Abstract
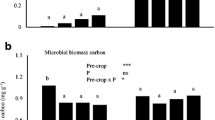
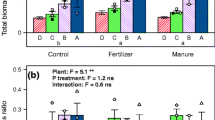
In soils with low P availability, several legumes have been shown to mobilise less labile P pools and a greater capacity to take up P than cereals. But there is little information about the size of various soil P pools in the rhizosphere of legumes in soil fertilised with P although P fertiliser is often added to legumes to improve N2 fixation. The aim of this study was to compare the growth, P uptake and the changes in rhizosphere soil P pools in five grain legumes in a soil with added P. Nodulated chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.), faba bean (Vicia faba L.), white lupin (Lupinus albus L.), yellow lupin (Lupinus luteus L.) and narrow-leafed lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) were grown in a loamy sand soil low in available P to which 80 mg P kg−1 was added and harvested at flowering and maturity. At maturity, growth and P uptake decreased in the following order: faba bean > chickpea > narrow-leafed lupin > yellow lupin > white lupin. Compared to the unplanted soil, the depletion of labile P pools (resin P and NaHCO3-P inorganic) was greatest in the rhizosphere of faba bean (54% and 39%). Of the less labile P pools, NaOH-P inorganic was depleted in the rhizosphere of faba bean while NaOH-P organic and residual P were most strongly depleted in the rhizosphere of white lupin. The results suggest that even in the presence of labile P, less labile P pools may be depleted in the rhizosphere of some legumes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bünemann EK, Heenan DP, Marschner P, McNeill AM (2006) Long-term effects of crop rotation, stubble management and tillage on soil phosphorus dynamics. Aus J Soil Res 44:611–618. doi:10.1071/SR05188
French R, Sweetingham M, Shea G (2001) A comparison of the adaptation of yellow lupin (Lupinus luteus L.) and narrow-leafed lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) to acid sandplain soils in low rainfall agricultural areas of Western Australia. Aus J Agric Res 52:945–954
George TS, Turner BL, Gregory PJ, Cade-Menun BJ, Richardson AE (2006) Depletion of organic phosphorus from oxisols in relation to phosphatase activities in the rhizosphere. Eur J Soil Sci 57:47–57. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2006.00767.x
Gerke J (1992) Phosphate, aluminium and iron in the soil solution of three different soils in relation to varying concentrations of citric acid. Zeitsch Pflanzenern Bdkde 155:339–343. doi:10.1002/jpln.19921550417
Grayston SJ, Vaughan D, Jones D (1997) Rhizosphere carbon flow in trees, in comparison with annual plants: the importance of root exudation and its impact on microbial activity and nutrient availability. Appl Soil Ecol 5:29–56. doi:10.1016/s0929-1393(96)00126-6
Hanson WC (1950) The photometric determination of phosphorus in fertilizers using the phosphovanado-molybdate complex. J Sci Food Agric 1:172–173. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740010604
Hedley MJ, Stewart JWB, Chauhan BS (1982) Changes in inorganic and organic soil-phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and by laboratory incubations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46:970–976
Henrikson A, Selmer-Olsen AR (1970) Automatic methods for determining nitrate and nitrite in water and soil extracts. Analyst 95:514–518
Hinsinger P, Plassard C, Tang CX, Jaillard B (2003) Origins of root-mediated pH changes in the rhizosphere and their responses to environmental constraints: a review. Plant Soil 248:43–59
Kamh M, Horst W, Amer F, Mostafa H, Maier P (1999) Mobilization of soil and fertilizer phosphate by cover crops. Plant Soil 211:19–27. doi:10.1023/a:1004543716488
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen—inorganic forms. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 643–698
Kouno K, Tuchiya Y, Ando T (1995) Measurement of soil microbial biomass phosphorus by an anion exchange membrane method. Soil Biol Biochem 27:1353–1357
Kuo S (1996) Phosphorus. In: Spark DL (ed) Methods of soil analysis, 3rd edn. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 869–919
Lambers H, Chapin FS, Pons TL (1998) Plant physiological ecology. Springer, New York
Li C-J, Liang R-X (2005) Root cluster formation and citrate exudation of white lupin (Lupinus albus L) as related to phosphorus availability. J Integr Plant Biol 47:172–177. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7909.2005.00012.x
Li H, Shen J, Zhang F, Clairotte M, Drevon J, Le Cadre E, Hinsinger P (2008) Dynamics of phosphorus fractions in the rhizosphere of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and durum wheat (Triticum turgidum durum L.) grown in monocropping and intercropping systems. Plant Soil 312:139–150. doi:10.1007/s11104-007-9512-1
Li H, Shen J, Zhang F, Marschner P, Cawthray G, Rengel Z (2010) Phosphorus uptake and rhizosphere properties of intercropped and monocropped maize, faba bean, and white lupin in acidic soil. Biol Fertil Soils 46:79–91
