Abstract
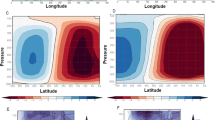
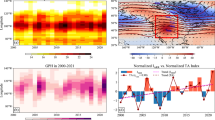
The summertime ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau is formed by two influences, the Asian summer monsoon (ASM) and air column variations. Total ozone over the Tibetan Plateau in summer was ∼33 Dobson units (DU) lower than zonal mean values over the ocean at the same latitudes during the study period 2005–2009. Satellite observations of ozone profiles show that ozone concentrations over the ASM region have lower values in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) than over the non-ASM region. This is caused by frequent convective transport of low-ozone air from the lower troposphere to the UTLS region combined with trapping by the South Asian High. This offset contributes to a ∼20-DU deficit in the ozone column over the ASM region. In addition, along the same latitude, total ozone changes identically with variations of the terrain height, showing a high correlation with terrain heights over the ASM region, which includes both the Tibetan and Iranian plateaus. This is confirmed by the fact that the Tibetan and Iranian plateaus have very similar vertical distributions of ozone in the UTLS, but they have different terrain heights and different total-column ozone levels. These two factors (lower UTLS ozone and higher terrain height) imply 40 DU in the lower-ozone column, but the Tibetan Plateau ozone column is only ∼33 DU lower than that over the non-ASM region. This fact suggests that the lower troposphere has higher ozone concentrations over the ASM region than elsewhere at the same latitude, contributing ∼7 DU of total ozone, which is consistent with ozonesonde and satellite observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dessler, A. E., and S. C. Sherwood, 2004: Effect of convection on the summertime extratropical lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res., 109, D23301, doi: 10.1029/2004JD005209.
Fishman, J., J. K. Creilson, A. E. Wozniak, and P. J. Crutzen, 2005: Interannual variability of stratospheric and tropospheric ozone determined from satellite measurements. J. Geophys. Res., 110, D20306, doi: 10.1029/2005JD005868.
Froidevaux, L., and Coauthors, 2008: Validation of Aura Microwave Limb Sounder stratospheric ozone measurements. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D15S20, doi: 10.1029/2007JD008771.
Fu, R., and Coauthors, 2006: Short circuit of water vapor and polluted air to the global stratosphere by convective transport over the Tibetan Plateau. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 5664–5669.
Gettelman, A., D. E. Kinnison, T. J. Dunkerton, and G. P. Brasseur, 2004: Impact of monsoon circulations on the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res., 109, D22101, doi: 10.1029/2004JD004878.
Gille, J., and Coauthors, 2008: High Resolution Dynamics Limb Sounder: Experiment overview, recovery, and validation of initial temperature data. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D16S43, doi: 10.1029/2007JD008824.
Kalnay, E., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77(3), 437–471.
Li, Q., and Coauthors, 2005: Trapping of Asian pollution by the Tibetan anticyclone: A global CTM simulation compared with EOS MLS observations. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L14826, doi: 10.1029/2005GL022762.
Liu, J. J., D. B. A. Jones, J. R. Worden, D. Noone, M. Parrington, and J. Kar, 2009: Analysis of the summertime buildup of tropospheric ozone abundances over the Middle East and North Africa as observed by the Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer instrument. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D05304, doi: 10.1029/2008JD010993.
Liu, Y., W. Li, X. Zhou, and J. He, 2003: Mechanism of formation of the ozone valley over the Tibetan plateau in summer-transport and chemical process of ozone. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 20, 103–109.
Livesey, N. J., and Coauthors, 2007: Version 2.2 Level 2 data quality and description document for EOS MLS, Jet Propul. Lab., Pasadena, Calif. [Available at http://mls.jpl.nasa.gov].
Livesey, N. J., and Coauthors, 2008: Validation of Aura Microwave Limb Sounder O3 and CO observations in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D15S02, doi: 10.1029/2007JD008805.
McCormick, M. P., J. M. Zawodny, R.E. Viega, J. C. Larson, and P. H. Wang, 1989: An overview of SAGE I and II ozone measurements. Planet. Space Sci., 37, 1567–1586.
Nardi, B., and Coauthors, 2008: Initial validation of ozone measurements from the High Resolution Dynamics Limb Sounder. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D16S36, doi: 10.1029/2007JD008837.
