Abstract
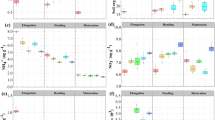
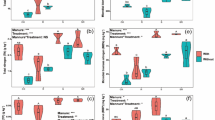
Effects of application of rice straw (RS), farmyard manure (FYM), municipal biowaste compost (MBCom), and municipal biowaste charcoal (MBCha) on soil microbial biomass N, mineral N, and nitrogen-fixing activity (NFA) of a model paddy microcosm were examined in comparison with urea fertilizer. When microcosms were added with urea, NFA decreased with increasing rates of fertilization, and it was negligible (less than 4% of the control, no urea fertilization) in the soils treated with more than 60 mg kg−1 urea–N. The addition of RS, with the highest C/N ratio among the organic wastes used, stimulated N2 fixation most effectively (40% increase compared to the control). MBCom, with the lowest C/N ratio and a comparable mineral N content to 60 mg kg−1 urea–N, decreased N2 fixation (50% decrease), but it was not markedly suppressed unlike urea. In spite of the fact that FYM contained a relatively large N, expressed as low C/N ratio, its effect on N2 fixation was small (14% decrease). FYM and MBCom did not stimulate NFA as RS did. This may be explained by the fact that N concentrations of microbial biomass N and available N were higher in the soils than in soil treated with RS. The effect of MBCha addition on N2 fixation was small (14% decrease). The present study demonstrated that organic wastes might affect N2 fixation depending upon the amount of available N in the waste-treated soils, but that organic-waste-treated soils generally support higher N2 fixation than chemical-fertilizer-treated soils.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi K, Watanabe I, Kobayashi M, Takahashi E (1989) Effect of application of glucose, cellulose, and rice straw on nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction and soil–nitrogen components) in anaerobic soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 35:235–249
Charyulu PBBN, Rao VR (1979) Nitrogen fixation in some Indian rice soils. Soil Sci 128:86–89
Choudhury ATMA, Kennedy IR (2004) Prospects and potentials for systems of biological nitrogen fixation in sustainable rice production. Biol Fertil Soils 39:219–227
Fu F, Bell PRF (2003) Factors affecting N2 fixation by the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium sp. GBRTRLI101. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 45:203–209
Harada N, Nishiyama M, Matsumoto S (2001) Inhibition of methanogens increases photo-dependent nitrogenase activities in anoxic paddy soil amended with rice straw. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35:231–238
Inubushi K, Wada H, Takai Y (1984) Determination of microbial biomass-nitrogen in submerged soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 30:455–459
Kanungo PK, Ramakrishnan B, Rao VR (1997) Placement effect of organic sources on nitrogenase activity and nitrogen fixing bacteria in flooded rice soil. Biol Fertil Soils 25:103–108
Knowles R, Denike D (1974) Effect of ammonium–, nitrite– and nitrate–nitrogen on anaerobic nitrogenase activity in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 6:353–358
Kondo M, Yasuda M (2003) Effects of temperature, water regime, light, and soils properties on 15N2 fixation associated with decomposition of organic matter in paddy soils. JARQ 37:113–119
Kyaw KM, Toyota K, Okazaki M, Motobayashi T, Tanaka H (2005) Nitrogen balance in a paddy field planted with whole crop rice (Oryza sativa cv. Kusahonami) during two rice-growing seasons. Biol Fertil Soils 42:72–82
Matsuguchi T, Tangchem B, Patiyuth S (1976) Flora of free-living nitrogen fixing bacteria in paddy fields in Thailand and their nitrogen-fixing activity. Soil Microorganisms 18:7–19 (in Japanese)
Mulvaney RL (1996) Nitrogen–inorganic forms. In: Sparks DL (ed) Method of soil analysis. Part 3. Chemical method. Soil Science Society of America, Inc., Madison, pp 1123–1184
Oyediran G, Adachi K, Senboku T (1996) Effect of application of rice straw and cellulose on methane emission and biological nitrogen fixation in a subtropical paddy field. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 42:701–711
Rao RV (1976) Nitrogen fixation as influenced by moisture content, ammonium sulphate and organic sources in a paddy soil. Soil Biol Biochem 8:445–449
Roper MM (1983) Field measurements of nitrogenase activity in soils amended with wheat straw. Aust J Agric Res 34:725–739
Roper MM, Ladha JK (1995) Biological N2 fixation by heterotrophic and phototrophic bacteria association with rice straw. Plant Soil 174:211–224
Smith JH, Peckenpaugh RE (1986) Straw decomposition in irrigated soil: comparison of twenty-three cereal straws. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:928–932
Sorger GJ (1969) Regulation of nitrogen fixation in Azotobacter vinelandii OP: the role of nitrate reductase. J Bacteriol 98:56–61
Webb J, Harrison R, Ellis S (2000) Nitrogen fluxes in three arable soils in the UK. Eur J Agron 13:207–223
Yoneyama T, Lee K, Yoshida T (1977) Decomposition of rice residues in tropical soils. I. The effect of rice straw on nitrogen fixation by heterotrophic bacteria in some Philippine soils. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23:287–295
Yoshida T, Roncal RA, Bautista EM (1973) Atmospheric nitrogen fixation by photosynthetic microorganisms in a submerged Philippine soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:117–123
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Ezawa T. and Dr. Matsumura S. for providing FYM and MBCom, respectively. A part of this study was financially supported by the TUA&T 21 Century Program (Evolution and Survival of Technology based Civilization).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, H., Kyaw, K.M., Toyota, K. et al. Influence of application of rice straw, farmyard manure, and municipal biowastes on nitrogen fixation, soil microbial biomass N, and mineral N in a model paddy microcosm. Biol Fertil Soils 42, 501–505 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-005-0043-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-005-0043-8