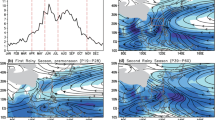
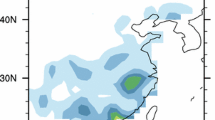
Abstract
The present study investigates the influence of South China Sea (SCS) SST and ENSO on winter (January–February–March; JFM) rainfall over South China and its dynamic processes by using station observations for the period 1951–2003, Met Office Hadley Center SST data for the period 1900–2008, and ERA-40 reanalysis data for the period 1958–2002. It is found that JFM rainfall over South China has a significant correlation with Niño-3 and SCS SST. Analyses show that in El Niño or positive SCS SST anomaly years, southwesterly anomalies at 700 hPa dominate over the South China Sea, which in turn transports more moisture into South China and favors increased rainfall. A partial regression analysis indicates that the independent ENSO influence on winter rainfall occurs mainly over South China, whereas SCS SST has a larger independent influence on winter rainfall in northern part of South China. The temperature over South China shows an obvious decrease at 300 hPa and an increase near the surface, with the former induced by Niño-3 and the latter SCS SST anomalies. This enhances the convective instability and weakens the potential vorticity (PV), which explains the strengthening of ascending motion and the increase of JFM rainfall over South China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan, J. C. L., Y. M. Liu, K. C. Chow, Y. H. Ding, W. K. M. Lau, and K. L. Chan, 2004: Design of a regional climate model for the simulation of South China summer monsoon rainfall. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 82, 1645–1665.
Chan, J. C. L., and W. Zhou, 2005: PDO, ENSO and the early summer monsoon rainfall over south China. Geophys. Res. Let., 32, L08810, doi: 10.1029/2004GL022015.
Chang, C. P., Y. Zhang, and T. Li, 2000: Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical Pacific SSTs. Part II: Meridional structure of the monsoon. J. Climate, 13, 4326–4340.
Chen, L. T., 1977: Impact of the SST anomalies in the equatorial eastern Pacific on the tropical atmospheric circulation and rainfall during the rainy period in China. Chinese J. Amos. Sci., 1, 1–12. (in Chinese)
Chen, W., H. F. Graf, and R. H. Huang, 2000: The interannual variability of East Asian winter monsoon and its relation to the summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 17, 48–60.
Chen, W., L. Wang, Y. Xue, and S. Sun, 2009: Variabilities of the spring river runoff system in eastern China and their relations to precipitation and sea surface temperature. Int. J. Climatol., 29, 1381–1394.
Ertel, H., 1942: Ein neuer hydrodynamischer wirbelsatz. Meteorologische Zeitschrift. Braunschweig, 59, 277–281. (in German)
Fu, C. B., and X. L. Teng, 1988: Climate anomalies in China associated with El Niño/Southern Oscillation. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., Special Issue, 133–141. (in Chinese)
Gibson, J. K., P. Kallberg, S. Uppala, A. Hernandez, A. Normura, and E. Serrano, 1997: ERA description, ECMWF reanalysis project report series1. ECMWF, Reading, 66pp.
Hoskins, B. J., M. E. McIntyre, and A. W. Robertson, 1985: On the use and significance of isentropic potential vorticity maps. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 111, 877–946.
Huang, R. H., and Y. F. Wu, 1989: The influence of ENSO on the summer climate change in China and its mechanisms. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 6, 21–32.
Huang, R. H., and L. T. Zhou, 2002: Research on the characteristics, formation mechanism and prediction of severe climate disasters in China. Journal of Natural Disasters, 11, 1–9. (in Chinese)
Huang, R. H., Y. H. Xu, and L. T. Zhou, 1999: The interdecadal variation of summer rainfall in China and the drought trend in North China. Plateau Meteorology, 18, 465–475. (in Chinese)
Huang, R. H., L. T. Zhou, and W. Chen, 2003: The progresses of recent studies on the variabilities of the East Asian monsoon and their causes. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 20, 55–69.
Inoue, T., and J. Matsumoto, 2004: A comparison of summer sea level pressure over East Eurasia between NCEP/NCAR reanalysis and ERA-40 for the period 1960–99. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 82, 951–958.
Lau, K. M., and H. Y. Weng, 2001: Coherent model of global SST and summer rainfall over China: An assessment of the regional impacts of the 1997–98 El Niño. J. Climate, 14, 1294–1208.
Lau, N. C., M. J. Nath, and H. Wang, 2004: Simulation by a GFDL GCM of ENSO-related variability of the coupled atmosphere-ocean system in the East Asian monsoon region. East Asian Monsoon, C.-P. Chang, Ed., World Scientific Publishing Co., 271–300.