Pan, L. L., W. J. Randel, B. L. Gary, M. J. Mahoney, and E. J. Hintsa, 2004: Definitions and sharpness of the extratropical tropopause: A trace gas perspective. J. Geophys. Res., 109, D23103, doi: 10.1029/2004JD004982.
Park, M., W. J. Randel, A. Gettelman, S. T. Massie, and J. H. Jiang, 2007: Transport above the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone inferred from Aura Microwave Limb Sounder tracers. J. Geophys. Res., 112, D16309, doi: 10.1029/2006JD008294.
Park, M., W. J. Randel, L. K. Emmons, P. F. Bernath, K. A. Walker, and C. D. Boone, 2008: Chemical isolation in the Asian monsoon anticyclone observed in Atmospheric Chemistry Experiment (ACE-FTS) data. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 757–764.
Qiu, Y. Y., M. Wei, A. L. Jiang, and J. C. Tong, 2008: General characteristics of the total low center above the Tibetan plateau and (low) though above the Rocky mountains—one the cause of static deficit/depletion above the high mountains. Climatic and Environmental Research, 13(5), 617–628. (in Chinese)
Randel, W. J., and M. Park, 2006: Deep convective influence on the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone and associated tracer variability observed with Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS). J. Geophys. Res., 111, D12314, doi: 10.1029/2005JD006490.
Randel, W. J., M. Park, L. Emmons, D. Kinnison, P. Bernath, K. Walker, C. Boone, and H. Pumphrey, 2010: Asian monsoon transport of pollution to the stratosphere. Science, 328, 611–613.
Schoeberl, M. R., and Coauthors, 2006: Overview of the EOS aura mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 44(5), 1066–1074.
Tian, W., M. Chipperfield, and Q. Huang, 2008: Effects of the Tibetan Plateau on total column ozone distribution. Tellus, 60B, 622–635.
Tobo, Y., Y. Iwasaka, D. Zhang, G. Shi, Y.-S. Kim, K. Tamura, and T. Ohashi, 2008: Summertime “ozone valley” over the Tibetan Plateau derived from ozonesondes and EP/TOMS data. Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, L16801, doi: 10.1029/2008GL034341.
Worden, J., and Coauthors, 2009: Observed vertical distribution of tropospheric ozone during the Asian summertime monsoon. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D13304, doi: 10.1029/2008JD010560.
Ye, Z., and Y. Xu, 2003: Climate characteristics of ozone over Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res., 108(D20), 4654, doi: 10.1029/2002JD003139.
Zheng, X., X. Zhou, J. Tang, Y. Qin, and C. Chan, 2004: A meteorological analysis on a low tropospheric ozone event over Xining, north western China on 26–27 July 1996. Atmos. Environ., 38, 261–271.
Zhou, R., and Y. Chen, 2005: Ozone variations over the Tibetan and Iranian Plateaus and their relationship with the South Asia High. Journal of University of Science and Technology of China, 35(6), 899–898. (in Chinese)
Zhou, X., and C. Luo, 1994: Ozone valley over Tibetan Plateau. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 8, 505–506.
Zhou, X., and R. Zhang, 2005: Decadal variations of temperature and geopotential height over the Tibetan Plateau and their relations with Tibet ozone depletion. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L18705.
Zhou, X., W. Li, L. Chen, and Y. Liu, 2006: Study on ozone change over the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 20(2), 129–143.
Ziemke, J. R., S. Chandra, B. N. Duncan, L. Froidevaux, P. K. Bhartia, P. F. Levelt, and J. W. Waters, 2006: Tropospheric ozone determined from Aura OMI and MLS: Evaluation of measurements and comparison with the Global Modeling Initiative’s Chemical Transport Model. J. Geophys. Res., 111, D19303, doi: 10.1029/2006JD007089.
Zou, H., 1996: Seasonal variation and trends of TOMS ozone over Tibet. Geophys. Res. Lett., 23, 1029–1032.
Zou, H., and Y. Gao, 1997: Vertical ozone profile over Tibet using Sage I and II data. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 14(4), 505–512.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bian, J., Yan, R., Chen, H. et al. Formation of the summertime ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau: The Asian summer monsoon and air column variations. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 28, 1318–1325 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-011-0174-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-011-0174-9