation experiments to assess the potential impact of new observing systems on hurricane forecasting. Marine Technology Society Journal, 49, 140–148.
Auligné, T., F. Rabier, L. Lavanant, and M. Dahoui, 2003: First results of the assimilation of AIRS data in Météo-France Numerical Weather Prediction model. Proc. 13th International TOVS Study Conf., Adele, Canada.
Benjamin, S. G., and Coauthors, 2004: An hourly assimilation–forecast cycle: The RUC. Mon. Wea. Rev., 132, 495–518, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132<0495:AHACTR>2.0.CO;2.
Bessho, K., and Coauthors, 2016: An introduction to himawari-8/9 -Japan’s New-Generation Geostationary Meteorological Satellites. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 94, 151–183.
Boukabara, S., and Coauthors, 2016a: Community global observing system simulation experiment (OSSE) package (CGOP): Description and usage. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 33, 1759–1777, https://doi.org/10.1175/JTECH-D-16-0012.1.
Boukabara, S., and Coauthors, 2016b: S4: An O2R/R2O infrastructure for optimizing satellite data utilization in NOAA numerical modeling systems: A step toward bridging the gap between research and operations. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 97, 2359–2378, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-14-00188.1.
Boukabara, S., and Coauthors, 2018: Community global observing system simulation experiment (OSSE) package CGOP: Perfect observations simulation validation. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 35, 207–226, https://doi.org/10.1175/JTECH-D-17-0077.1.
Cardinali, C., 2009: Monitoring the observation impact on the short -range forecast. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 135, 239–250, https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.366.
Chahine, M. T., and Coauthors, 2006: AIRS: Improving weather forecasting and providing new data on greenhouse gases. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 87, 911–926, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-87-7-911.
Chen, Y., Y. Han, P. Van Delst, and F. Z. Weng, 2010: On water vapor Jacobian in fast radiative transfer model. J. Geophys. Res., 115, https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD013379.
Chen, Y., Y. Han, and F. Z. Weng, 2012: Comparison of two transmittance algorithms in the community radiative transfer model: Application to AVHRR. J. Geophys. Res., 117, https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JD016656.
Cintineo, R. M., J. A. Otkin, T. A. Jones, S. Koch, and D. J. Stensrud, 2016: Assimilation of synthetic GOES-R ABI infrared brightness temperatures and WSR-88D radar observations in a high-resolution OSSE. Mon. Wea. Rev., 144(9), 3159–3180, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-15-0366.1.
Collard, A. D., and A. P. McNally, 2009: The assimilation of infrared atmospheric sounding interferometer radiances at ECMWF. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 135, 1044–1058, https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.410.
Ferretti, R., and C. Faccani, 2005: Data assimilation of highdensity observations. II: Impact on the forecast of the precipitation for the MAP/SOP IOP2b. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 131, 43–61, https://doi.org/10.1256/qj.03.56B.
Gambacorta, A., and Coauthors, 2014: An experiment using high spectral resolution CrIS measurements for atmospheric trace gases: Carbon monoxide retrieval impact study. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 11, 1639–1643, https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2014.2303641.
Gelaro, R., and Coauthors, 2015: Evaluation of the 7-km GEOS-5 nature run. NASA/TM-2014-104606/VOL36, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, 285 pp.
Hamill, T. M., 1999: Hypothesis tests for evaluating numerical precipitation forecasts. Wea. Forecasting, 14(2), 155–167, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0434(1999)014<0155:HTFENP>2.0.CO;2.
Hannon, S. E., L. L. Strow, and W. W. McMillan, 1996: Atmospheric infrared fast transmittance models: A comparison of two approaches. Proc. SPIE Volume 2830, Optical Spectroscopic Techniques and Instrumentation for Atmospheric and Space Research II, Denver, CO, United States, SPIE, 94–105, https://doi.org/10.1117/12.256106.
Hilton, F., N. C. Atkinson, S. J. English, and J. R. Eyre, 2009: Assimilation of IASI at the Met Office and assessment of its impact through observing system experiments. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 135, 495–505, https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.379.