Linquist BA, Singleton PW, Cassman KG (1997) Inorganic and organic phosphorus dynamics during a build-up and decline of available phosphorus in an Ultisol soil. Soil Sci 162:254–264
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic, London
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Neumann G, Römheld V (2002) Root-induced changes in the availability of nutrients in the rhizosphere. In: Waisel Y, Eshel A, Kafkafi U (eds) Plant roots: the hidden half, 3rd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 617–649
Neumann G, Massonneau A, Martinoia E, Römheld V (1999) Physiological adaptations to phosphorus deficiency during proteoid root development in white lupin. Planta 208:373–382
Nuruzzaman M, Lambers H, Bolland MDA, Veneklaas EJ (2005a) Phosphorus benefits of different legume crops to subsequent wheat grown in different soils of Western Australia. Plant Soil 271:175–187. doi:10.1007/s11104-004-2386-6
Nuruzzaman M, Lambers H, Bolland MDA, Veneklaas EJ (2005b) Phosphorus uptake by grain legumes and subsequently grown wheat at different levels of residual phosphorus fertiliser. Aus J Agric Res 56:1041–1047. doi:10.1071/ar05060
Nuruzzaman M, Lambers H, Bolland MDA, Veneklaas EJ (2006) Distribution of carboxylates and acid phosphatase and depletion of different phosphorus fractions in the rhizosphere of a cereal and three grain legumes. Plant Soil 281:109–120. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-3936-2
Nziguheba G, Merckx R, Palm CA, Rao MR (2000) Organic residues affect phosphorus availability and maize yields in a Nitisol of western Kenya. Biol Fertility Soils 32:328–339
Pearse S, Veneklaas E, Cawthray G, Bolland M, Lambers H (2006) Carboxylate release of wheat, canola and 11 grain legume species as affected by phosphorus status. Plant Soil 288:127–139. doi:10.1007/s11104-006-9099-y
Rayment GE, Lyons DJ (2010) Soil chemical methods: Australasia. CSIRO publishing, Collingwood
Reuter DJ, Robinson JB (1997) Plant analysis: an interpretation manual, vol 2nd edition. CSIRO publishing, Collingwood
Richardson AE (2001) Prospects for using soil microorganisms to improve the acquisition of phosphorus by plants. Aus J Plant Physiol 28:897–906. doi:10.1071/pp01093
Richardson AE, Hadobas PA, Hayes JE (2001) Extracellular secretion of Aspergillus phytase from Arabidopsis roots enables plants to obtain phosphorus from phytate. Plant J 25:641–649. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00998.x
Rose T, Hardiputra B, Rengel Z (2010) Wheat, canola and grain legume access to soil phosphorus fractions differs in soils with contrasting phosphorus dynamics. Plant Soil 326:159–170. doi:10.1007/s11104-009-9990-4
Schoenau JJ, O’Halloran IP (2008) Sodium bicarbonate-extractable phosphate. In: Carter MR, Gregorich EG (eds) Soil sampling and methods of analysis, 2nd edn. CRC press, Boca Raton, pp 89–94
Searle PL (1984) The berthelot or indophenol reaction and its use in the analytical chemistry of nitrogen, a review. Analyst 109:549–568
Stevens DP, Cox JW, Chittleborough DJ, (Australia) CRCfSaLM (1997) Analysis and storage of water samples for determining molybdate reactive phosphorus CRC technical report; 2/97. Cooperative Research Centre for Soil & Land Management, Urrbrae
Tang CX, Robson AD (1993) Lupinus species differ in their requirements for iron. Plant Soil 157:11–18
Tang C, Robson AD, Longnecker NE, Buirchell BJ (1995) The growth of lupinus species on alkaline soils. Aus J Agric Res 46:255–268
Tang C, Fang RY, Raphael C (1998) Factors affecting soil acidification under legumes II. Effect of phosphorus supply. Aus J Agric Res 49:657–664
Tarafdar JC, Claassen N (2003) Organic phosphorus utilization by wheat plants under sterile conditions. Biol Fertil Soils 39:25–29. doi:10.1007/s00374-003-0671-9
Tiessen H, Moir JO (1993) Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. In: Carter MR (ed) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp 75–86
Veneklaas EJ, Stevens J, Cawthray GR, Turner S, Grigg AM, Lambers H (2003) Chickpea and white lupin rhizosphere carboxylates vary with soil properties and enhance phosphorus uptake. Plant Soil 248:187–197. doi:10.1023/a:1022367312851
Vu DT, Tang C, Armstrong RD (2008) Changes and availability of P fractions following 65 years of P application to a calcareous soil in a Mediterranean climate. Plant Soil 304:21–33. doi:10.1007/s11104-007-9516-x
Wang X, Tang C, Guppy C, Sale P (2008) Phosphorus acquisition characteristics of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and white lupin (Lupinus albus L.) under P deficient conditions. Plant Soil 312:117–128. doi:10.1007/s11104-008-9589-1
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Australian Research Council. HMH acknowledges the support from the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia, and Universiti Sains Malaysia for her studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mat Hassan, H., Marschner, P., McNeill, A. et al. Growth, P uptake in grain legumes and changes in rhizosphere soil P pools. Biol Fertil Soils 48, 151–159 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-011-0612-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-011-0612-y