Abstract
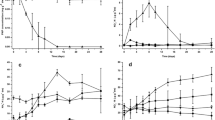
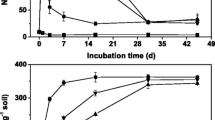
The aim of this work was to study variations in the composition of eubacteria and ammonia-oxidizing populations of soil, both determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE), after the addition of a pharmaceutical fungal biomass, treated to degrade its DNA. This waste can be used as an amendment. The fungal biomass waste was added at three rates: 0.05, 0.1, and 1% per dry weight of soil. Control soil, without any amendment, was also investigated. Total DNA was extracted, purified, and amplified by using either universal (eubacteria) or specific (amoA) primers. Amplicons were separated by DGGE. Sequencing was also carried out to better assess the diversity of ammonia oxidizing bacteria. Changes in the composition of eubacterial community were detected after 3 days only in the soil treated with the highest dose, while the ammonia oxidizing population responded more promptly (after 1 day) with evident modifications at level of Nitrosolobus like sequences.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adinarayana K, Prabhakar T, Srinivasulu V, Anitha Rao M, Jhansi Lakshmi P, Ellaiah P (2003) Optimization of process parameters for cephalosporin C production under solid state fermentation from Acremonium chrysogenum. Process Biochem 39:171–177
Aescht E, Foissner W (1992) Effects of mineral and organic fertilizers on the microfauna in a high-altitude reafforestation trial. Biol Fertil Soils 13:17–24
Agnelli A, Ascher J, Corti G, Ceccherini MT, Nannipieri P, Pietramellara G (2004) Distribution of microbial communities in a forest soil profile investigated by microbial biomass, soil respiration and DGGE of total and extracellular DNA. Soil Biol Biochem 36:859–868
Andersen JT, Schäfer T, Jørgensen PL, Møller A (2001) Using inactivated microbial biomass as fertilizer: the fate of antibiotic resistance genes in the environment. Res Microbiol 152:823–833
Avrahami S, Conrad R (2003) Patterns of community change among Ammonia-oxidizers in meadow soils upon long term incubation at different temperatures. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6152–6164
Bäckman JSK, Hermanssona A, Tebbe CC, Lindgren PE (2003) Liming induces growth of a diverse flora of ammonia-oxidising bacteria in acid spruce forest soil as determined by SSCP and DGGE. Soil Biol Biochem 35:1337–1347
Belser LW, Schmidt EL (1978) Diversity of ammonia-oxidizing nitrifier population of a soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 36:584–588
Boon N, De Windt W, Verstraete W, Top EM (2002) Evaluation of nested PCR-DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) with group-specific 16S rRNA primers for the analysis of bacterial communities from different wastewater treatment plants. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39:101–112
Burton SAQ, Prosser JI (2001) Autotrophic ammonia oxidation at low pH through urea hydrolysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2952–2957
Ceccherini MT, Castaldini M, Piovanelli C, Hastings RC, McCarthy AJ, Bazzicalupo M, Miclaus N (1998) Effects of swine manure fertilization on autotrophic ammonia oxidizing bacteria in soil. Appl Soil Ecol 7:149–157
Ceccherini MT, Castaldini M, Azzini A, Fancelli S, Bazzicalupo M, Miclaus N (2001) Occurrence of Azospirillum brasilense in soils amended with swine manure. Ann Microbiol 51:29–38
Dabo A, Durand P, Morand S, Diakite M, Langand J, Imbert-Establet D, Doumbo O, Jourdane J (1997) Distribution and genetic diversity of Schistosoma haematobium within its bulinid intermediate hosts in Mali. Acta Trop 66:15–26
Felske A, Akkermans ADL (1998) Spatial homogeneity of abundant bacterial 16S rRNA molecules in grassland soils. Microb Ecol 36:31–36
Fromin N, Hamelin J, Tarnawski S, Roesti D, Jourdain-Miserez K, Forestier N, Teyssier-Cuvelle S, Gillet F, Aragno M, Rossi P (2002) Statistical analysis of denaturing gel electrophoresis (DGGE) fingerprinting patterns. Environ Microbiol 4:634–643
Gutiérrez S, Velasco J, Fernandez FJ, Martìn JF (1992) The cefG gene of Cephalosporium acremonium is linked to the cefEF gene and encodes a Deacetylcephalosporin C Acetyltransferase closely related to Homoserine O-Acetyltransferase. J Bacteriol 179:3056–3064
Haselwandter K, Krismer R, Holzmann H, Reid CPP (1988) Hydroxamate siderophore content of organic fertilizers. J Plant Nutr 11:959–967
Hastings RC, Ceccherini MT, Miclaus N, Saunders JR, Bazzicalupo M, McCarthy AJ (1997) Direct molecular biological analysis of ammonia oxidizing bacteria populations in cultivated soil plots treated with swine manure. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 23:45–54