Hilton, F., and Coauthors, 2012: Hyperspectral Earth observation from IASI: Five years of accomplishments. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 93, 347–370, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00027.1.
Hoffman, R. N., and R. Atlas, 2016: Future observing system simulation experiments. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 97, 1601–1616, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-15-00200.1.
Honda, T., and Coauthors, 2018a: Assimilating all-sky Himawari-8 satellite infrared radiances: A case of typhoon Soudelor (2015). Mon. Wea. Rev., 146, 213–229, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-16-0357.1.
Honda, T., S. Kotsuki, G. Y. Lien, Y. Maejima, K. Okamoto, and T. Miyoshi, 2018b: Assimilation of Himawari-8 allsky radiances every 10 minutes: Impact on precipitation and flood risk prediction. J. Geophys. Res., 123, 965–976, https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD027096.
Huang, X. Y., M. Chen, W. Wang, J.-W. Kim, B. Skamarock, and T. Henderson, 2007: Development of Digital Filter Initialization for WRF and its implementation at IUM. Preprints: 8th Annual WRF User’s Workshop, NCAR, Boulder, CO, NCAR.
Jin, X., J. Li, T. J. Schmit, J. L. Li, M. D. Goldberg, and J. J. Gurka, 2008: Retrieving clear-sky atmospheric parameters from SEVIRI and ABI infrared radiances. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D15310, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD010040.
Jones, T. A., S. Koch, and Z. L. Li, 2017: Assimilating synthetic hyperspectral sounder temperature and humidity retrievals to improve severe weather forecasts. Atmospheric Research, 186, 9–25, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.11.004.
Joo, S., J. Eyre, and R. Marriott, 2013: The impact of Metop and other satellite data within the Met Office global NWP system using an Adjoint-based sensitivity method. Mon. Wea. Rev., 141, 3331–3342, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-12-00232.1.
Keyser, D., 2018: PREPBUFR processing at NCEP. Tech. rep., National Centers for Environmental Prediction. Available online at https://doi.org/www.emc.ncep.noaa.gov/mmb/dataprocessing/prepbufr.doc/document.htm.
Le Marshall, J., and Coauthors, 2005: Impact of atmospheric infrared sounder observations on weather forecasts. Eos, 86(11), 109–116, https://doi.org/10.1029/2005EO110002.
Le Marshall, J., and Coauthors, 2006a: Improving global analysis and forecasting with AIRS. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 87, 891–895, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-87-7-891.
Le Marshall, J., J. Jung, T. Zapotocny, J. Derber, R. Treadon, S. Lord, M. Goldberg, and W. Wolf, 2006b: The application of AIRS radiances in numerical weather prediction. Aust. Meteor. Mag., 55, 213–217.
Li, J., W. W. Wolf, W. P. Menzel, W. J. Zhang, H.-L. Huang, and T. H. Achtor, 2000: Global soundings of the atmosphere from ATOVS measurements: The algorithm and validation. J. Appl. Meteor., 39, 1248–1268, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(2000)039<1248:GSOTAF>2.0.CO;2.
Li, Z. L., J. Li, W. P. Menzel, J. P. Nelson III, T. J. Schmit, E. Weisz, and S. A. Ackerman, 2009: Forecasting and nowcasting improvement in cloudy regions with high temporal GOES Sounder infrared radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D09216, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD010596.
Li, J., J. L. Li, J. Otkin, T. J. Schmit, and C.-Y., Liu, 2011: Warning information in a preconvection environment from the geostationary advanced infrared sounding system—a simulation study using the IHOP Case. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 50, 776–783, https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JAMC2441.1.
Li, J., P. Wang, H. Han, J. L. Li, and J. Zheng, 2016: On the assimilation of satellite sounder data in cloudy skies in numerical weather prediction models. Journal of Meteorological Research, 30, 169–182, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-016-5114-2.
