Abstract
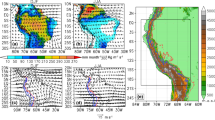
The variability of the summer rainfall over China is analyzed using the EOF procedure with a new parameter (namely, mode station variance percentage) based on 1951–2000 summer rainfall data from 160 stations in China. Compared with mode variance friction, the mode station variance percentage not only reveals more localized characteristics of the variability of the summer rainfall, but also helps to distinguish the regions with a high degree of dominant EOF modes representing the analyzed observational variable. The atmospheric circulation diagnostic studies with the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis daily data from 1966 to 2000 show that in summer, abundant (scarce) rainfall in the belt-area from the upper-middle reaches of the Yangtze River northeastward to the Huaihe River basin is linked to strong (weak) heat sources over the eastern Tibetan Plateau, while the abundant (scarce) rainfall in the area to the south of the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River is closely linked to the weak (strong) heat sources over the tropical western Pacific.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Longxun, Zhu Qiangen, Luo Huibang, He Jinhai, Dong Min, and Feng Zhiqiang, 1991: East Asian Monsoon. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 362pp. (in Chinese)
Guan Zhaoyong, K. Ashok, and T. Yamagata, 2003: Summertime response of the tropical atmosphere to the Indian ocean dipole sea surface temperature anomalies. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 81, 533–561.
He, H.-Y., J. W. McGinnis, Z. Song, and M. Yanai, 1987: Onset of the Asian summer monsoon in 1979 and the effect of the Tibetan Plateau. Mon. Wea. Rev., 115, 1966–1995.
Huang, Ronghui, and Li Weijing, 1988: Influence of the heat source anomaly over the tropical western Pacific on the subtropical high over East Asia. Scientia Atmospherica Sinica, 12(special issue), 95–107. (in Chinese)
Huang, R., and F. Sun, 1992: Impacts of the tropical western Pacific on the East Asian summer monsoon. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 70, 243–256.
Huang Ronghui, and Sun Feng-ying, 1994: The thermodynamic condition of the tropical western Pacific warm pool and the effects of convection above it on climatic anomalies in the summer of East Asia. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 18, 141–151.
Luo, H., and M. Yanai, 1984: The large-scale circulation and heat sources over the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas during the early summer of 1979. Part II: Heat and moisture budgets. Mon. Wea. Rev., 112, 966–989.
Luo Huibang, and Chen Rong, 1995: The anomalies of the atmospheric heat sources in the eastern Tibetan Plateau in summer on the circulation and precipitation. Scientia Meteorologica Sinica, 15, 94–102.
Murakami, T., 1987: Effects of the Tibetan Plateau. Monsoon Meteorology, C.-P. Chang and T. N. Krishnamurti, Eds., Oxford Univ. Press, New York, 235–270.
Nitta, T., 1987: Convective activities in the western tropical Pacific and their impact on the Northern Hemisphere summer circulation. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 64, 373–390.
Shi Neng, Chun Yun, and Pan Huijuan, 2000: Study on summer climate base state in China. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 16, 131–138. (in Chinese)
Wang Xiaochun, and Wu Guoxiong, 1996: Regional characteristics of summer precipitation anomalies over China identified in a spatial uniform network. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 54 (3), 324–332. (in Chinese)
Yanai, M., S. Esbensen, and J.-H. Chu, 1973: Determination of bulk properties of tropical cloud clusters from large-scale heat and moisture budgets. J. Atmos. Sci., 30, 611–627.
Yanai, M., C. Li, and Z. Song, 1992: Seasonal heating of the Tibetan Plateau and its effects on the evolution of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 70, 189–221.
Yang Hui, 2001: Anomalous atmospheric circulation, heat sources and moisture sinks in relation to great precipitation anomalies in the Yangtze River valley. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 972–983.
Zhang Yongsheng, and Wu Guoxiong, 1999: Diagnostic investigations on the mechanism of the onset of Asian summer monsoon and abrupt seasonal transitions over the Northern Hemisphere. Part II: The role of surface sensible heating over Tibetan Plateau and surrounding regions. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 57 (1), 56–73. (in Chinese)
Zhao Ping, and Chen Longxun, 2001a: The climatological characteristics of the atmospheric heat sources over the Tibetan Plateau in 35 years and their relationships with precipitation in China. Science in China (D), 31, 327–332. (in Chinese)
Zhao Ping, and Chen Longxun, 2001b: Interannual variability of atmospheric heat source/sink over the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau and its relation to circulation. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 106–116.
Zou Li, and Ni Yunqi, 1997: Impact of ENSO on the variability of the summer monsoon over Asia and the summer rainfall in China. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 13, 306–314. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jian, M., Qiao, Y., Yuan, Z. et al. The impact of atmospheric heat sources over the eastern Tibetan Plateau and the tropical western Pacific on the summer rainfall over the Yangtze-River basin. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 23, 149–155 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-006-0015-4
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-006-0015-4