Abstract
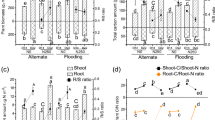
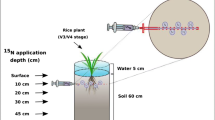
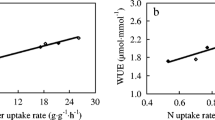
The objective of this study was to determine the effect of drought stress and elevated CO2 concentrations around the shoots on N rhizodeposition of young wheat plants. In a pot experiment, the plant N pool was labeled through 15NH3 application to shoots at nontoxic NH3 concentrations, and the impact of low water supply (40% field capacity), elevated CO2 (720 μmol mol−1 CO2), and the combination of both factors on the 15N distribution was studied. Total 15N rhizodeposition ranged from 5 to 11% of the total 15N recovered in the plant/soil system. Elevated CO2 concentration as well as drought stress increased the belowground transport of N and increased the relative portion of N rhizodeposition on total 15N in the plant/soil system. However, while the increased N rhizodeposition with elevated CO2 was the result of increased total belowground N transport, drought stress additionally increased the portion of 15N found in rhizodeposition vs roots. Elevated CO2 intensified the effect of drought stress. The percentage of water soluble 15N in the 15N rhizodeposition was very low under all treatments, and it was significantly decreased by the drought-stressed treatments.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark H, Newton PCD, Barker DJ (1999) Physiological and morphological responses to elevated CO2 and a soil moisture deficit of temperate pasture species growing in an established plant community. J Exp Bot 50:233–242
Cowling DW, Lockyer DR (1981) Increased growth of ryegrass exposed to ammonia. Nature 292:337–338
Imsande J, Touraine B (1994) N demand and the regulation of nitrate uptake. Plant Physiol 105:3–7
Janzen HH (1990) Deposition of nitrogen into the rhizosphere by wheat roots. Soil Biol Biochem 22:1155–1160
Janzen HH, Bruinsma Y (1989) Methodology for the quantification of root and rhizosphere nitrogen dynamics by exposure of shoots to 15N-labelled ammonia. Soil Biol Biochem 21:189–196
Janzen HH, Bruinsma J (1993) Rhizosphere N-deposition by wheat under varied water stress. Soil Biol Biochem 25:631–632
Jensen ES (1996) Rhizodeposition of N by pea and barley and its effect on soil N dynamics. Soil Biol Biochem 28:65–71
Kraffczyk I, Trolldenier G, Beringer H (1984) Soluble root exudates of maize: influence of potassium supply and rhizosphere microorganisms. Soil Biol Biochem 16:315–322
Maroco JP, Edwards GE, Ku Maurice SB (1999) Photosynthetic acclimation of maize to growth under elevated levels of carbon dioxide. Planta 210:115–125
McNeill AM, Zhu C, Fillery IRP (1997) Use of in situ 15N-labelling to estimate the total below-ground nitrogen of pasture legumes in intact soil-plant systems. Aust J Agric Res 48:295–304
Meharg AA (1994) A critical review of labelling techniques used to quantify rhizosphere carbon flow. Plant Soil 166:55–62
Merbach W (1997) C-Freisetzung durch Pflanzenwurzeln. Stapfia 50:321–326
Merbach W, Schulze J (1998) 15N-Freisetzung durch Weizenwurzeln unter Bodenbedingungen. Mitt Ges Pflanzenbauwiss 11:231–232
Merbach W, Mirus E, Knof G, Remus R, Ruppel S, Russow R, Gransee A, Schulze J (1999) Release of carbon and nitrogen compounds by plant roots and their possible ecological importance. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 162:373–383
Merbach W, Schulze J, Richert M, Rrocco E, Mengel K (2000) A comparison of different 15N application techniques to study the N net rhizodeposition in the plant-soil system. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 163:375–379
Mulholland BJ, Craigon J, Black CR, Colls JJ, Atherton J, Landon G (1997) Impact of elevated atmospheric CO2 and O3 on gas exchange and chlorophyll content in spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Exp Bot 48:1853–1863
Reining E, Merbach W, Knof G (1995) 15N distribution in wheat and chemical fractionation of root-borne 15N in the soil. Isot Environ Health Stud 31:345–349
Rovira AD (1969) Plant root exudates. Bot Rev 35:35–57
Russelle MP, Allan DL, Gourley CJP (1994) Direct assessment of symbiotically fixed nitrogen in the rhizosphere of alfalfa. Plant Soil 159:233–243
Schmidtke K (2005) How to calculate nitrogen rhizodeposition in the pea (Pisum sativum L.) and grasspea (Lathyrus sativus L.) using a continuous 15N labelling split-root technique. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1893–1897
Schorring JK, Nielson NE, Jensen HE, Gottschau A (1989) Nitrogen losses from field-grown spring barley plants as affected by rate of nitrogen application. Plant Soil 116:167–175
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) (Me 1072/1-3). We thank S. Remus for help with the 15N analysis. The outstanding technical support of K. Blasinski in setting up the ammoniation chambers is appreciated. Further, we wish to thank E. Kirkby for improving the English text.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulze, J., Merbach, W. Nitrogen rhizodeposition of young wheat plants under elevated CO2 and drought stress. Biol Fertil Soils 44, 417–423 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-007-0218-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-007-0218-6