Li, J., Z. L. Li, P. Wang, T. J. Schmit, W. G. Bai, and R. Atlas, 2017: An efficient radiative transfer model for hyperspectral IR radiance simulation and applications under cloudy-sky conditions. J. Geophys. Res., 122, 7600–7613, https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JD026273.
Lim, A., and Coauthors, 2017: Impact analysis of LEO hyperspectral sensor IFOV size on the next-generation high-resolution NWP model forecast performance. Proc. 27th International TOVS Study Conf., Darmstadt, Germany, NOAA.
Liu, Z.-Q., and F. Rabier, 2002: The interaction between model resolution, observation resolution and observation density in data assimilation: A one-dimensional study. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 128, 1367–1386, https://doi.org/10.1256/003590002320373337.
Liu, Z. Q., and F. Rabier, 2003: The potential of high-density observations for numerical weather prediction: A study with simulated observations. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 129, 3013–3035, https://doi.org/10.1256/qj.02.170.
Lynch, P., and X. Y. Huang, 1992: Initialization of the HIRLAM Model using a Digital Filter. Mon. Wea. Rev., 120, 1019–1034, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1992)120<1019:IOTHMU>2.0.CO;2.
Ma, Z. Z., E. S. Maddy, B. L. Zhang, T. Zhu, and S. A. Boukabara, 2017: Impact assessment of himawari-8 AHI data assimilation in NCEP GDAS/GFS with GSI. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 34, 797–815, https://doi.org/10.1175/JTECH-D-16-0136.1.
Mallick, S., D. Dutta, and K.-H. Min, 2017: Quality assessment and forecast sensitivity of global remote sensing observations. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 34(3), 371–382, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-016-6109-8.
McNally, A. P., P. D. Watts, J. A. Smith, R. Engelen, G. A. Kelly, J. N. Thépaut, and M. Matricardi, 2006: The assimilation of AIRS radiance data at ECMWF. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 132, 935–957, https://doi.org/10.1256/qj.04.171.
McNally, A. P., M. Bonavita, and J.-N. Thépaut, 2014: The role of satellite data in the forecasting of hurricane sandy. Mon. Wea. Rev., 142, 634–646, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-13-00170.1.
Menzel, W. P., F. C. Holt, T. J. Schmit, R. M. Aune, A. J. Schreiner, G. S. Wade, and D. G. Gray, 1998: Application of GOES-8/9 soundings to weather forecasting and nowcasting. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 79, 2059–2077, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1998)079<2059:AOGSTW>2.0.CO;2.
Menzel, W. P., T. J. Schmit, P. Zhang, and J. Li, 2018: Satellitebased atmospheric infrared sounder development and applications. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 99, 583–603, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-16-0293.1.
Migliorini, S., 2012: On the equivalence between radiance and retrieval assimilation. Mon. Wea. Rev., 140, 258–265, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-10-05047.1.
Peckham, S. E., T. G. Smirnova, S. G. Benjamin, J. M. Brown, and J. S. Kenyon, 2016: Implementation of a digital filter initialization in the WRF model and its application in the Rapid Refresh. Mon. Wea. Rev., 144, 99–106, https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-15-0219.1.
Schmit, T. J., M. M. Gunshor, W. P. Menzel, J. J. Gurka, J. Li, and A. S. Bachmeier, 2005: Introducing the next-generation advanced baseline imager on GOES-R. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 86, 1079–1096, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-86-8-1079.
Schmit, T. J., J. Li, S. A. Ackerman, and J. J. Gurka, 2009: Highspectral-and high-temporal-resolution infrared measurements from geostationary orbit. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 26, 2273–2292, https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JTECHA1248.1.
Schmit, T. J., P. Griffith, M. M. Gunshor, J. M. Daniels, S. J. Goodman, and W. J. Lebair, 2017: A closer look at the ABI on the GOES-R series. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 98, 681–698, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-15-00230.1.
