Abstract
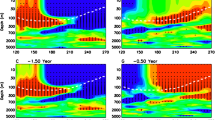
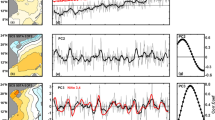
The curved surface of the maximum sea temperature anomaly (MSTA) was created from the JEDAC subsurface sea temperature anomaly data at the tropical Pacific between 1955 and 2000. It is quite similar to the depth distribution of the 20°C isotherm, which is usually the replacement of thermocline. From the distribution and moving trajectory of positive or negative sea temperature anomalies (STA) on the curved surface we analyzed all the El Nino and La Niña events since the later 1960s. Based on the analyses we found that, using the subsurface warm pool as the beginning point, the warm or cold signal propagates initially eastward and upward along the equatorial curved surface of MSTA to the eastern Pacific and stays there several months and then to turn north, usually moving westward near 10°N to western Pacific and finally propagates southward to return to warm pool to form an off-equator closed circuit. It takes about 2 to 4 years for the temperature anomaly to move around the cycle. If the STA of warm (cold) water is strong enough, there will be two successive El Nino (La Niña) events during the period of 2 to 4 years. Sometime, it becomes weak in motion due to the unsuitable oceanic or atmospheric condition. This kind process may not be considered as an El Niño (La Niña) event, but the moving trajectory of warm (cold) water can still be recognized. Because of the alternate between warm and cold water around the circuits, the positive (negative) anomaly signal in equatorial western Pacific coexists with negative (positive) anomaly signal near 10°N in eastern Pacific before the outbreak of El Nino (La Niña) event. The signals move in the opposite directions. So it appears as El Nino (La Niña) in equator at 2-4 years intervals. The paper also analyzed several exceptional cases and discussed the effect and importance of oceanic circulation in the evolution of El Nino / La Niña event.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chao Qingchen, and Chao Jiping, 2001: The influence of western tropical Pacific and eastern Indian Ocean on the development of ENSO event. Progress in Natural Science, 11 (12), 1293–1300 (in Chinese).
Chao Jiping, Yuan Shaoyu, Chao Qingchen, and Tian Jiwei, 2002: The source of the subface warm water of the warm pool in the equatorial western Pacific-the analysis on the El Nino event in 1997/ 1998. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci.(in Chinese), (to be published).
Gill, A.E., and E. M. Rasmusson, 1983: The 1982-83 climate anomaly in equatorial Pacific. Nature, 306, 229–234.
Li Chongyin, and Mu Mingquan, 1999: The occurrence of the El Niño event and the subsurface temperature anomaly of warm pool in the equatorial western Pacific. Chinese J. Almos, Sci., 23, 513–521 (in Chinese).
McPhaden, M. J., S. P. Havers, L. J. Maugum, and J. M. Tool, 1990: Variability in the weastern equatorial Pacific ocean during 1986-1987 El Niño / Southern Oscillation event. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 20(2), 190–208.
McPhaden, M. J., 1999: Genesis and evolution of the 1997-98 El Niño. Science, 283, 950–953.
Rasmusson, E. M, and T. H. Carpenter, 1982: Variations in tropical sea surface temperature and surface wind fields associated with the Southern Osccillation/ El Niño. Mon. Wea. Rew., 110, 354–384.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiping, C., Shaoyu, Y., Qingchen, C. et al. A data analysis study on the evolution of the El Niño/ La Niña cycle. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 19, 837–844 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-002-0048-2
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-002-0048-2