Abstract
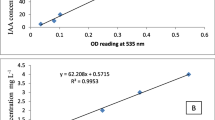
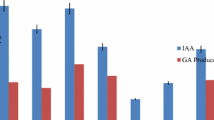
Phosphate-solubilizing strains of A. chroococcum isolated from the wheat rhizosphere were evaluated for their ability to solubilize tricalcium phosphate (TCP), Mussoorie rock phosphate (MRP) and also for indole-acetic-acid (IAA) production. Strains were selected on the basis of the clearance zone on solid agar media of Pikovskaya and Jensen's media containing TCP, and phosphate solubilization in Jensen's liquid culture medium containing both TCP and MRP. Mutants of the best phosphate-solubilizing (TCP 1.52 μg ml–1 MRP 0.19 μg ml–1), IAA-producing A. chroococum strain P-4, were developed and screened for P solubilization and phytohormone production. Five mutants solubilized more P (in the range of 1.5–1.7 μg/ml–1 of TCP and 0.19–0.22 μg ml–1 of MRP) than the parent strains. In vitro growth emergence studies of three wheat varieties, viz. C-306, WH-542 and HD-2009, showed better performance with phosphate-solubilizing mutants than with the parent strain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, V., Narula, N. Solubilization of inorganic phosphates and growth emergence of wheat as affected by Azotobacter chroococcum mutants. Biol Fertil Soils 28, 301–305 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050497
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050497