Abstract
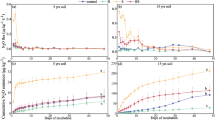
An aerobic 15N microcosmic experiment was conducted to compare the inhibitory effects of the biological nitrification inhibitor (BNI), methyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate (MHPP) at rates of 500 and 1000 mg kg−1 with the synthetic nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) at 1% of applied NH4+, on the gross nitrification rate (n_gross) and on the abundance and community composition of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) of two contrasting soils (pH: 5.10 vs. 8.15, clay content 17.8 vs. 30.8). DMPP inhibited 56.6% of n_gross in the acidic soil and 50.3% in the calcareous soil, whereas MHPP inhibited 18.3–55.5% of n_gross in the acidic soil and 14.1–20.2% in the calcareous soil. MHPP used at the high rate showed the same inhibition on n_gross as DMPP in the acidic soil but not in the calcareous soil. DMPP and MHPP likely regulated n_gross by causing niche differentiation between AOA and AOB. Moreover, the community composition of AOB was more sensitive to nitrification inhibitor application than that of AOA, particularly in the acidic soil. However, the response of AOB community composition was less sensitive to the application of MHPP than to that of DMPP. MHPP mainly targeted Nitrosospira clusters 3a.2, 3b.2, and 9 of the AOB in the acidic soil.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalos D, Jeffery S, Sanz-Cobena A, Guardia G, Vallejo A (2014) Meta-analysis of the effect of urease and nitrification inhibitors on crop productivity and nitrogen use efficiency. Agric Ecosyst Environ 189:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.03.036
Barraclough D, Puri G (1995) The use of 15N pool dilution and enrichment to separate the heterotrophic and autotrophic pathways of nitrification. Soil Biol Biochem 27:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(94)00141-M
Beeckman F, Motte H, Beeckman T (2018) Nitrification in agricultural soils: impact, actors and mitigation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 50:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cophio.2018.01.014
Benckiser G, Christ E, Herbert T, Weiske A, Blome J, Hardt M (2013) The nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole-phosphat (DMPP) - quantification and effects on soil metabolism. Plant Soil 371:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1664-6
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA et al (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37:852–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
Byrne MP, Tobin JT, Forrestal PJ, Danaher M, Nkwonta CG, Richards K, Cummins E, Hogan SA, O'Callaghan TF (2020) Urease and nitrification inhibitors-As mitigation tools for greenhouse gas emissions in sustainable dairy systems: a Review. Sustainability 12:6018. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156018
Cheng Y, Wang J, Wang J, Chang SX, Wang S (2017) The quality and quantity of exogenous organic carbon input control microbial NO3- immobilization: a meta-analysis. Soil Biol Biochem 115:357–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.09.006
Cheng Y, Wang J, Wang J, Wang S, Chang SX, Cai Z, Zhang J, Niu S, Hu S (2020) Nitrogen deposition differentially affects soil gross nitrogen transformations in organic and mineral horizons. Earth-Sci Rev 201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.103033
Chu H, Fujii T, Morimoto S, Lin X, Yagi K, Hu J, Zhang J (2007) Community structure of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria under long-term application of mineral fertilizer and organic manure in a sandy loam soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:485–491. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01536-06
Coskun D, Britto DT, Shi WM, Kronzucker HJ (2017a) How plant root exudates shape the nitrogen cycle. Trends Plant Sci 22:661–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2017.05.004
Coskun D, Britto DT, Shi WM, Kronzucker HJ (2017b) Nitrogen transformations in modern agriculture and the role of biological nitrification inhibition. Nat Plants 3:17074. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2017.74
Cui L, Li D, Wu Z, Xue Y, Xiao F, Zhang L, Song Y, Li Y, Zheng Y, Zhang J, Cui Y (2021) Effects of nitrification inhibitors on soil nitrification and ammonia volatilization in three soils with different pH. Agronomy-Basel 11:1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081674
Daims H, Lebedeva EV, Pjevac P, Han P, Herbold C, Albertsen M, Jehmlich N, Palatinszky M, Vierheilig J, Bulaev A, Kirkegaard RH, von Bergen M, Rattei T, Bendinger B, Nielsen PH, Wagner M (2015) Complete nitrification by Nitrospira bacteria. Nature 528:504–509. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16461
Di HJ, Cameron KC (2016) Inhibition of nitrification to mitigate nitrate leaching and nitrous oxide emissions in grazed grassland: a review. J Soils Sed 16:1401–1420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1403-8