Hornek R, Pommerening-Röser A, Koops HP, Farnleitner AH, Kreuzinger N, Kirschner A, Mach RL (2006) Primers containing universal bases reduce multiple amoA gene specific DGGE band patterns when analysing the diversity of beta-ammonia oxidizers in the environment. J Microbiol Met 66:147–155
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism. Academic, New York, pp 21–132
Klotz MG, Norton JM (1998) Multiple copies of ammonia monooxygenase (amo) operons have evolved under biased AT/GC mutational pressure in ammonia-oxidizing autotrophic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 168:303–311
Kowalchuk G (1999) Fungal community analysis using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). In: Akkermans ADL, Van Elsas FJ, de Bruijn FJ (eds) Molecular microbial ecology manual 3.4.6:1–16. Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR, De Boer W, Prosser JI, Embley TM, Woldendorp JW (1997) Analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria of the β-subdivision of the class Proteobacteria in coastal sand dunes by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and sequencing of PCR-amplified 16S ribosomal DNA fragments. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1489–1497
McTavish H, Fuchs JA, Hooper AB (1993) Sequence of the gene coding for ammonia monooxygenase in Nitrosomonas europaea. J Bacteriol 175:2436–2444
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nannipieri P, Ascher J, Ceccherini MT, Landi L, Pietramellara G, Renella G (2003) Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur J Soil Sci 54:655–670
Norton JM, Low JM, Klotz MG (1996) The gene encoding ammonia monooxygenase subunit A exists in three nearly identical copies in Nitrosospira NpAV. FEMS Microbiol Lett 139:181–188
Øvreås L, Jensen S, Daae FL, Torsvik V (1998) Microbial community changes in a perturbed agricultural soil investigated by molecular and physiological approaches. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2739–2742
Phillips CJ, Harris D, Dollhopf SL, Gross KL, Prosser JI, Paul EA (2000) Effects of agronomic treatments on structure and function of ammonia-oxidizing communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5410–5418
Purkhold U, Pommerening-Röser A, Juretschko S, Schmid MC, Koops HP, Wagner M (2000) Phylogeny of all recognized species of ammonia oxidizers based on comparative 16S rRNA and amoA sequence analysis: implications for molecular diversity surveys. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5368–5382
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704–4712
Rowan AK, Snape JR, Fearnside D, Barer MR, Curtis TP, Head IM (2003) Composition and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities in wastewater treatment reactors of different design treating identical wastewater. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 43:195–206
Sakano Y, Kerkhof L (1998) Assessment of changes in microbial community structure during operation of an ammonia biofilter with molecular tools. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4877–4882
Smalla K, Wieland G, Buchner A, Zock A, Parzy J, Kaiser S, Roskot N, Heuer H, Berg G (2001) Bulk and rhizosphere soil bacterial communities studied by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis: plant-dependent enrichment and seasonal shifts revealed. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4742–4751
Tatusova TA, Madden TL (1999) Blast 2 sequences—a new tool for comparing protein and nucleotide sequences. FEMS Microbiol Lett 174:247–250
Torsvik V, Daae FL, Sandaa R-A, Øvreås L (1998) Novel techniques for analysing microbial diversity in natural and perturbed environments. J Biotechnol 64:53–62
Turpeinen R, Kairesalo T, Häggblom MM (2004) Microbial community structure and activity in arsenic-chromium- and copper-contaminated soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47:39–50
Van de Peer Y, De Wachter R (1997) Construction of evolutionary distance trees with TREECON for Windows: accounting for variation in nucleotide substitution rate among sites. Comput Appl Biosci 13:227–230
Webster G, Embley TM, Prosser JI (2002) Grassland management regimens reduce small-scale heterogeneity and species diversity of B-proteobacterial ammonia oxidizer populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:20–30
Zhou J, Xia B, Juang H, Palumbo AV, Tiedje JM (2004) Microbial diversity and heterogeneity in sandy subsurface soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1723–1734
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ceccherini, M.T., Ascher, J., Pietramellara, G. et al. The effect of pharmaceutical waste-fungal biomass, treated to degrade DNA, on the composition of eubacterial and ammonia oxidizing populations of soil. Biol Fertil Soils 44, 299–306 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-007-0204-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-007-0204-z