Seemann, S. W., J. Li, W. P. Menzel, and L. E. Gumley, 2003: Operational retrieval of atmospheric temperature, moisture, and ozone from MODIS infrared radiances. J. Appl. Meteor., 42, 1072–1091, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(2003)042<1072:OROATM>2.0.CO;2.
Seemann, S. W., E. E. Borbas, R. O. Knuteson, G. R. Stephenson, and H.-L. Huang, 2008: Development of a global infrared land surface emissivity database for application to clear sky sounding retrievals from multispectral satellite radiance measurements. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 47, 108–123, https://doi.org/10.1175/2007JAMC1590.1.
Skamarock, W. C., and M. L. Weisman, 2009: The impact of positive-definite moisture transport on NWP precipitation forecasts. Mon. Wea. Rev., 137, 488–494, https://doi.org/10.1175/2008MWR2583.1.
Strow, L. L., S. E. Hannon, S. De Souza-Machado, H. Motteler, and D. Tobin, 2003: An overview of the AIRS radiative transfer model. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 41, 303–313, https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2002.808244.
Wang, H. L., X.-Y. Huang, and Y. S. Chen, 2013: An observing system simulation experiment for the impact of MTG Candidate Infrared Sounding mission on regional forecasts: system development and preliminary results. ISRN Meteorology, 2013, 971501, https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/971501.
Wang, P., J. Li, J. L. Li, Z. L. Li, T. J. Schmit, and W. G. Bai, 2014: Advanced infrared sounder subpixel cloud detection with imagers and its impact on radiance assimilation in NWP. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 1773–1780, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013GL059067.
Wang, P., and Coauthors, 2015: Assimilation of thermodynamic information from advanced infrared sounders under partially cloudy skies for regional NWP. J. Geophys. Res., 120, 5469–5484, https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD022976.
Wang, P., J. Li, Z. L. Li, A. H. N. Lim, J. L. Li, T. J. Schmit, and M. D. Goldberg, 2017: The impact of cross-track infrared sounder (CrIS) cloud -cleared radiances on hurricane Joaquin (2015) and Matthew (2016) Forecasts. J. Geophys. Res., 122, 13201–13218, https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD027515.
Wei, H. L., P. Yang, J. Li, B. A. Baum, H.-L. Huang, S. Platnick, Y. X. Hu, and L. Strow, 2004: Retrieval of semitransparent ice cloud optical thickness from Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) measurements. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 42, 2254–2267, https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2004.833780.
Yang, J., Z. Q. Zhang, C. Y. Wei, F. Lu, and Q. Guo, 2017: Introducing the new generation of Chinese geostationary weather satellites, Fengyun 4. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 1637–1658, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-16-0065.1.
Zhang, S. X., Z. X. Pu, D. J. Posselt, and R. Atlas, 2017: Impact of CYGNSS ocean surface wind speeds on numerical simulations of a hurricane in observing system simulation experiments. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 34, 375–383, https://doi.org/10.1175/JTECH-D-16-0144.1.
Zhu, Y. Q., J. Derber, A. Collard, D. Dee, R. Treadon, G. Gayno, and J. A. Jung, 2014: Enhanced radiance bias correction in the National Centers for Environmental Prediction’s Gridpoint Statistical Interpolation data assimilation system. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 140(682), 1479–1492, https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.2233.
Acknowledgements
This work is partly supported by the NESDIS OPPA OSSE program (Grant No. NA15NES4320001). The views, opinions, and findings contained in this report are those of the authors and should not be construed as an official NOAA or U. S. government position, policy, or decision. Thanks to the Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation for providing the “S4” supercomputer [Supercomputer for Satellite Simulations and Data Assimilation Boukabara et al. (2016b)], physically located at SSEC, University of Wisconsin-Madison, as the main computational resource for this research study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Li, J., Wang, P. et al. Value-added Impact of Geostationary Hyperspectral Infrared Sounders on Local Severe Storm Forecasts—via a Quick Regional OSSE. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 35, 1217–1230 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-018-8036-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-018-8036-3