Ferretti G, Galamini G, Deltedesco E, Gorfer M, Fritz J, Faccini B, Mentler A, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, Coltorti M, Keiblinger KM (2021) Gross ammonification and nitrification rates in soil amended with natural and NH4-enriched chabazite zeolite and nitrification inhibitor DMPP. Appl Sci-Basel 11:2605. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062605
Haichar FZ, Santaella C, Heulin T, Achouak W (2014) Root exudates mediated interactions belowground. Soil Biol Biochem 77:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.06.017
Hart SC, Stark JM, Davidson EA, Firestone MK (1994) Nitrogen mineralization, immobilization and nitrification. In: RW Weaver, S Angle, P Bottomley, D Bezdicek, S Smith, A Tabatabai, A Wollum (Eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Microbiological and biochemical properties. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, pp: 985–1018
Harty MA, McGeough KL, Carolan R, Muller C, Laughlin RJ, Lanigan GJ, Richards KG, Watson CJ (2017) Gross nitrogen transformations in grassland soil react differently to urea stabilisers under laboratory and field conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 109:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.01.025
Hink L, Gubry-Rangin C, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2018) The consequences of niche and physiological differentiation of archaeal and bacterial ammonia oxidisers for nitrous oxide emissions. ISME J 12:1084–1093. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-017-0025-5
Hu HW, He JZ (2017) Comammox-a newly discovered nitrification process in the terrestrial nitrogen cycle. J Soils Sediments 17:2709–2717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1851-9
Jiang X, Hou X, Zhou X, Xin X, Wright A, Ji Z (2015) pH regulates key players of nitrification in paddy soils. Soil Biol Biochem 81:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.10.025
Kaur-Bhambra J, Wardak DLR, Prosser JI, Gubry-Rangin C (2022) Revisiting plant biological nitrification inhibition efficiency using multiple archaeal and bacterial ammonia-oxidising cultures. Biol Fertil Soils. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-020-01533-1
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR (2001) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, a model for molecular ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:485–529. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.485
Lam SK, Suter H, Mosier AR, Chen D (2017) Using nitrification inhibitors to mitigate agricultural N2O emission: a double-edged sword? Global Change Biol 23:485–489. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13338
Lan T, Suter H, Liu R, Yuan S, Chen D (2018) Effects of nitrification inhibitors on gross N nitrification rate, ammonia oxidizers, and N2O production under different temperatures in two pasture soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:28344–28354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2873-6
Li C, Hu HW, Chen QL, Chen D, He JZ (2020) Growth of comammox Nitrospira is inhibited by nitrification inhibitors in agricultural soils. J Soils Sediments 20:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02442-z
Liu R, Suter H, He JZ, Hayden H, Chen D (2015a) Influence of temperature and moisture on the relative contributions of heterotrophic and autotrophic nitrification to gross nitrification in an acid cropping soil. J Soils Sediments 15:2304–2309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1170-y
Liu R, Hayden H, Suter H, He JZ, Chen DL (2015b) The effect of nitrification inhibitors in reducing nitrification and the ammonia oxidizer population in three contrasting soils. J Soils Sediments 15:1113–1118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1086-6
Liu S, Chi Q, Shan J, Zhu B, Zhang X, Cheng Y, Cai Z, Zhang J, Yan X, Mueller C (2020) Evaluation of the effectiveness of N process inhibitors in paddy rice via a 15N tracing approach. Soil Biol Biochem 147:107855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107855
Lu Y, Zhang X, Jiang J, Kronzucker HJ, Shen W, Shi W (2019) Effects of the biological nitrification inhibitor 1,9-decanediol on nitrification and ammonia oxidizers in three agricultural soils. Soil Biol Biochem 129:48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.11.008
Menendez S, Barrena I, Setien I, Gonzalez-Murua C, Estavillo JM (2012) Efficiency of nitrification inhibitor DMPP to reduce nitrous oxide emissions under different temperature and moisture conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 53:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.04.026
Murphy DV, Recous S, Stockdale EA, Fillery IRP, Jensen LS, Hatch DJ, Goulding KWT (2003) Gross nitrogen fluxes in soil: theory, measurement and application of 15N pool dilution techniques. Adv Agron 79:69–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(02)79002-0