Li, C. Y., W. Zhou, X. L. Jia, and X. Wang, 2006: Decadal/interdecadal variations of the ocean temperature and its impacts on the climate. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 23(6), 964–981, doi: 10.1007/s00376-006-0964-7.
Lin, Z. D., and R. Y. Lu, 2009: The ENSO’s effect on Eastern China rainfall in the following early summer. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 26, 333–342, doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-0333-4.
Nitta, T., and Z. Z. Hu, 1996: Summer climate variability in China and its association with 500-hPa height and tropical convection. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 74, 425–445.
Rasmusson, E. M., and T. H. Carpenter, 1982: Variations in tropical sea surface temperature and surface wind fields associated with the Southern Oscillation/El Niño. Mon. Wea. Rev., 110, 354–384.
Rayner, N. A., D. E. Parker, E. B. Horton, C. K. Folland, L. V. Alexander, D. P. Rowell, E. C. Kent, and A. Kaplan, 2003: Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res., 108(D14), 4407, doi: 10.1029/2002JD002670.
Uppala, S., 2002: ECMWF reanalysis, 1957–2001, ERA-40. ERA-40 Project Report Series, No. 3, 1–10.
Wang, B., R. Wu, and X. Fu, 2000: Pacific -East Asian teleconnection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J. Climate, 13, 1517–1536.
Wang, L., W. Chen, and R. H. Huang, 2008: Interdecadal modulation of PDO on the impact of ENSO on the East Asian winter monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, L20702, doi: 10.1029/2008GL035287.
Wu, G. X., and Y. M. Liu, 2000: Thermal adaptation, overshooting, dispersion, and subtropical anticyclone. Part I: Thermal adaptation and overshooting. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 24, 433–446. (in Chinese)
Wu, R., Z. Z. Hu, and B. P. Kirtman, 2003: Evolution of ENSO-related rainfall anomalies in East Asia and the processes. J. Climate, 16, 3741–3757.
Wu, R., III. J. L. Kinter, and B. P. Kirtman, 2005: Discrepancy of interdecadal changes in the Asian region among the NCEP-NCAR reanalysis, objective analyses, and observations. J. Climate, 18, 3048–3067.
Yang, F. L., and K.M. Lau, 2004: Trend and variability of China precipitation in spring and summer: Linkage to sea-surface temperatures. International Journal of Climatology, doi: 10.1002/joc.1094.
Yang, S., and K. M. Lau, 1998: Influences of sea surface temperature and ground wetness on Asian summer monsoon. J. Climate, 11, 3230–3246.
Yang, S., K. M. Lau, and K. M. Kim, 2002: Variations of the East Asian jet stream and Asian-Pacific-American winter climate anomalies. J. Climate, 15, 306–325.
Zhang, R. H., A. Sumi, and M. Kimoto, 1999: A diagnostic study of the impact of El Niño on the precipitation in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 16, 229–241.
Zhang, R. H., and A. Sumi, 2002: Moisture circulation over East Asia during El Niño episode in Northern winter, spring and autumn. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 80, 213–227.
Zhou, L. T., and R. H. Huang, 2003: Research on the characteristics of interdecadal variability of summer climate in China and its possible cause. Climatic and Environmental Research, 8, 274–290. (in Chinese)
Zhou, L. T., 2010: Impact of East Asian winter monsoon on rainfall over southeastern China and its dynamical process. International Journal of Climatology, doi:10.1002/joc.2101.
Zhou, L. T., and R. H. Huang, 2010a: An assessment of the quality of surface sensible heat flux derived from reanalysis data through comparison with station observations in Northwest China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 27(3), 500–512, doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-9081-8.
Zhou, L. T., and R. H. Huang, 2010b: Interdecadal variability of summer rainfall in Northwest China and its possible causes. International Journal of Climatology, 30(4), 549–557, doi: 10.1002/joc.1923.
Zhou, L. T., and R. Wu, 2010: Respective impacts of East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO on winter rainfall in China. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D02107, doi: 10.1029/2009JD012502.
Zhou, W., C. Y. Li, and J. C. L. Chan, 2006: The interdecadal variations of the summer monsoon rainfall over South China. Meteorol Atmos. Phys., 93, 165–175, doi: 10.1007/S00703-006-018-9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, LT., Tam, CY., Zhou, W. et al. Influence of South China Sea SST and the ENSO on winter rainfall over South China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 27, 832–844 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-9102-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-9102-7