Nair D, Abalos D, Philippot L, Bru D, Mateo-Marin N, Petersen SO (2021) Soil and temperature effects on nitrification and denitrification modified N2O mitigation by 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate. Soil Biol Biochem 157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108224
Nardi P, Akutsu M, Pariasca-Tanaka J, Wissuwa M (2013) Effect of methyl 3-4-hydroxyphenyl propionate, a Sorghum root exudate, on N dynamic, potential nitrification activity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea. Plant Soil 367:627–637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1494-y
Nardi P, Laanbroek HJ, Nicol GW, Renella G, Cardinale M, Pietramellara G, Weckwerth W, Trinchera A, Ghatak A, Nannipieri P (2020) Biological nitrification inhibition in the rhizosphere: determining interactions and impact on microbially mediated processes and potential applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev 44:874–908. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuaa037
O'Sullivan CA, Fillery IRP, Roper MM, Richards RA (2016) Identification of several wheat landraces with biological nitrification inhibition capacity. Plant Soil 404:61–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2822-4
Ouyang Y, Evans SE, Friesen ML, Tiemann LK (2018) Effect of nitrogen fertilization on the abundance of nitrogen cycling genes in agricultural soils: a meta-analysis of field studies. Soil Biol Biochem 127:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.08.024
Phillips CJ, Harris D, Dollhopf SL, Gross KL, Prosser JI, Paul EA (2000) Effects of agronomic treatments on structure and function of ammonia-oxidizing communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5410–5418. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.66.12.5410-5418.2000
Prosser JI, Hink L, Gubry-Rangin C, Nicol GW (2020) Nitrous oxide production by ammonia oxidizers: Physiological diversity, niche differentiation and potential mitigation strategies. Global Change Bio 26:103–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14877
Prosser JI, Nicol GW (2012) Archaeal and bacterial ammonia-oxidisers in soil: the quest for niche specialisation and differentiation. Trends Microbiol 20:523–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2012.08.001
Puttanna K, Gowda N, Rao E (1999) Effect of concentration, temperature, moisture, liming and organic matter on the efficacy of the nitrification inhibitors benzotriazole, o-nitrophenol, m-nitroaniline and dicyandiamide. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 54:251–257
Ruser R, Schulz R (2015) The effect of nitrification inhibitors on the nitrous oxide (N2O) release from agricultural soils-a review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 178:171–188. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201400251
Sahrawat KL (2008) Factors affecting nitrification in soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 39:1436–1446. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620802004235
Shen T, Stieglmeier M, Dai J, Urich T, Schleper C (2013) Responses of the terrestrial ammonia-oxidizing archaeon Ca. Nitrososphaera viennensis and the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium Nitrosospira multiformis to nitrification inhibitors. FEMS Microbiol Lett 344:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6968.12164
Shi XZ, Hu HW, Muller C, He JZ, Chen DL, Suter HC (2016) Effects of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate on nitrification and nitrifiers in two contrasting agricultural soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:5236–5248. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01031-16
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312–1313. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
Subbarao GV, Nakahara K, Hurtado MP, Ono H, Moreta DE, Salcedo AF, Yoshihashi AT, Ishikawa T, Ishitani M, Ohnishi-Kameyama M, Yoshida M, Rondon M, Rao IM, Lascano CE, Berry WL, Ito O (2009) Evidence for biological nitrification inhibition in Brachiaria pastures. P Natl Acad Sci USA 106:17302–17307. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0903694106
Subbarao GV, Nakahara K, Ishikawa T, Ono H, Yoshida M, Yoshihashi T, Zhu YY, Zakir H, Deshpande SP, Hash CT, Sahrawat KL (2013a) Biological nitrification inhibition (BNI) activity in sorghum and its characterization. Plant Soil 366:243–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1419-9
Subbarao GV, Sahrawat KL, Nakahara K, Rao IM, Ishitani M, Hash CT, Kishii M, Bonnett DG, Berry WL, Lata JC (2013b) A paradigm shift towards low-nitrifying production systems: the role of biological nitrification inhibition (BNI). Ann Bot-London 112:297–316. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcs230
Subbarao GV, Yoshihashi T, Worthington M, Nakahara K, Ando Y, Sahrawat KL, Rao IM, Lata JC, Kishii M, Braun HJ (2015) Suppression of soil nitrification by plants. Plant Sci 233:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.01.012
Subbarao GV, Kishii M, Bozal-Leorri A, Ortiz-Monasterio I, Gao X, Ibba MI, Karwat H, Gonzalez-Moro MB, Gonzalez-Murua C, Yoshihashi T, Tobita S, Kommerell V, Braun HJ, Iwanaga M (2021) Enlisting wild grass genes to combat nitrification in wheat farming: a nature-based solution. P Natl Acad Sci USA 118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2106595118
Van Kessel MAHJ, Speth DR, Albertsen M, Nielsen PH, Op den Camp HJM, Kartal B, Jetten MSM, Lucker S (2015) Complete nitrification by a single microorganism. Nature 528:555–559. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16459
Wang B, Zhao J, Guo Z, Ma J, Xu H, Jia Z (2015) Differential contributions of ammonia oxidizers and nitrite oxidizers to nitrification in four paddy soils. ISME J 9:1062–1075. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.194
Wang JY, Chadwick DR, Cheng Y, Yan XY (2018) Global analysis of agricultural soil denitrification in response to fertilizer nitrogen. Sci Total Environ 616:908–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.229
Wang X, Bai J, Xie T, Wang W, Zhang G, Yin S, Wang D, Yan B (2021) Effects of biological nitrification inhibitors on nitrogen use efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions in agricultural soils: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112338
Wu D, Zhang Y, Dong G, Du Z, Wu W, Chadwick D, Bol R (2021) The importance of ammonia volatilization in estimating the efficacy of nitrification inhibitors to reduce N2O emissions: a global meta-analysis. Environ Pollut 271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116365
Xia LL, Lam SK, Chen DL, Wang JY, Tang Q, Yan XY (2017) Can knowledge-based N management produce more staple grain with lower greenhouse gas emission and reactive nitrogen pollution? A meta-analysis. Global Change Bio 23:1917–1925. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13455
Yang M, Fang YT, Sun D, Shi YL (2016) Efficiency of two nitrification inhibitors (dicyandiamide and 3, 4-dimethypyrazole phosphate) on soil nitrogen transformations and plant productivity: a meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 6:22075. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22075
Zhang HJ, Wu ZJ, Zhou QX (2004) Dicyandiamide sorption-desorption behaviour on soils and peat humus. Pedosphere 14: 395–399. doi: 10.1002/jpln.200321305
Zhang M, Wang W, Tang L, Heenan M, Xu Z (2018) Effects of nitrification inhibitor and herbicides on nitrification, nitrite and nitrate consumptions and nitrous oxide emission in an Australian sugarcane soil. Biol Fertil Soils 54:697–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-018-1293-6
Zerulla W, Barth T, Dressel J, Erhardt K, Locquenghien K, Pasda G (2001) 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) – a new nitrification inhibitor for agriculture and horticulture. Biol Fertil Soils 34:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740100380
Zhou X, Wang S, Ma S, Zheng X, Wang Z, Lu C (2020) Effects of commonly used nitrification inhibitors-dicyandiamide (DCD), 3, 4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP), and nitrapyrin-on soil nitrogen dynamics and nitrifiers in three typical paddy soils. Geoderma 380:114637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114637
Zhu G, Ju X, Zhang J, Mueller C, Rees RM, Thorman RE, Sylvester-Bradley R (2019) Effects of the nitrification inhibitor DMPP (3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate) on gross N transformation rates and N2O emissions. Biol Fertil Soils 55:603–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-019-01375-6
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of the People’s Republic of China (42077096) and the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province, China (2021JDRC0034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ting Lan is responsible for discussion, methodology, writing, and funding acquisition. Mengxiao Li and Xiaoqian He conducted the experiment and performed most laboratory analyses. Ouping Deng, Wei Zhou, Ling Luo, and Guangdeng Chen performed data analyses. Shu Yuan, Jing Ling, Min Zeng, and Xuesong Gao read and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 28 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, T., Li, M., He, X. et al. Effects of synthetic nitrification inhibitor (3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate; DMPP) and biological nitrification inhibitor (methyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate; MHPP) on the gross N nitrification rate and ammonia oxidizers in two contrasting soils. Biol Fertil Soils 58, 333–344 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-022-01628-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-022-01628-x